How to find listening Ports on Windows
How to find listening Ports on Windows
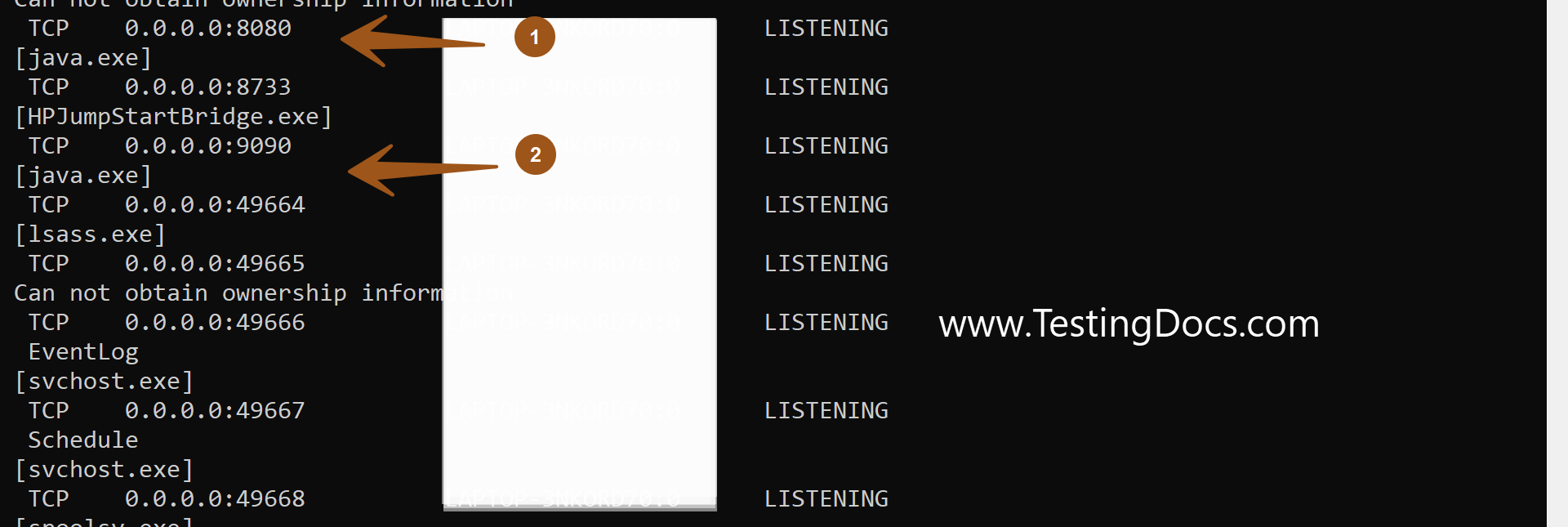
NETSTAT command is used to display network protocol statistics and the TCP/IP network connections. The command has various command-line switches. -a option displays the listening ports on the Windows machine.
NETSTAT command
The most useful command-line flags are the -a and -b
-a displays the listening ports
-b option displays the application that runs on the port. This option requires elevation. We need to open the command shell using Admin privileges.
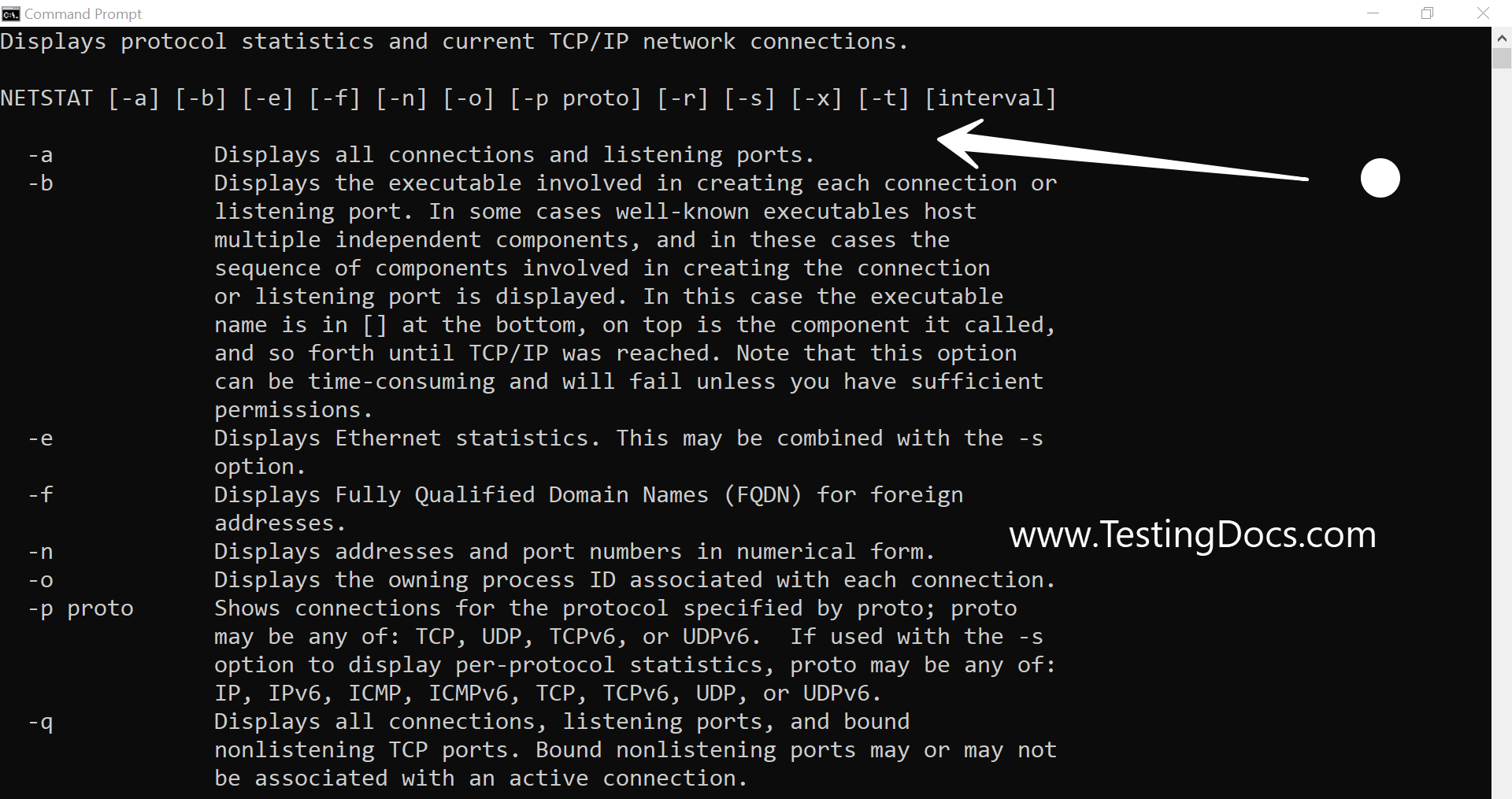
netstat Command Flags
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
netstat |
Displays active connections. |
netstat -a |
Shows all active connections and listening ports. |
netstat -n |
Displays addresses and port numbers in numerical form. |
netstat -o |
Shows active connections along with the Process ID (PID). |
netstat -p [protocol] |
Displays connections for a specific protocol (TCP, UDP, etc.). |
netstat -r |
Displays the routing table. |
netstat -s |
Shows network statistics by protocol. |
netstat -b |
Displays the executable responsible for each connection. |
netstat -an |
Shows all connections in numerical format. |
netstat -ano |
Shows all connections with numerical addresses and PIDs. |
Examples
To know which process listens on a particular port using the -b option. For example,
/> netstat -ab