Single Sign-On (SSO) Server
Single Sign-On (SSO) Server
Single Sign-On (SSO) is a user authentication process that allows a user to log in once and gain access to multiple applications or systems without having to log in again for each one.
How Does it Work?
Imagine you have several apps—like email, calendar, and file storage—all provided by the same company. Instead of typing your username and password every time you open a new app, SSO lets you sign in just once. After that, you can move freely between all the apps without logging in again.
Here’s a simple breakdown of how it works:
- User tries to access an app (e.g., a company dashboard).
- The app checks if the user is already authenticated.
- If not, the user is redirected to the SSO server (the central login system).
- The user enters their credentials (username and password) on the SSO server.
- If the credentials are correct, the SSO server creates a session and sends a secure token back to the original app.
- The app validates the token and grants access.
- Now, when the user visits another app that uses the same SSO system, they’re automatically logged in—no need to enter credentials again!
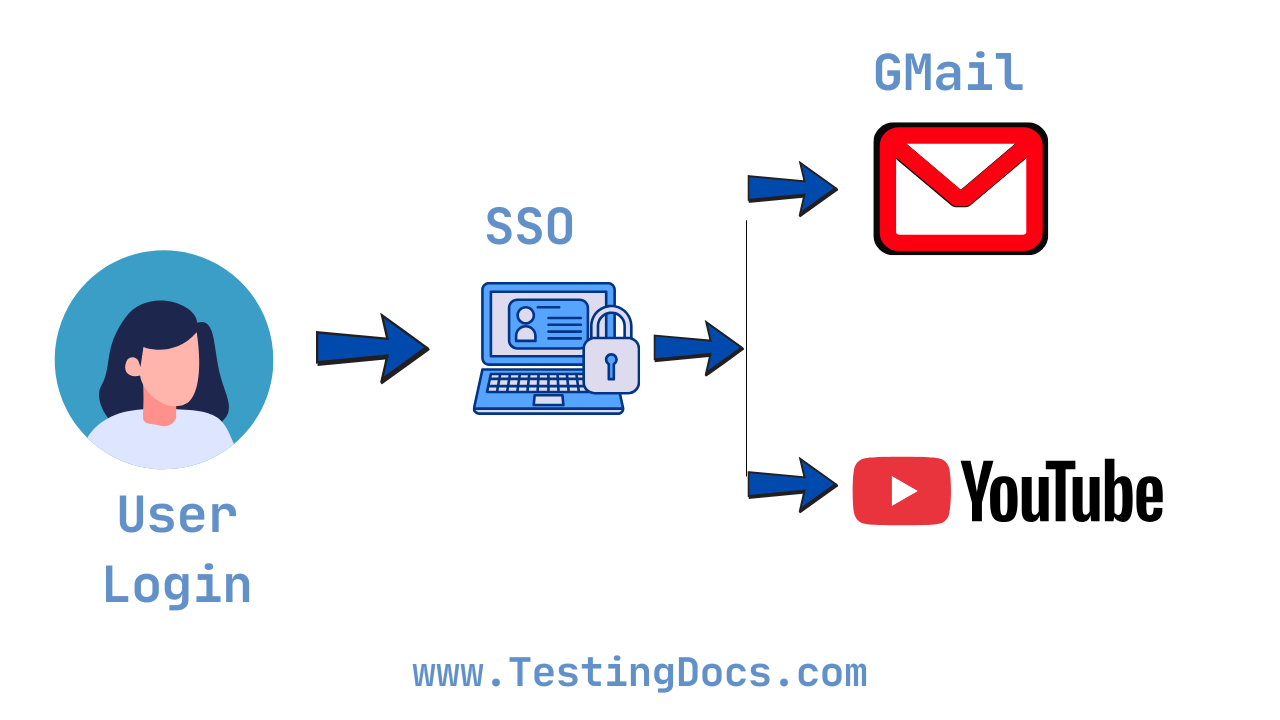
Real-World Example
When you log in to your Google account, you can access Gmail, YouTube, Google Drive, and more—all without signing in again. That’s SSO in action!
Benefits of SSO
Some of the benefits of SSO server are as follows:
- Convenience: Users only need to remember one set of login details.
- Improved Security: Fewer passwords mean fewer chances of weak or reused passwords.
- Easier Management: Admins can control access to all connected apps from one place.
- Faster Access: Less time spent logging in means more productivity.
In summary, an SSO server acts like a trusted gatekeeper that verifies your identity once and then vouches for you across multiple services.