Java Swing CardLayout
Java Swing CardLayout
In this tutorial, you will learn about Java Swing CardLayout.
In Java Swing, CardLayout is a layout manager used to manage multiple components (like panels) where only one component is visible at a time. Think of it like a deck of cards—only the top card is visible, and you can flip to the next one when needed.
This is useful when you want to create wizard-style interfaces, tab-like behavior, or step-by-step forms in your GUI. The CardLayout manages components in a stack, with only the top visible at a given point in time. Users can choose which components to display through GUI components like buttons, combo boxes, etc.
Basic Methods of CardLayout
-
first(container)– Shows the first card. -
next(container)– Shows the next card. -
previous(container)– Shows the previous card. -
last(container)– Shows the last card. -
show(container, name)– Shows the card with the specified name.
Java Demo Program
package com.testingdocs.swing.layouts;
/****************************************
* Filename: CardLayoutDemo.java
* Package : com.testingdocs.swing.layouts
* Java Tutorials - www.TestingDocs.com
*****************************************/
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.text.AttributeSet.ColorAttribute;
import javax.swing.text.StyleConstants.ColorConstants;
public class CardLayoutDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final String card1Text = "Card 1";
final String card2Text = "Card 2";
final String card3Text = "Card 3";
final JPanel cards;
// buttons
final String NEXT = "NEXT";
final String PREVIOUS = "PREVIOUS";
// Create a frame
JFrame frame = new JFrame("CardLayout Demo - www.TestingDocs.com");
//Create cards.
JPanel card1 = new JPanel();
card1.add(new JButton("Button Card 1"));
JPanel card2 = new JPanel();
card2.add(new JButton("Button Card 2"));
JPanel card3 = new JPanel();
card3.add(new JButton("Button Card 3"));
cards = new JPanel(new CardLayout());
cards.add(card1, card1Text);
cards.add(card2, card2Text);
cards.add(card3, card3Text);
class ControlActionListenter implements ActionListener {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
CardLayout cl = (CardLayout) (cards.getLayout());
String cmd = e.getActionCommand();
if (cmd.equals(NEXT)) {
cl.next(cards);
} else if (cmd.equals(PREVIOUS)) {
cl.previous(cards);
}
}
}
ControlActionListenter cal = new ControlActionListenter();
JButton btn1 = new JButton("Next Card");
btn1.setActionCommand(NEXT);
btn1.addActionListener(cal);
JButton btn2 = new JButton("Previous Card");
btn2.setActionCommand(PREVIOUS);
btn2.addActionListener(cal);
// add buttons
JPanel controlButtons = new JPanel();
controlButtons.add(btn1);
controlButtons.add(btn2);
Container pane = frame.getContentPane();
pane.add(cards, BorderLayout.CENTER);
pane.add(controlButtons, BorderLayout.PAGE_END);
//Frame properties
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setSize(400, 200);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
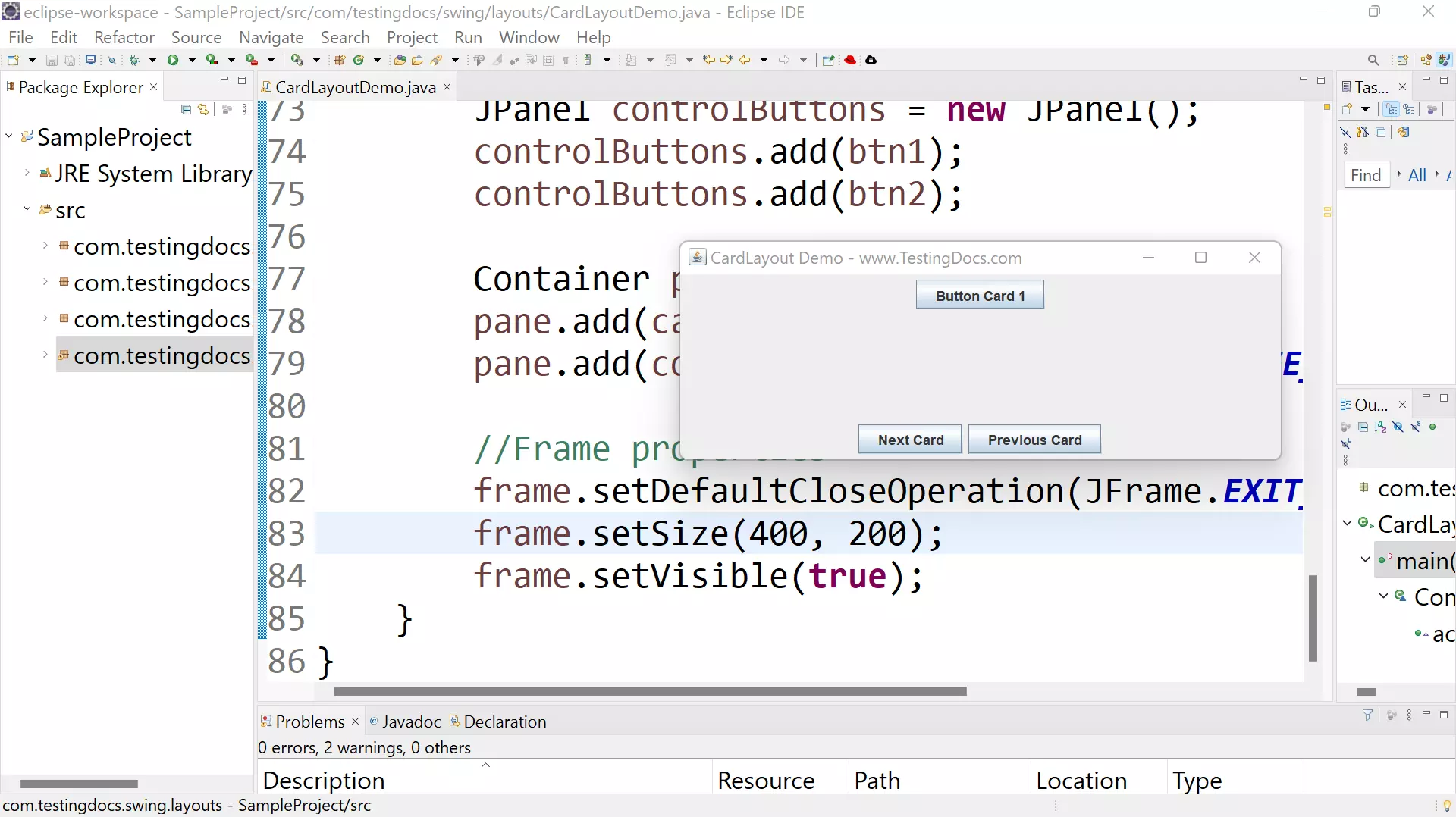
Output
Run the Java application to view the output.
—
Java Tutorial on this website:


