C Strings
C Strings
In this tutorial, we will learn about C Strings. Strings are a sequence of characters. C language has no in-built string data type. A string is stored in an array of characters.
Declare a String
The general syntax to declare a string in the C language is as follows:
char <string_variable_name>[size];
For example, to declare an eleven-character string:
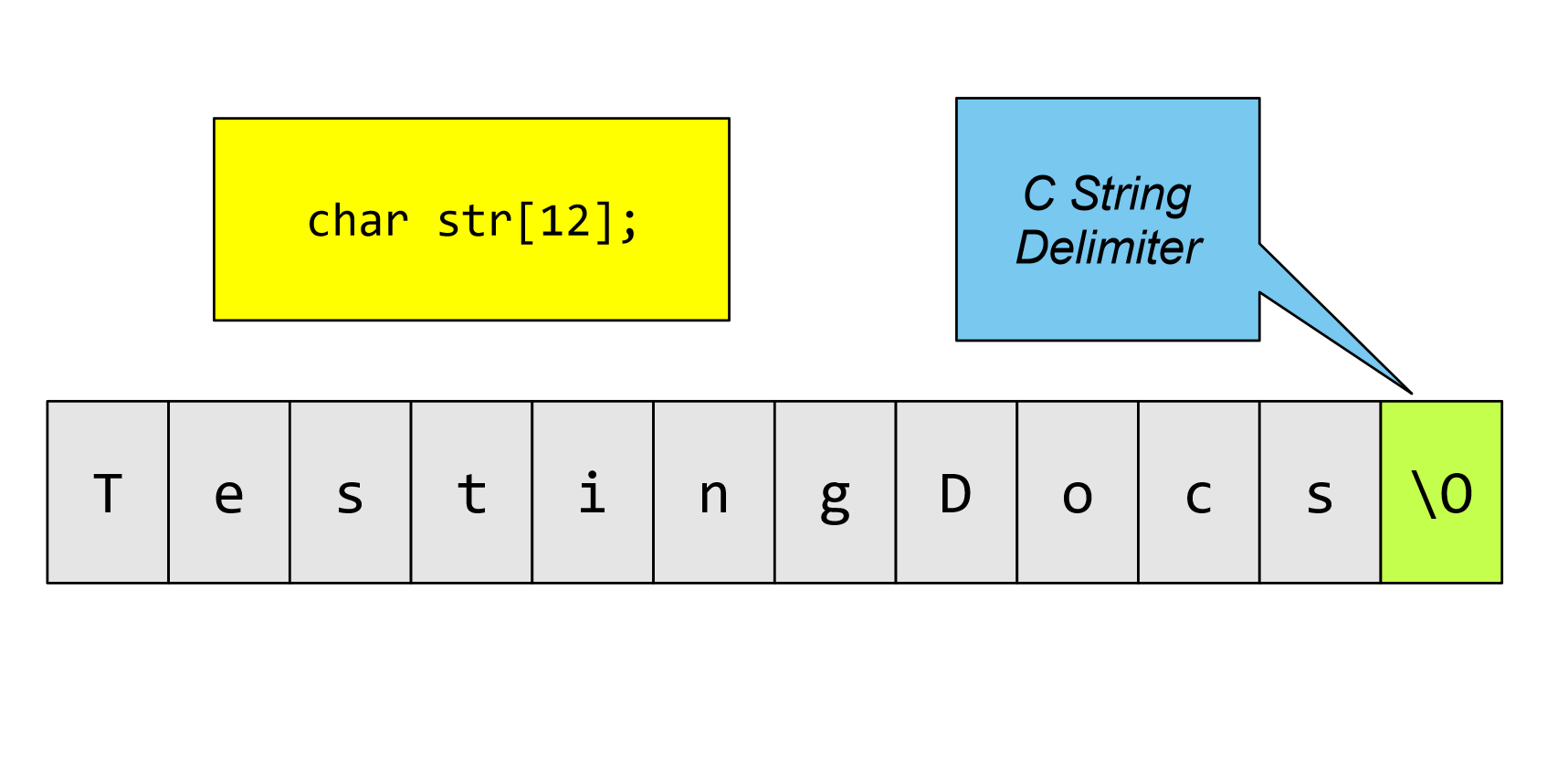
char str[12];
The storage space must contain space for the string data and the space for the string delimiter.
