CMM Levels
CMM Levels
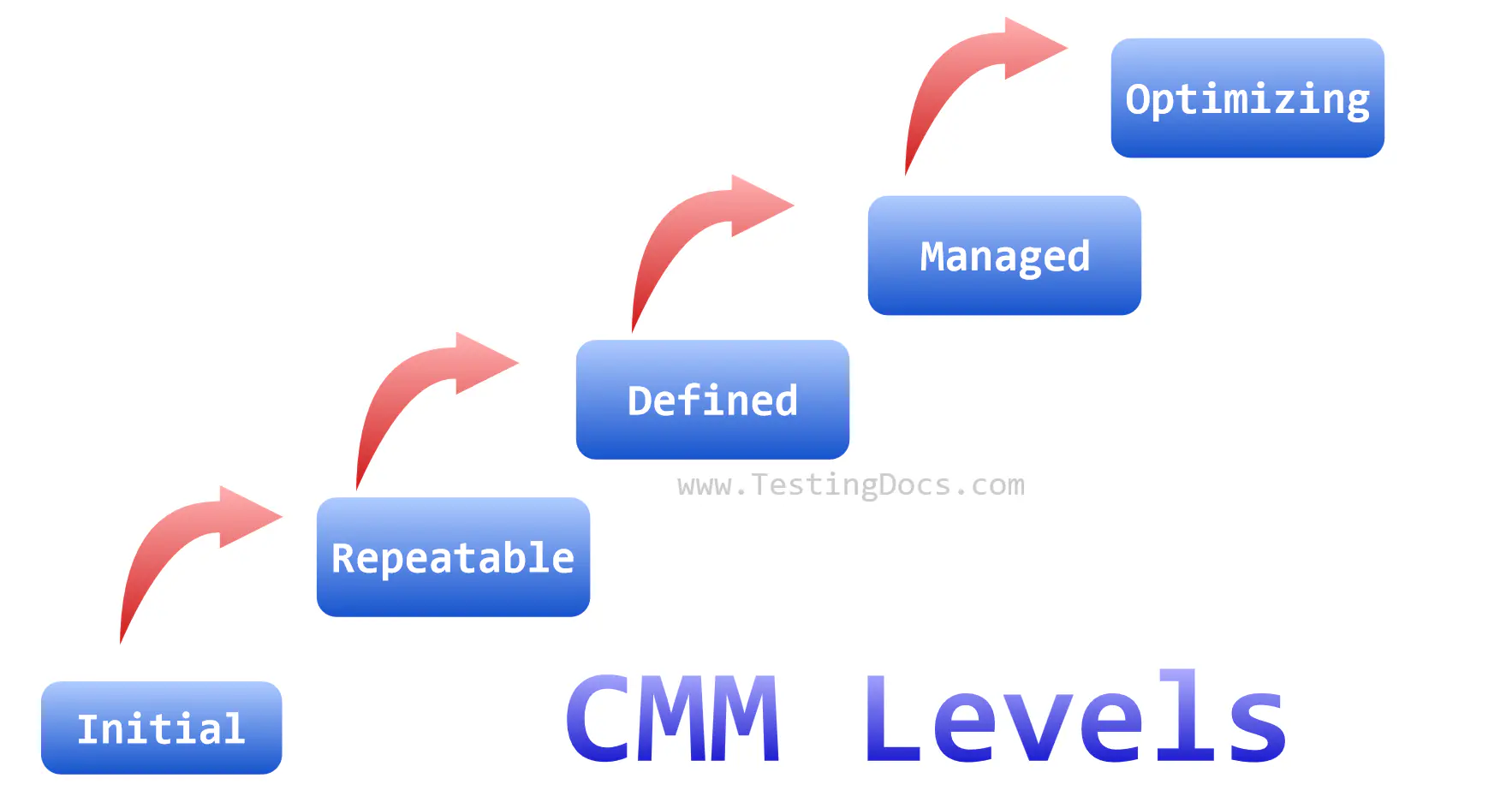
In this tutorial, we will learn about different CMM Levels. The capability Maturity Model defines five maturity levels. The CMM Levels are as follows:
- Level 1 -> Initial
- Level 2 -> Repeatable
- Level 3 -> Defined
- Level 4 -> Managed
- Level 5 -> Optimizing
Initial
This is the initial level. The process followed by the organization is ad-hoc, chaotic, uncontrolled, and has no defined KPAs( Key Process Areas). The process followed by the organization is undocumented, and the environment is unstable.
It follows no defined process model. The software development process at this level is ad hoc and often chaotic. The project’s success depends on heroes and luck. There are no general practices for planning, monitoring, or controlling the process. It’s impossible to predict the time and cost to develop the software. The software test process is also ad hoc like the rest.
Repeatable
The process followed by the organization is managed to some extent. The process is generally reactive. Previous success criteria are considered as their process model for the development and maintenance. Different KPA’s at this level are:
- RM-Requirement Management
- PP-Project Planning
- PT-Project Tracking
- SM-Subcontract Management
- QA-Quality Assurance
- CM-Configuration Management
This level is best described as project-level thinking. Basic project management processes are in place to track the project’s cost, schedule, functionality, and quality. Lessons learned from previous similar projects are applied. There’s a sense of discipline. Basic software Testing Practices such as Test plans and Test Cases are used.
Defined
The process followed by the organization is managed, and efforts are made to control and assure quality. Risks in the organization are managed. Incidents are resolved and prevented from reoccurrence. It has a standard process for development and maintenance. There is a permanent organization focus on the software.
Different KPA’s at this level are:
- PF-Process Focus(SEPG)
- PD-Process definition
- TP-Training Program
- IM-Integrated Software Management
- PE-Product Engineering
- IC-Intergroup Coordination
- PR-Peer Reviews
Organizational, not just project-specific thinking, comes into play at this level. Common management and engineering activities are standardized and documented. Test documents and plans are reviewed and approved before testing begins. The Test group is independent of developers. The Test results are used to determine when the project is ready. Training programs are used to ensure understanding and compliance.
Regression Testing is performed as appropriate. Effective methods are used to test the Software. Test Plans, Test procedures, and Test cases are appropriately changed whenever requirements, design, etc. For system Testing, test cases and procedures are planned and prepared by an independent Test Group.
Managed
The process followed by the organization is measured, controlled, and documented. Quality is controlled and assured; incidents are prevented. The organization also emphasizes customer satisfaction.
The organization set quantitative quality goals. The process capability is measured and operated within limits. Different KPA’s at this level are:
- PA-Quantitative Process management
- QM-Quality Management
At this level, the organization’s process is under statistical control. Product quality is specified quantitatively beforehand(for example, this product won’t be released until it has fewer than 0.5 defects per thousand lines of code), and the software isn’t released until the goals are met. Project performance is predictable, and quality is consistently high. Only some companies in the world are at CMM Level 4 or above.
Optimizing
The main focus for the organization at this level is optimizing the process. The organization strives to improve the process continually.
The organization focuses on continuous process improvement. Software processes are evaluated to prevent known defects from recurring, and innovations using new technologies and methods are identified. Different KPA’s at this level are:
- DP-Defect Prevention
- TI-Technology Change Management
- PCM-Process Change Management
The focus is on continuous process improvement. The impact of new processes and Technologies can be predicted and effectively implemented when required.
—
Software Testing Tutorials:
https://www.testingdocs.com/software-testing-tutorials/
More information: