Types of MAC Addresses
Types of MAC Addresses
In computer networking, every device connected to a network has a unique identifier known as a MAC address. These addresses are essential for communication between devices on a Local Area Network (LAN). Understanding the types of MAC addresses helps in identifying how data is delivered to different devices on the network.
What is a MAC Address?
MAC stands for Media Access Control. A MAC address is a hardware address that uniquely identifies each device on a network. It is a 48-bit address typically written in hexadecimal format, such as 00:1A:2B:3C:4D:5E. MAC addresses are assigned by the hardware manufacturer and are usually burned into the Network Interface Card (NIC) of the device.
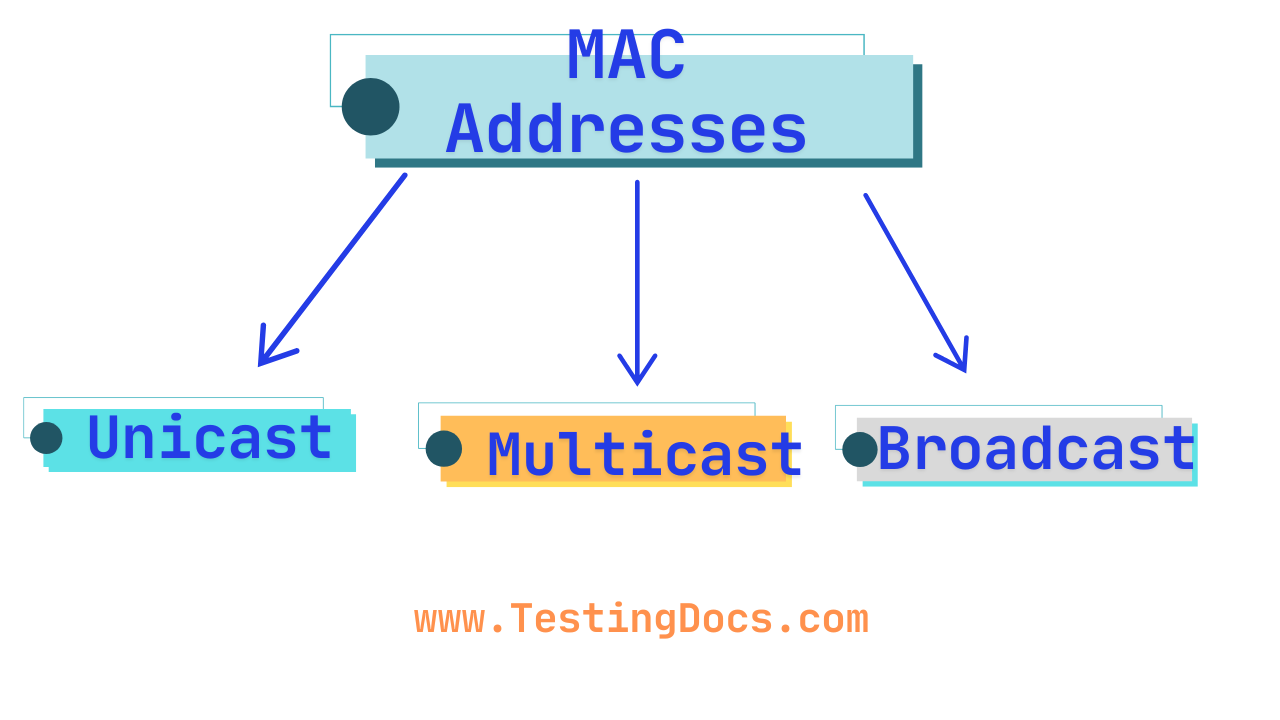
Types of MAC Addresses
There are three main types of MAC addresses used in networking, based on the destination of the data packet:
- Unicast
- Multicast
- Broadcast
Unicast MAC Address
A unicast MAC address is used to deliver data to a specific device on the network. It uniquely identifies a single network interface. When a device sends data using a unicast address, only the device with the matching MAC address receives the data. Most MAC addresses in daily use are unicast.
One to One Communication
Example: The communication between two computers.
Multicast MAC Address
A multicast MAC address is used to deliver data to a group of devices, rather than just one. Devices that are part of a multicast group will listen for traffic addressed to the multicast MAC address. It is commonly used in video conferencing, streaming, and other group-based data transmission.
One to Many Communication
Example: One device sending data to a group of devices.
Broadcast MAC Address
A broadcast MAC address is used to send data to all devices on the local network. The broadcast MAC address is FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF. Every device on the local network will process packets addressed to this MAC address. It is often used in network discovery and ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) requests.
One to All Communication
Example: One device sends data to all devices on the network.