MySQL Storage Engines
MySQL Storage Engines
In this tutorial, you will learn about MySQL Storage Engines. MySQL Storage Engines are components that handle how data is stored, handled, and retrieved in MySQL tables. Each storage engine provides different features and performance optimizations, allowing users to choose the one that best suits their needs.
MySQL allows you to choose a storage engine per table. This makes it flexible to optimize tables based on how they are used.
When we create a database table using MySQL, we can choose the storage engine to use. The choice of storage engine made should be according to the best fit of the needs of the application.
Before we can use the storage engine, it should be compiled into the MySQL server and enabled to use. MySQL server uses a modular approach for storage engines. Each storage engine is a software module that is compiled into the server. We can enable storage engines at configuration time or at runtime. Some most common storage engines in MySQL are as follows:
List
MySQL supports many storage engines. MySQL allows us to choose from any of them when creating a table. Each storage engine has specific characteristics and features.
| MySQL Storage Engines | Description |
| InnoDB | InnoDB is an ACID-compliant transactional storage engine.
|
| MyISAM |
|
| MEMORY | In memory storage engine. Hash based, stored in memory.
|
| FEDERATED | Access to database tables located remotely
|
| EXAMPLE | Storage engine used only for development and testing |
| BLACKHOLE | Data stored in a table disappears because the engine discards it |
| CSV |
|
| NDB | MySQL’s cluster storage engine
|
| ARCHIVE | Archival storage engine. Mostly used for large number of records that will never be altered.
|
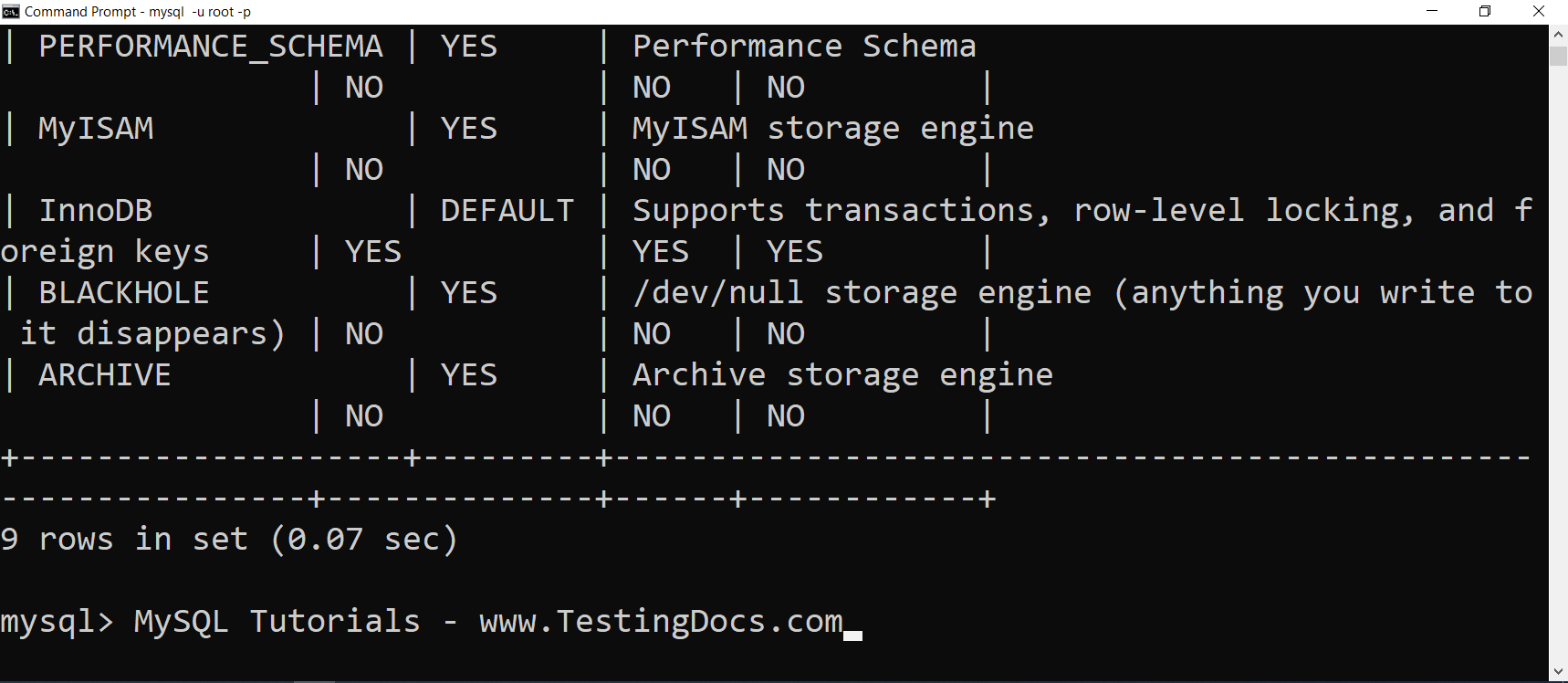
How to Check Available Storage Engines
You can run the following SQL command:
SHOW ENGINES;
This will display a list of available storage engines along with their support status and features.
To specify the storage engine, we can use the ENGINE clause of the CREATE TABLE statement. If we create a table without the explicit ENGINE option, the MySQL database server creates the table using the default storage engine. The default storage engine is defined by the default_storage_engine system variable.
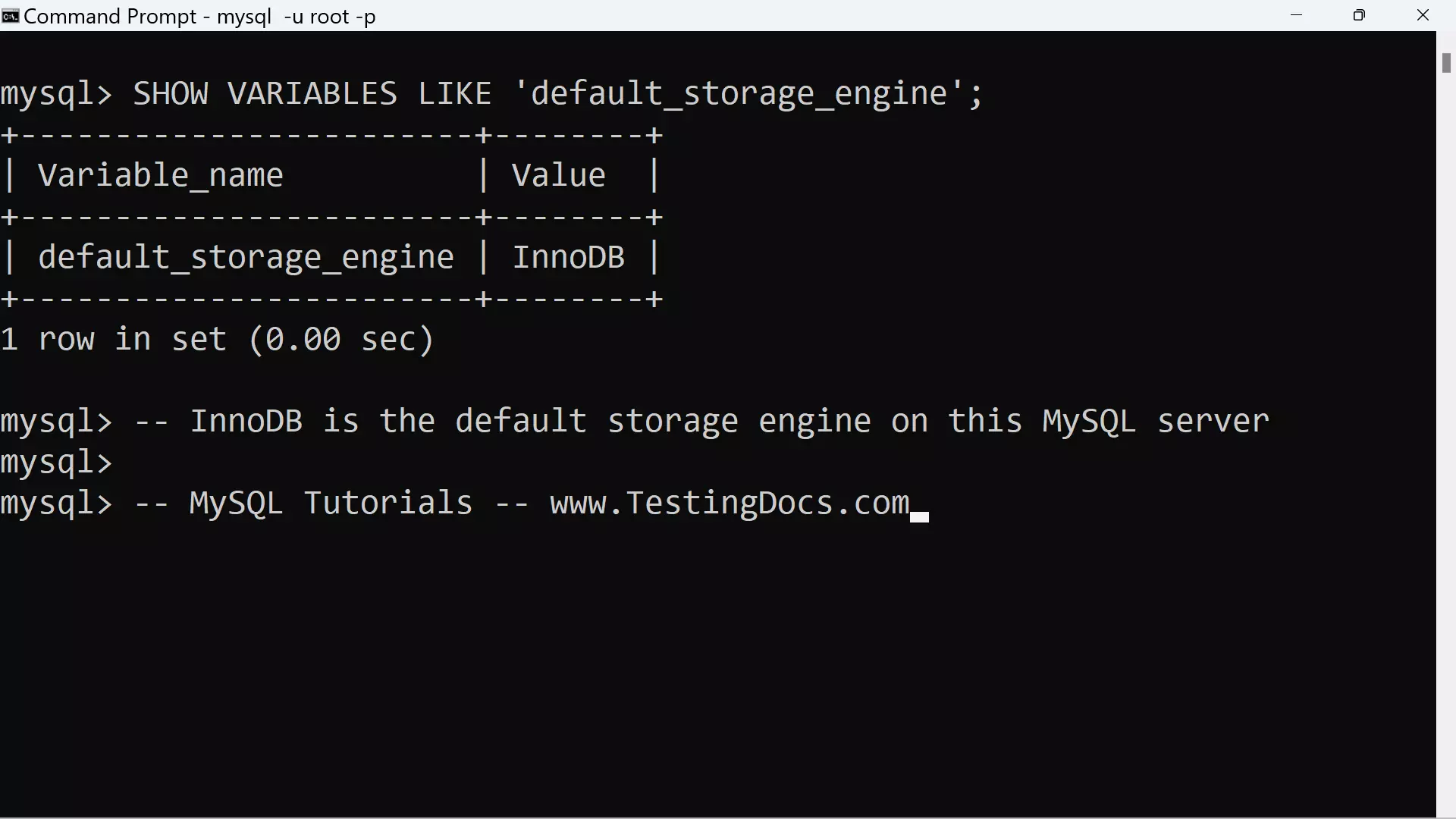
To know the default storage engine on the MySQL server, issue the following command using the MySQL client.
mysql> SHOW VARIABLES LIKE ‘default_storage_engine’;
+————————+——–+
| Variable_name | Value |
+————————+——–+
| default_storage_engine | InnoDB |
+————————+——–+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Conclusion
Choosing the right storage engine is crucial based on the use case:
-
Use InnoDB for most applications.
-
Use MEMORY for temporary and fast-access tables.
-
Use ARCHIVE for logging or storing historical records.
Display Engine Information
MySQL Tutorials
MySQL Tutorials on this website:
