What is Mathematical Induction?
What is Mathematical Induction?
Mathematical induction is a method to prove that some statement about the integer n is true for all n. In this method, first, we prove the statement when n has its smallest value, say p0. This is called the base case or basis or trivial case.
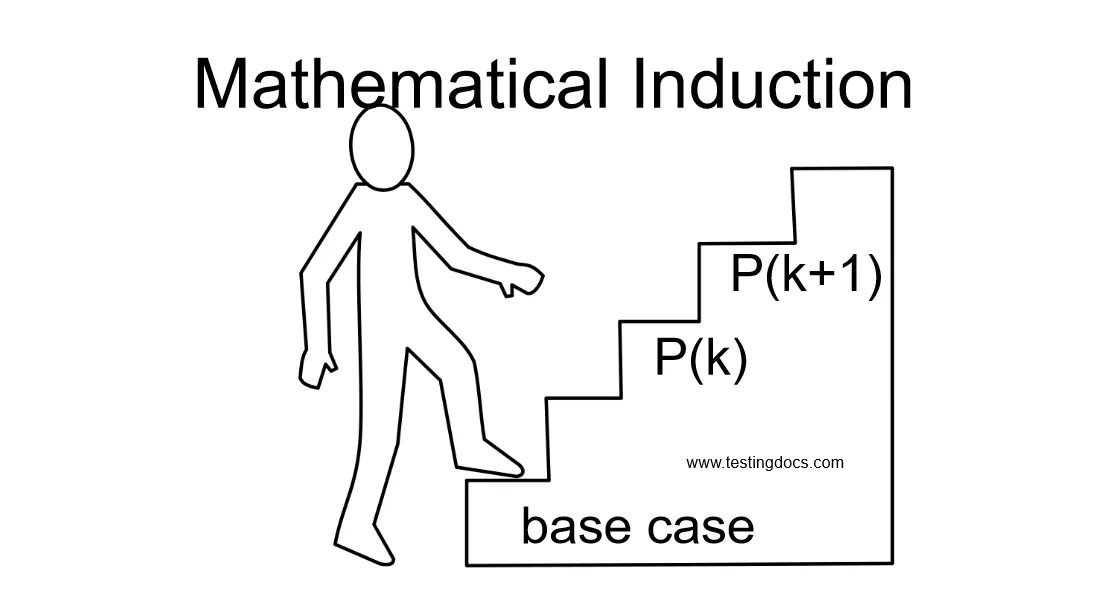
Then you prove the statement for k > p0, assuming that it has already been proved for all values between p0 and k, i.e You will assume that P(k) holds true. With that assumption we will prove the case for P(k+1) . This is called the induction.
Please see the above picture diagram for general idea about mathematical induction. This kind of proof is ideal for recurrences.
Principle of Mathematical Induction
The principle of mathematical induction is usually described in two forms. The one we have talked about is called the weak form.
If the statement p(base) holds true, and the statement P(k) ⇒ P(k+1) holds true for all k > base, then
P(n) is true for all integers n ≥ base.
Mathematical induction is a method of proving that a statement is true for all natural numbers. It’s particularly useful when dealing with sequences or series, and it relies on a two-step process:
Base Case: Verify that the statement is true for the initial value, usually n=1. This establishes the starting point of the induction.
Inductive Step: Assume that the statement is true for some arbitrary natural number
k. This assumption is known as the “inductive hypothesis.” Then, you need to show that if the statement holds for k, it must also hold for k+1.
Strong form:
If the statement p(base) holds true, and the statement
P(base)∧ P(b+1) ∧ … P(k)⇒ P(k+1)) holds true for all k > base, then
P(n) is true for all integers n ≥ base.
Example
Some of the examples are as follows:
#1
Using mathematical induction, let’s prove the formula for the Sum of N natural number squares.
#2
Another example of formula proof using mathematical induction:
