Linux top Command
Linux top Command
When working with Linux, monitoring system performance is an essential skill. One of the most commonly used tools for this purpose is the top command. It provides real-time information about running processes, CPU usage, memory usage,
and overall system load. For beginners, learning top is a great way to understand how Linux manages resources.
What is the Linux top Command?
The top command is a task manager program for Linux. It displays system statistics dynamically, updating every few seconds.
With top, you can see which processes are consuming the most CPU or memory and take necessary actions such as terminating a process if needed.
Basic Syntax
The general syntax of the top command is as follows :
$ top [options]Running top without any options will launch it in interactive mode,
where you can view and manage system processes in real-time.
Examples
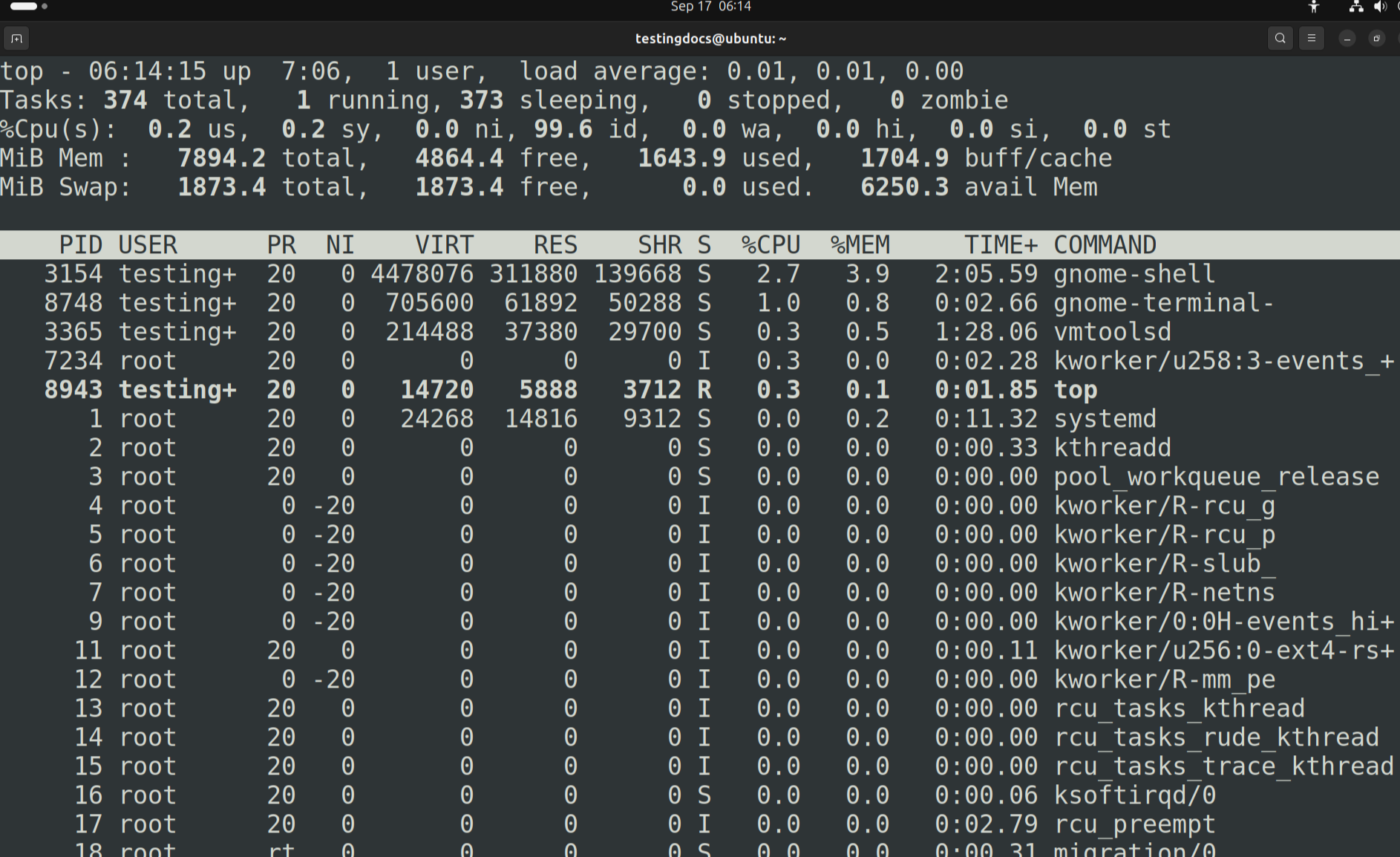
Run top Command
$ topThis will display a dynamic list of processes, CPU usage, memory consumption,
and system uptime. The display updates continuously until you exit by pressing q.
Show top Output for a Specific User
$ top -u usernameThis filters and shows only the processes belonging to a particular user.
Change Refresh Interval
$ top -d 5This sets the update interval to 5 seconds instead of the default (usually 3 seconds).
Display Processes by PID
$ top -p 1234Replace 1234 with the actual Process ID (PID) to monitor only that specific process.
Sort by Memory Usage
While inside top, press M to sort processes by memory usage.
The Linux top command is a powerful tool for monitoring system performance in real time. It helps administrators and users alike to keep an eye on CPU, memory, and process usage. Mastering top will make you more effective at diagnosing performance issues and managing your Linux system.

