Main Types of Language Models
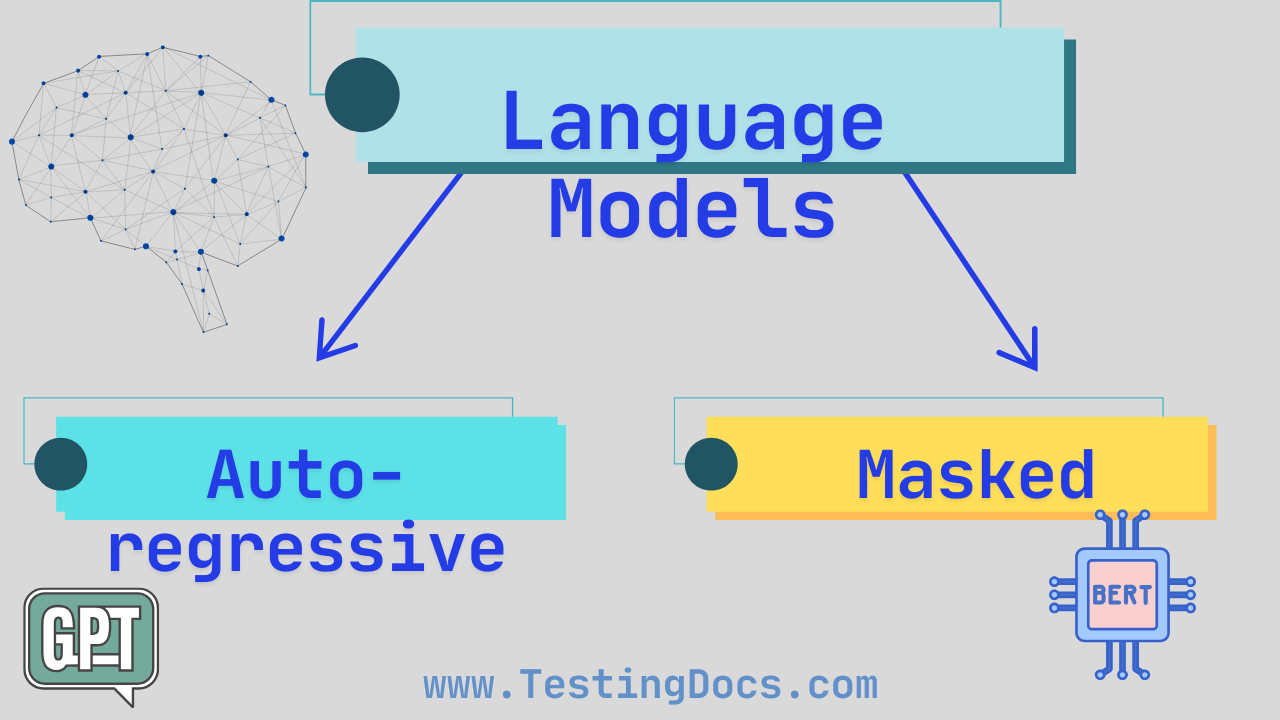
Main Types of Language Models
A language model is a type of artificial intelligence that learns patterns in human language so it can understand or generate text that sounds natural. It encodes statistical information about one or more languages.
Let’s explore two main types of language models you’ll often hear about:
- Autoregressive language model
- Masked language model
Autoregressive Language Model
An Autoregressive Language Model predicts the next word in a sentence based on the words that came before it. Think of it like reading a book one word at a time—you use what you’ve already read to guess what comes next. These models generate text step by step, always looking backward at the previous words to make their predictions.
For example, if you give the model the phrase “The sky is…”, it might predict “blue” as the next word because that’s a common phrase it has learned from lots of text during training. Popular examples of autoregressive models include GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) series by OpenAI.
Masked Language Model
A Masked Language Model works differently. Instead of predicting the next word, it tries to guess a hidden (or “masked”) word somewhere in the middle of a sentence, using the words that come both before and after it. This gives the model a more complete understanding of context.
For instance, if you give it the sentence “The cat sat on the ___,” with the word “mat” hidden, the model uses both “The cat sat on the” and any words that might follow (if present) to figure out the missing word. BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) is a well-known example of a masked language model.
Autoregressive vs. Masked Language Models
Some of the differences are as follows:
| Autoregressive Language Model | Masked Language Model | |
|---|---|---|
| Direction of Context | Uses only previous words (left-to-right) | Uses words from both before and after the masked word (bidirectional) |
| Primary Task | Predict the next word in a sequence | Predict a hidden (masked) word in the middle of a sentence |
| Best For | Text generation (e.g., chatbots, story writing) | Understanding context (e.g., question answering, sentiment analysis) |
| Example Models | GPT, GPT-2, GPT-3, GPT-4 | BERT, RoBERTa |
| Training Style | Causal language modeling | Masked language modeling |
Both types of models are powerful in their own ways. Autoregressive models shine when you need to create new, fluent text, while masked models excel at understanding the meaning behind existing text. As language models continue to evolve, many modern systems even combine ideas from both approaches to get the best of both worlds!