Java Tutorial
Welcome to the world of Java! This tutorial will start with the basics and cover all the essential concepts a beginner needs to know.
Java is a high-level, object-oriented, distributed, secure, multi-threaded, and portable programming language. Java is a general-purpose programming language intended to let Java developers Write Once and Run Anywhere (WORA). Java was first released in 1995. It was created by James Gosling and his team at Sun Microsystems (now owned by Oracle Corporation).
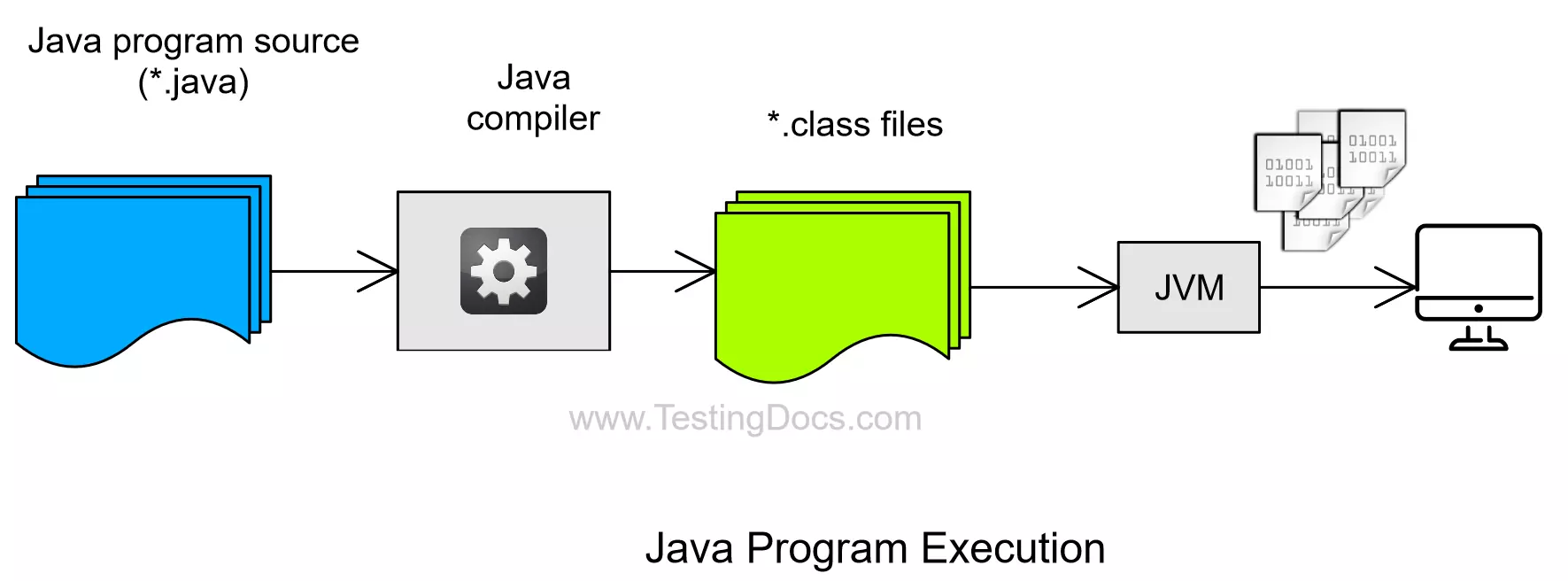
WORA means that the compiled Java code(Java bytecode) can run on many platforms that support Java without recompiling the Java source code. This allows Java to be cross-platform and platform-independent.
Java Platform
Java is designed to be platform-independent, meaning that Java programs can run on any platform (such as Windows, Mac, or Linux) without recompiling. This is achieved through the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), which translates Java code into bytecode that can be executed on any platform.
Java Download
You must install Java on your computer before you can start writing Java programs. The latest version of Java can be downloaded from the official website.
Java Editions
First Java Application
Once Java is installed, you must set your environment variables to point to the Java installation directory. This will allow you to run Java programs from the command line without changing the working directory to the Java install directories.
