Top-Down Testing
Top-Down Testing
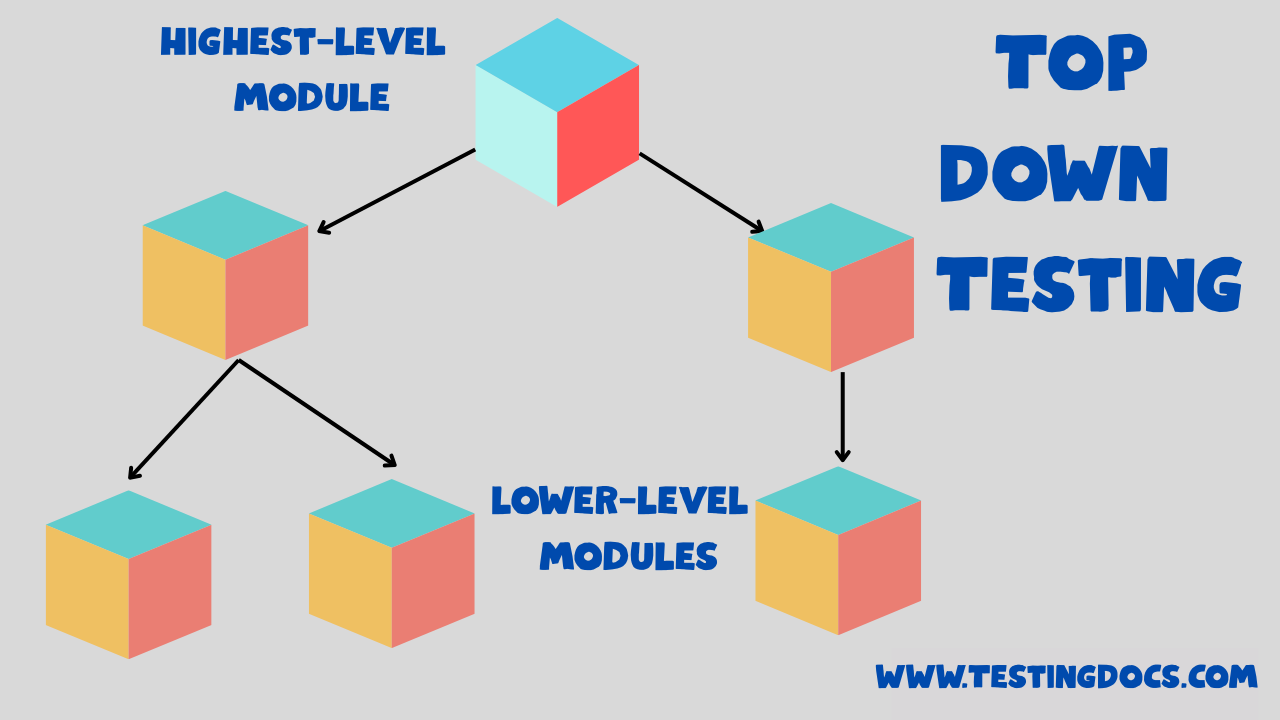
Top-down testing is an approach where testing begins from the highest-level module or component and works its way down to the smaller, more detailed modules. This method is conducted incrementally, testing each module step-by-step, starting from the top and then progressively adding lower-level modules.
Top-Down Testing is a type of Integration Testing, where you start testing the top-level modules first, which interact with lower-level components. As testing progresses, you work down the hierarchy, testing each module in isolation. If any modules are not yet implemented, they are replaced by stubs that mimic their behavior.
Testing Process
- Start with the highest-level module.
- Test its interaction with stubs representing lower-level modules.
- Gradually replace the stubs with actual lower-level modules as they become available.
- Continue testing until all modules have been integrated and tested.
High-level tests are generally broader in scope, focusing on how different components work together, while low-level tests are more granular, examining individual functionalities. The Top-Down approach emphasizes high-level testing at the start, ensuring the overall system works as expected before focusing on the details.
Advantages of Top-Down Testing
Early Detection of High-Level Errors
Since Top-Down Testing starts with the most crucial components, it helps identify potential design flaws or integration issues early on. This can save time by preventing problems from becoming harder to fix later.
Focus on Critical Components
Top-down testing prioritizes testing the most important modules first, ensuring that critical parts of the system are stable before adding more complexity.
Low-cost Test Environment
Testing high-level modules often requires a less complex test environment because stubs can be used instead of actual components. This can reduce the cost and time associated with setting up test environments.
Top-down testing allows for systematic testing within a structured framework. It also enables testing of various interfaces between modules, ensuring that each module functions properly regardless of the platform. It helps identify issues in the system architecture early by starting with the top-level modules, ensuring that they integrate correctly with the components that follow.