HTTP Protocol
HTTP Protocol
In this tutorial, we will learn about the HTTP protocol. HTTP stands for HyperText Transfer Protocol. It is an application-level protocol for data communication on the Internet. By default, it is connectionless and stateless.
The HTTP Protocol is the primary protocol for communicating and sending data between the web browser application(client) and the web server. Websites and web applications have web pages that are displayed on the browser. The text available on a web page is called hypertext. The HTTP protocol contains a set of rules for transferring hypertext between a browser( client) and a server on the Internet.
HTTP Client
An HTTP Client is software (like a web browser or mobile app) that sends requests to a server using the HTTP protocol to fetch or send data.
Examples: Chrome (client)
HTTP Server
An HTTP Server is software (like Apache or Nginx) that listens for incoming HTTP requests, processes them, and returns responses such as web pages, images, or data.
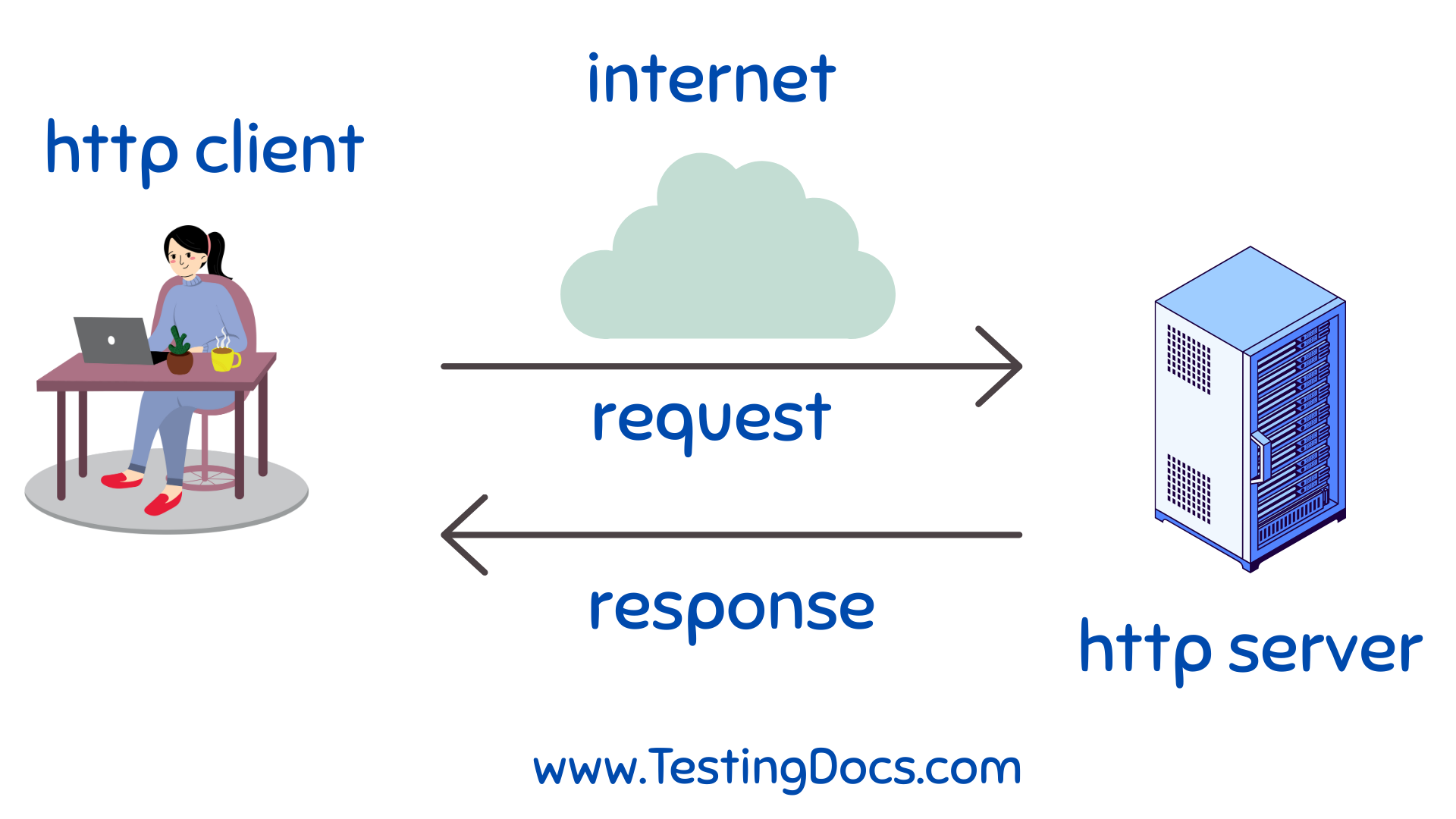
HTTP Communication
The client always initiates the communication, while the server waits for requests.
Clients typically send requests using methods like GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc.
Servers respond with status codes (e.g., 200 OK, 404 Not Found) and data.
Together, they form the client-server architecture, enabling web browsing and API communication.
Examples: Apache (server).
HTTPS
HTTPS is the secure version of the HTTP protocol. ‘S’ stands for Secure in the acronym. It is a secure way to send data between a web server and a web browser. HTTPS uses encryption technology to increase the security of data transfer between the client and the server.
By default, we can use this protocol for all communication. But it’s particularly important when sensitive data is transmitted like passwords, credit card numbers, confidential company data, etc.
HTTP Specification
The HTTP protocol provides a standardized way for computers to communicate on the World Wide Web. Web application pages are displayed on the browser. The text available on a web page is called hypertext. The HTTP protocol contains a set of rules to transfer hypertext between a browser and the server. HTTP specification specifies how client requests will be constructed and sent to the server, and how servers respond to these client requests.
HTTP Ports
The default HTTP ports are as follows:
- HTTP -> 80
- HTTPS -> 443
HTTP Methods
What is stateless?
When a client request is given multiple times to a server and a server is not recognizing that request then we call that behavior “stateless”. A webserver doesn’t recognize the client because of the HTTP protocol. Application Programmers can convert the stateless protocol into a stateful protocol. For example, we need to use a technique called session tracking.
What is stateful?
When the server recognizes the request of a client then that behavior is called stateful. Application programmers use session tracking to make the communication stateful. For example, online shopping portals.