Let’s start by writing a simple “Hello, World!” program in Java.
Popular IDEs
OOPS Concepts
Main method
Hello World
Java Comments
Java Packages
Data Types
In Java, a variable is a named container that stores a value. You can declare a variable in Java by specifying its data type (such as int or double) and a name for the variable.
Java Variables
Java Operators
Program Structure
Java Access Modifiers
Class and Object
Setters and Getters
Java Interface
Abstract Class
Java Testing Tools
JDBC Tutorials
JDBC stands for Java Database Connectivity. JDBC API defines classes and interfaces that allow Java applications to interact with databases. In the following tutorials, we will learn to execute SQL statements from Java programs using JDBC API.
The basic steps to execute SQL statement with JDBC API are:
- Configure Java development environment. ( JDK Install, IDE setup, etc.)
- Create a Java project and class
- Download and Install JDBC Driver. Set up a classpath or build a path for the driver.
- Load suitable JDBC Driver
- Establish a database connection
- Create an SQL statement to execute
- Execute the SQL statement
- Process the query ResultSet
- Close the database connection
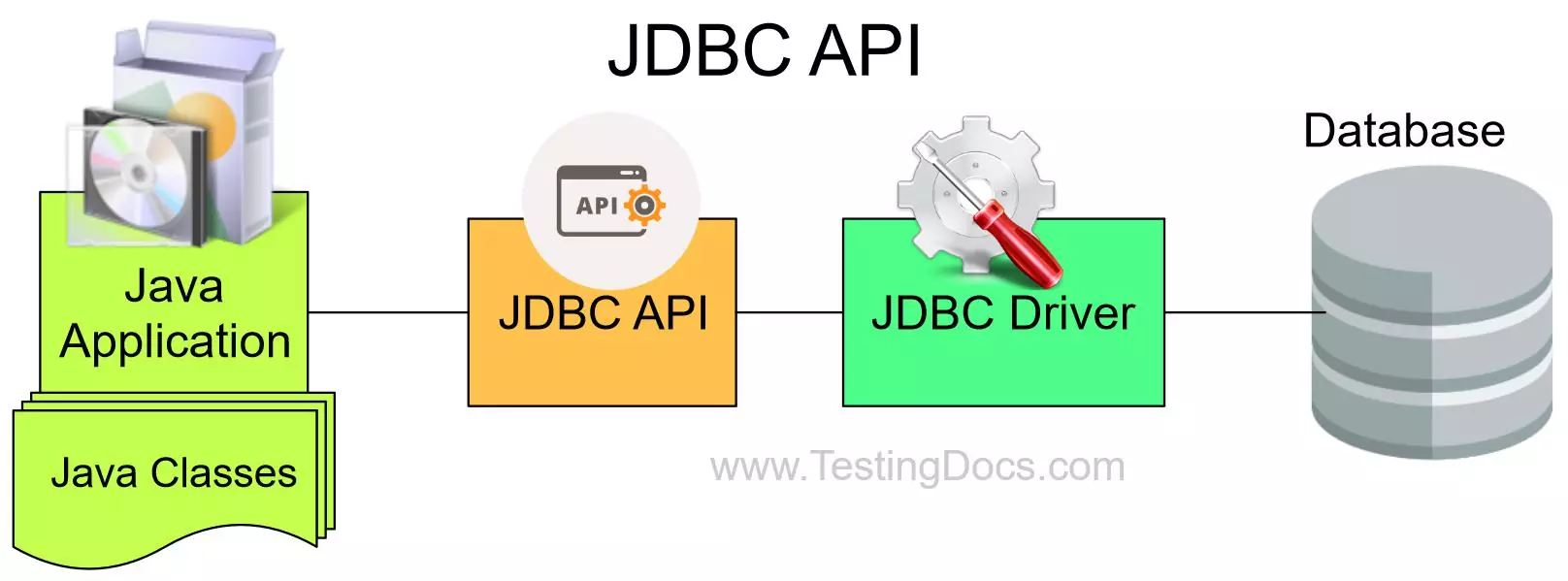
Java Database Connectivity API