What is Java Reflection?
What is Java Reflection?
Java Reflection is a powerful feature in the Java programming language that allows a program to inspect and manipulate the runtime behavior of classes, methods, fields, and constructors — even if they are private.
Java Reflection is a mechanism for manipulating classes, interfaces, and objects at the runtime of the Java program. Reflection API consists of methods to introspect the class at runtime.
Features of Java Reflection
Using Reflection you can create an instance of a class whose name is not known until runtime. Invoke methods on an object, set and get accessors and mutators for an object’s field which is unknown until runtime.
- Inspect classes, interfaces, fields, and methods at runtime.
- Create objects, invoke methods, and access fields dynamically.
- Allows working with classes unknown at compile time.
- Can bypass access control checks, such as accessing private fields or methods.

java.lang.reflect Package
To import and use Reflection API we have to use the below statement.
import java.lang.reflect.*;
ClassMethodFieldConstructorModifier
Class object
For every loaded class, the Java Runtime Environment maintains an associated Class object. The Class object “reflects” the class it represents You can use the Class object to discover information about a loaded class
• name
• modifiers
• superclasses
• implemented interfaces
• fields
• methods
• constructors
Sample ways to access the Class object for a loaded class
To get the Class object for an object notKnownAtRuntime
Class clz = notKnownAtRuntime.getClass();
Dynamic Class loading
The Class.forName(“classname”) method in Java is used to dynamically load a class at runtime.
Syntax:
Class.forName(“fully.qualified.ClassName”);
It loads the class specified by the string name.
It initializes the class (runs the static block and static initializations).
It returns the Class object associated with the class.
Example:
Class clz = Class.forName(“com.testingdocs.sample.program.SampleClass”);
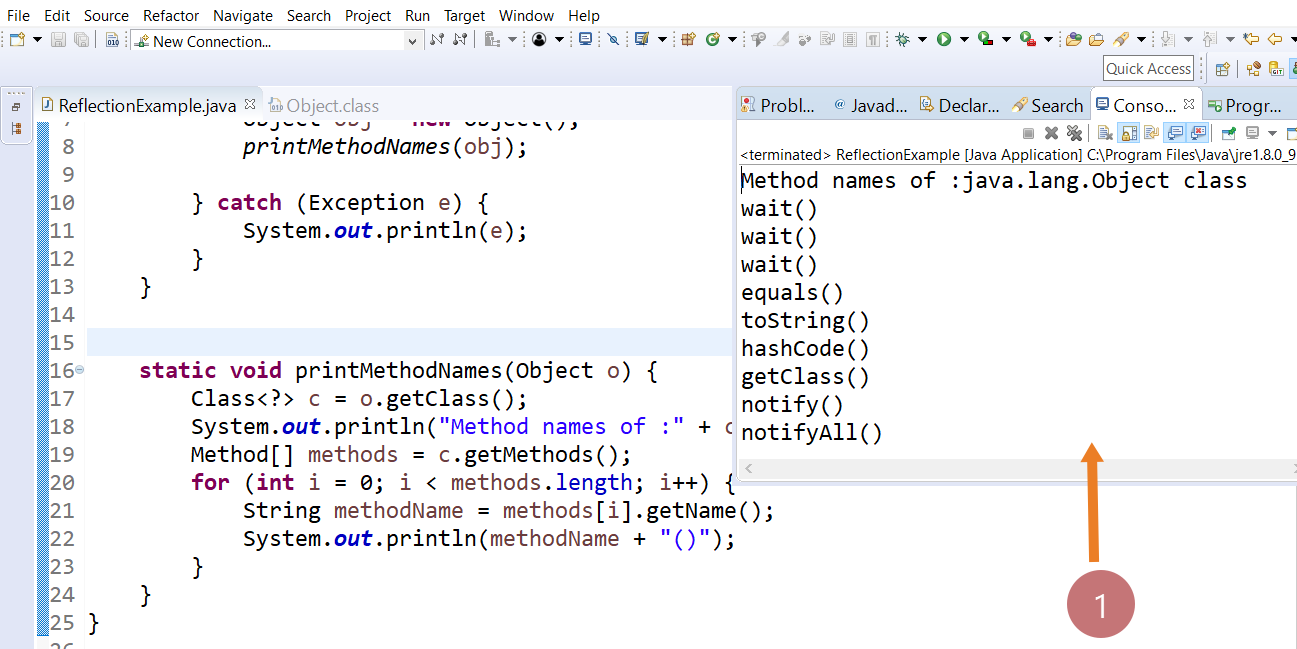
Java Program
In the below program we will print all the method names of Object class.
import java.lang.reflect.*;
public class ReflectionExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Object obj = new Object();
printMethodNames(obj);
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}static void printMethodNames(Object o) {
Class<?> c = o.getClass();
System.out.println("Method names of :" + c.getName() + " class");
Method[] methods = c.getMethods();
for (int i = 0; i < methods.length; i++) {
String methodName = methods[i].getName();
System.out.println(methodName + "()");
}
}
}
Program output
Method names of :java.lang.Object class
wait()
wait()
wait()
equals()
toString()
hashCode()
getClass()
notify()
notifyAll()