What is the difference between String Literal and String Object?
String Literals vs String Objects
String is associated with a string literal in the form of double-quoted text. You can assign a string literal directly into a String variable. String objects are created by a new operator and String constructor. However, this is not recommended in Java.
Strings are immutable
String is an immutable sequence of Unicode characters. It’s content cannot be modified. Many string functions appear to modify the contents, but they construct and return a new String. Strings are frequently used in programs.
There are two ways to construct a string. Implicit construction by assigning a string literal. Explicitly construction of a String object via the new operator and constructor. Examples below:
1.By assigning a string literal to a String reference
2. By new operator and constructor as shown below.
For example,
String s1 = “I’m IronMan”; // Implicit construction
String s2 = new String(“”); // Explicit construction
String literals are stored in string common pool. String objects allocated via the new operator are stored in the program heap memory. In the above example, s1 is stored in the string common pool. s2 object is stored in the heap memory.
Storage mechanism
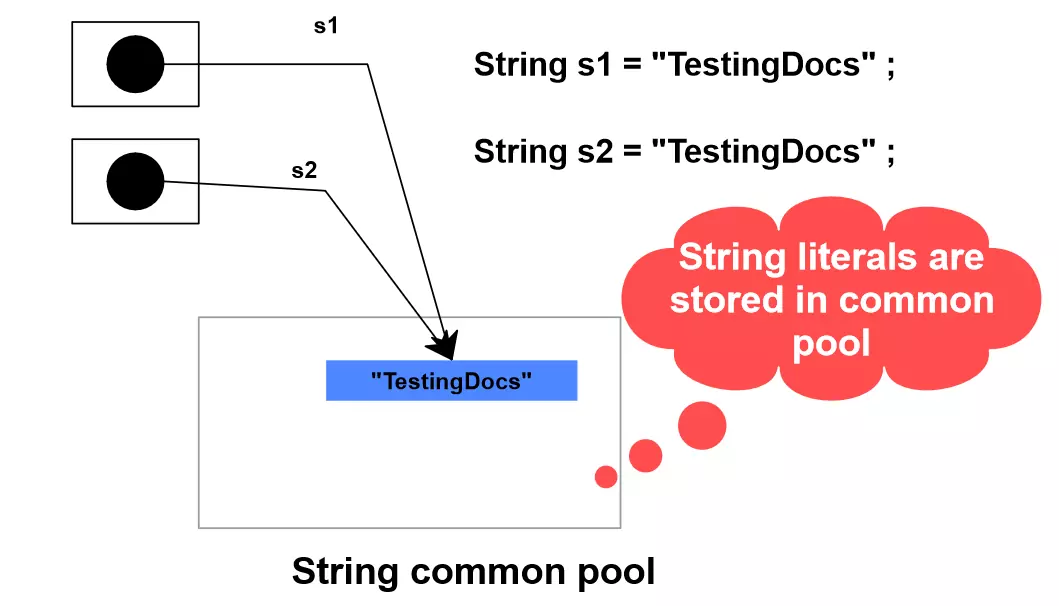
If two string literals have the same contents then they share the same storage in the string common pool.
1.String s1 = “TestingDocs”;
2.String s2 = “TestingDocs”;
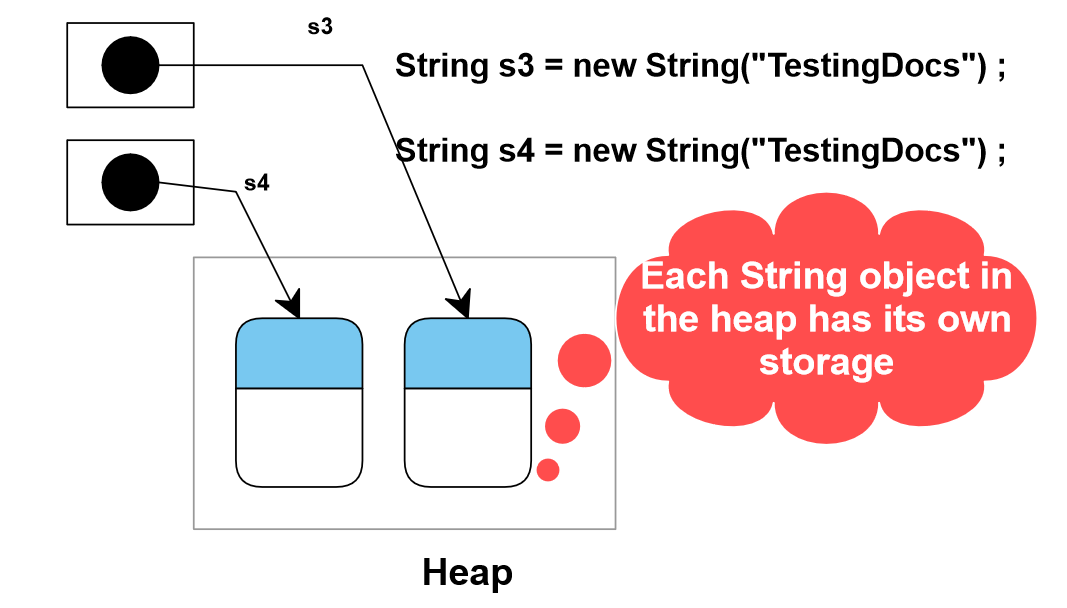
String objects created via the new operator are kept in the heap memory. Each String object has its own storage just like any other object. There is no sharing of storage in a heap even if two String objects have the same contents as shown below.
String s3 = new String(“TestingDocs”);
String s4 = new String(“TestingDocs”);
You can use the method equals() of the String class to compare the contents of two Strings. You can use the relational equality operator ‘==’ to compare the references of two objects.
s1 == s2; // true s1.equals(s2); // true s3 == s4; // false s3.equals(s4); // true