Initialize a String
We can declare and initialize a string at the same time. We can initialize the string in the same way that we initialize any variable by assigning a value to it when it is defined. For example, we can define a string and store the value “TestingDocs”, as shown below.
char str[12] = “TestingDocs”;
The value “TestingDocs” enclosed within double quotes is a string literal. Also, if we initialize the string we do not need to specify the array size. For example,
char name[] = “Emma”;
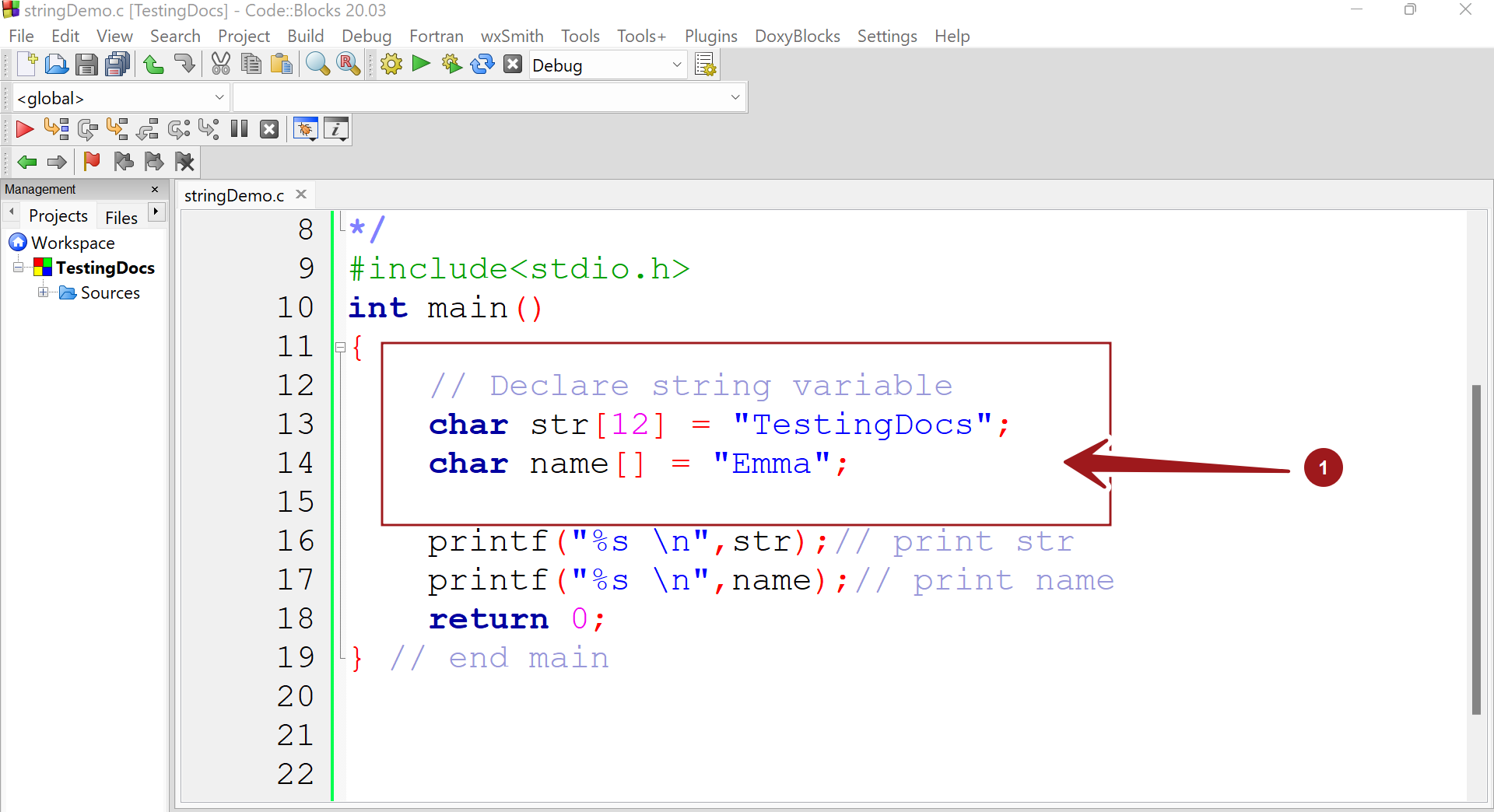
Example
Let’s declare two strings and print the strings to the console in the below program:
/**
**********************************
* Program Description:
* C Strings Demo Program
* Filename : stringDemo.c
* C Tutorials - www.TestingDocs.com
*************************************
*/
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
// Declare string variable
char str[12] = "TestingDocs";
char name[] = "Emma";
printf("%s \n",str);// print str
printf("%s \n",name);// print name
return 0;
} // end main