How to traverse a Collection in Java?
Introduction
We can traverse a collection of objects in Java by:
- using Iterators.
- using the for-each construct.
Iterator
public interface Iterator<E>
Iterator is an interface in the Java Collection framework that is used to iterate over a collection. An Iterator object enables us to traverse through a collection. We can get an Iterator for a collection by calling the iterator method.
Code listing
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
public class Demo {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
public Demo() {
list.add("One");
list.add("Two");
list.add("Three");
list.add("Four");
list.add("Five");
}
//traverse method using Iterator
public void traverse() {
Iterator<String> itr= list.iterator();
while(itr.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(itr.next());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Demo d = new Demo();
d.traverse();
}
}
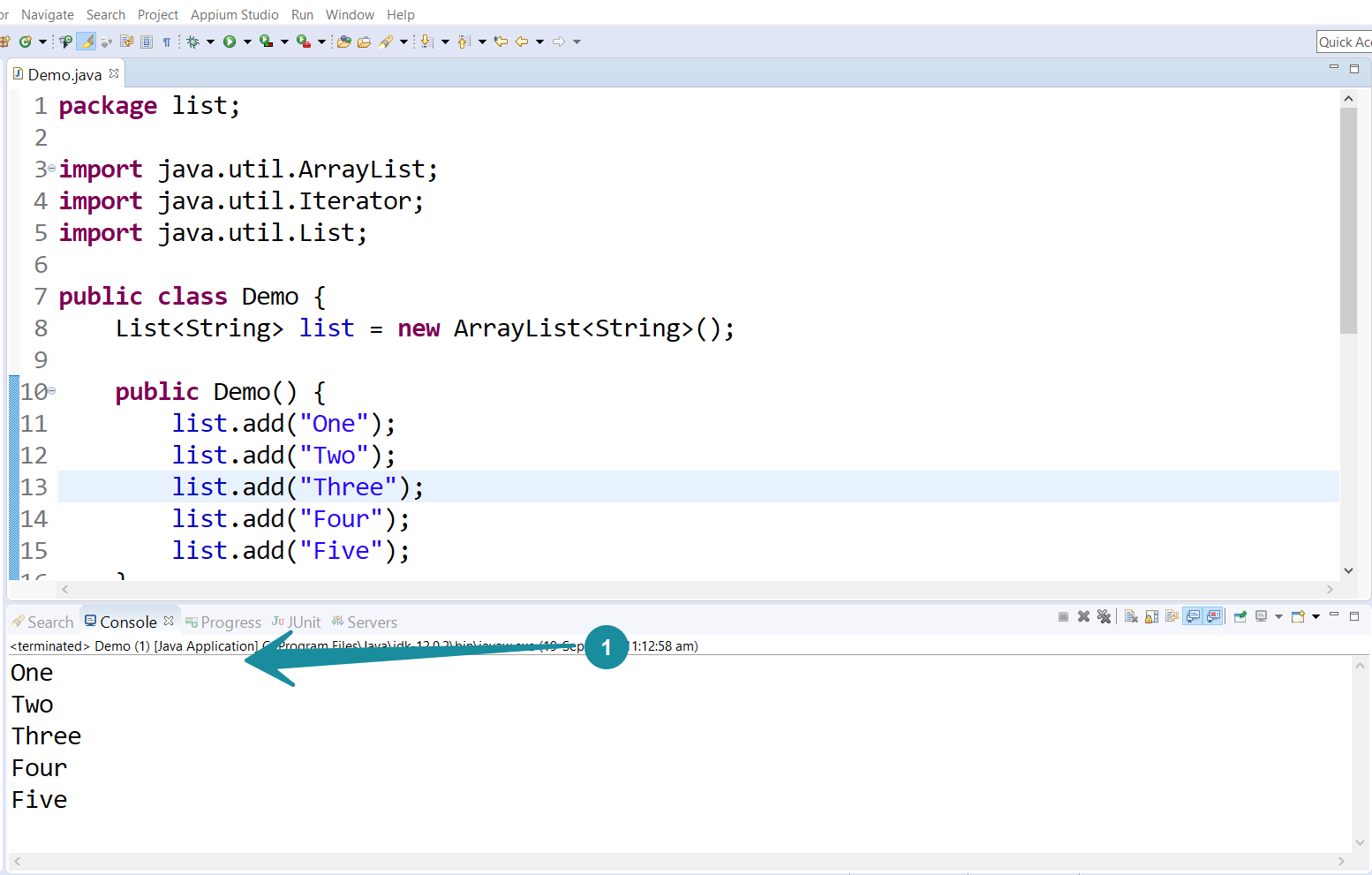
The hasNext() method returns true if the collection has more elements, and the next() method returns the next element in the collection. i.e list in this case.
for-each loop
The for-each loop allows us to traverse a collection using an enhanced for loop. For Example, the following snippet uses the for-each loop to print out each element of a collection.
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
public class Demo {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
public Demo() {
list.add("One");
list.add("Two");
list.add("Three");
list.add("Four");
list.add("Five");
}
//traverse method using for each
public void traverse() {
for(String str : list) {
System.out.println(str);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Demo d = new Demo();
d.traverse();
}
}

