Object Oriented Principles
Overview
Java is an object-oriented programming language. The key principles of object-oriented programming are
- Abstraction
- Encapsulation
- Inheritance
- Polymorphism
Abstraction
Abstraction is hiding implementation details or managing complexity at the system level. For example, when we think of a car, we think of a well-defined object with states and behavior. While driving a car we ignore many internal details of the car like the engine, gear system, brake system, etc. We manage the complexity of the car through abstractions. Abstractions allow us to shield from inevitable changes in the subsystems.
Encapsulation
Encapsulation is the binding of data and the methods that operate on the data. For example, you can make a method that changes a variable as private. This keeps the data safe from outside misuse of the data. Encapsulation is at the object level hiding data from outside the class.
Encapsulation acts like a protective shield that prevents code and data from outside interference. Access will be allowed through a well-defined interface. In the Java class, we have variables and methods.
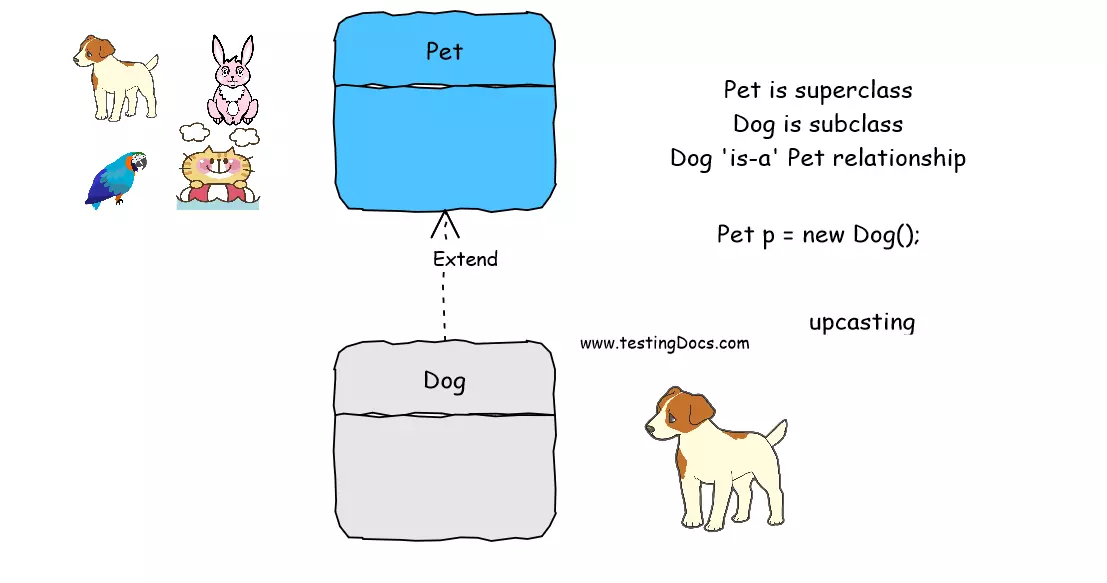
Inheritance
Inheritance is when one object called a subclass or child class acquires or inherits state and behavior from another object called the superclass or parent class. The child class and the parent class share an “IS-A” relationship. For example, the Cat is an animal. In Java, we use the extends keyword to use inheritance.
public Cat extends Pet {
…
}
Polymorphism
Polymorphism means having many forms and shapes. Java supports static as well as dynamic Polymorphism. It has the ability to process multiple objects of various classes through a single interface. Any object in Java is polymorphic in nature. We will discuss more static and dynamic polymorphism in detail in another post.
—
Java Tutorials
Java Tutorial on this website:
https://www.testingdocs.com/java-tutorial/
For more information on Java, visit the official website :