Linux free command
Linux free command
The free command is used to display the amount of free and used memory in the system, including RAM and swap space. It gives a quick overview of how memory is being allocated and utilized.
Basic Syntax
The general syntax of the free command is as follows:
$ free <options>
Example
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
free |
Shows memory usage in kilobytes (KB) by default. |
free -m |
Displays output in megabytes (MB). |
free -g |
Displays output in gigabytes (GB). |
free -h |
Shows memory usage in a human-readable format (automatically picks KB, MB, or GB). |
Screenshot
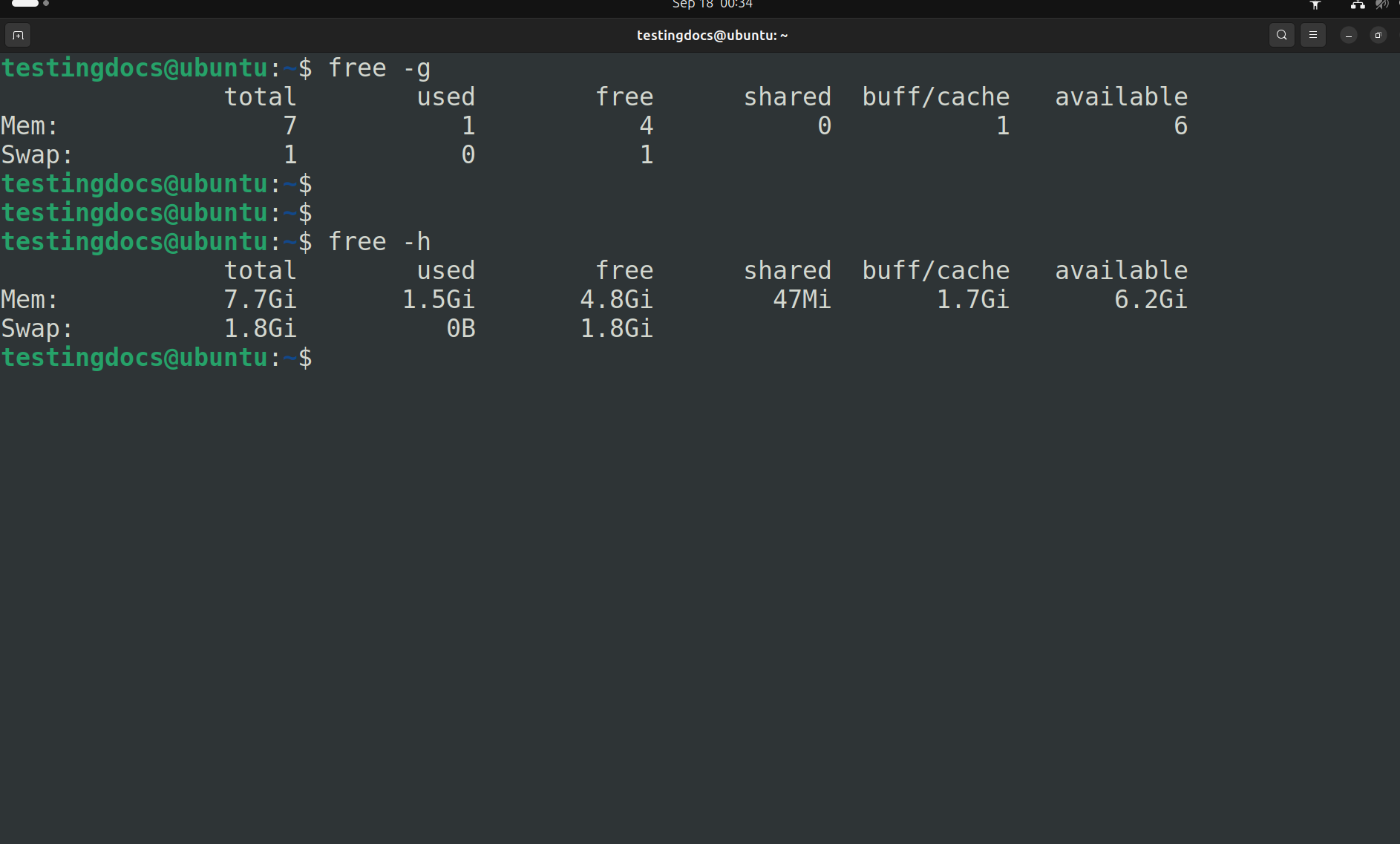
Explanation of Columns
-
total → Total installed memory (RAM or swap).
-
used → Memory currently in use.
-
free → Memory not being used at all.
-
shared → Memory shared between processes (e.g., tmpfs).
-
buff/cache → Memory used by kernel buffers and cache (can be reclaimed if needed).
-
available → Estimate of how much memory is available for new applications without swapping.

