Eclipse Platform Components
Eclipse Platform Components
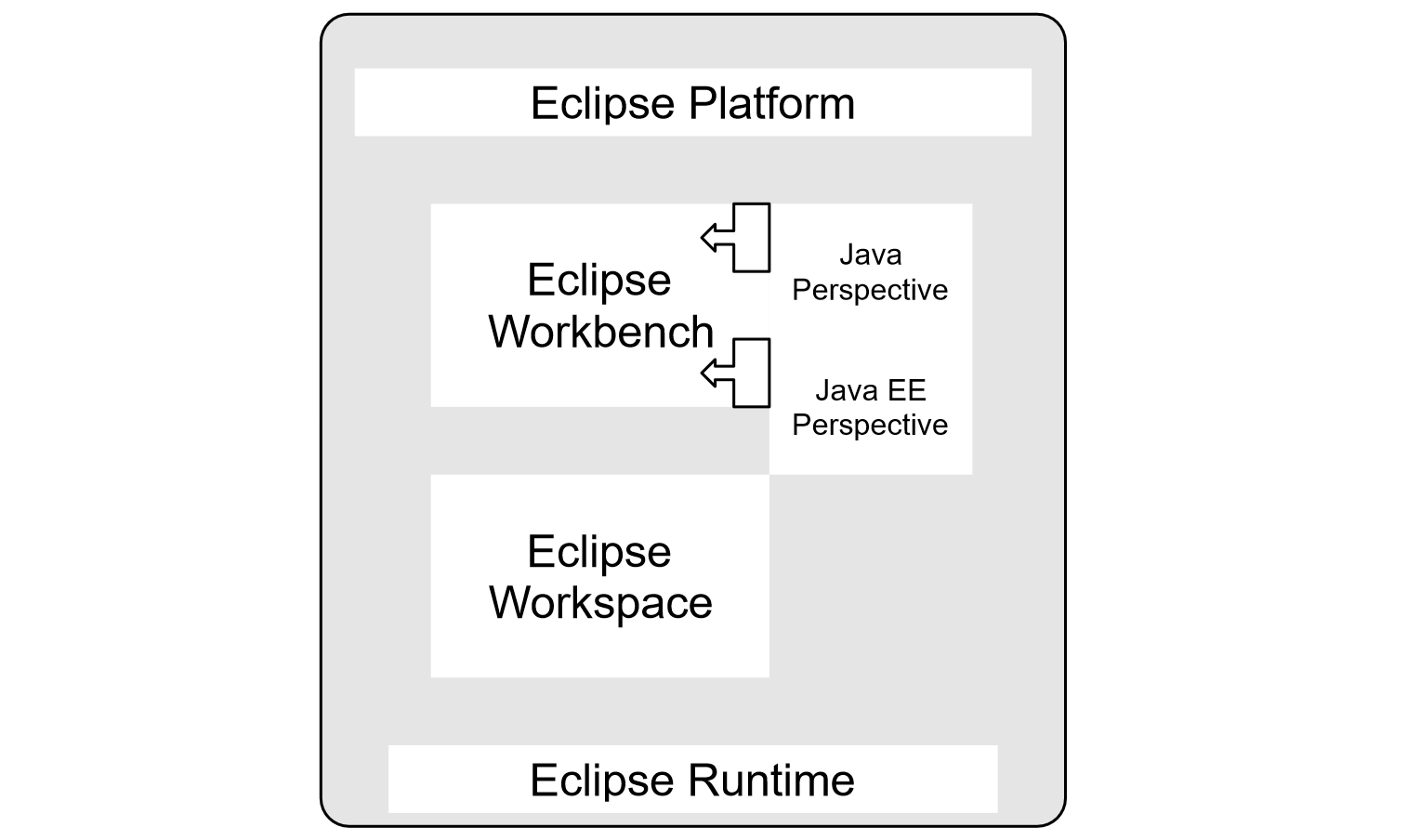
In this tutorial, we will learn Eclipse Platform Components. It consists of several sub-components. All the sub-systems run on top of Eclipse platform runtime. Some of the important Eclipse components are as follows:
- Eclipse Workbench
- Eclipse Workspace
- Eclipse Runtime
Eclipse Workspace
Eclipse Workspace is a directory where we can store project files, source and other project artifacts. We need to choose an Eclipse workspace to begin Eclipse workbench.
For example on Windows: C:\Users\<YourName>\eclipse-workspace
Eclipse Workbench
Eclipse Workbench is the desktop development environment for developing and building applications. Workbench window contains Eclipse perspectives.
The user interface (UI) of Eclipse that includes editors, views, and perspectives to interact with the workspace.
| Eclipse Workspace | Eclipse Workbench | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The directory where Eclipse stores project files, metadata, settings, and preferences. | The user interface (UI) of Eclipse that includes editors, views, and perspectives to interact with the workspace. |
| Purpose | Stores and organizes all your development projects and configurations. | Provides a GUI environment to work with projects and tools visually. |
| Scope | File-system based location on disk. | UI-level concept within Eclipse IDE. |
| Persistence | Data is stored even after Eclipse is closed. | Only active while Eclipse is running; reflects workspace contents. |
| Contains | Projects, settings files (.metadata), source code, build files, etc. | Editors, Views (like Project Explorer), Toolbars, Menus, and Perspectives. |
| Example | C:\Users\YourName\eclipse-workspace |
Java Perspective showing code editor, outline view, console, etc. |
Eclipse Perspective
An Eclipse perspective contains several views, menus, toolbars and editors suitable for a specific purpose. For example, Java perspective is designed to support Java standalone applications. Java EE perspective is designed to develop enterprise Java applications. Some examples of Eclipse perspectives:
- Java perspective
- Java EE perspective
- Debug
- Hibernate
- Git
- JBoss
- SpotBugs
Java Perspective
Java perspective is designed to support Java application development.
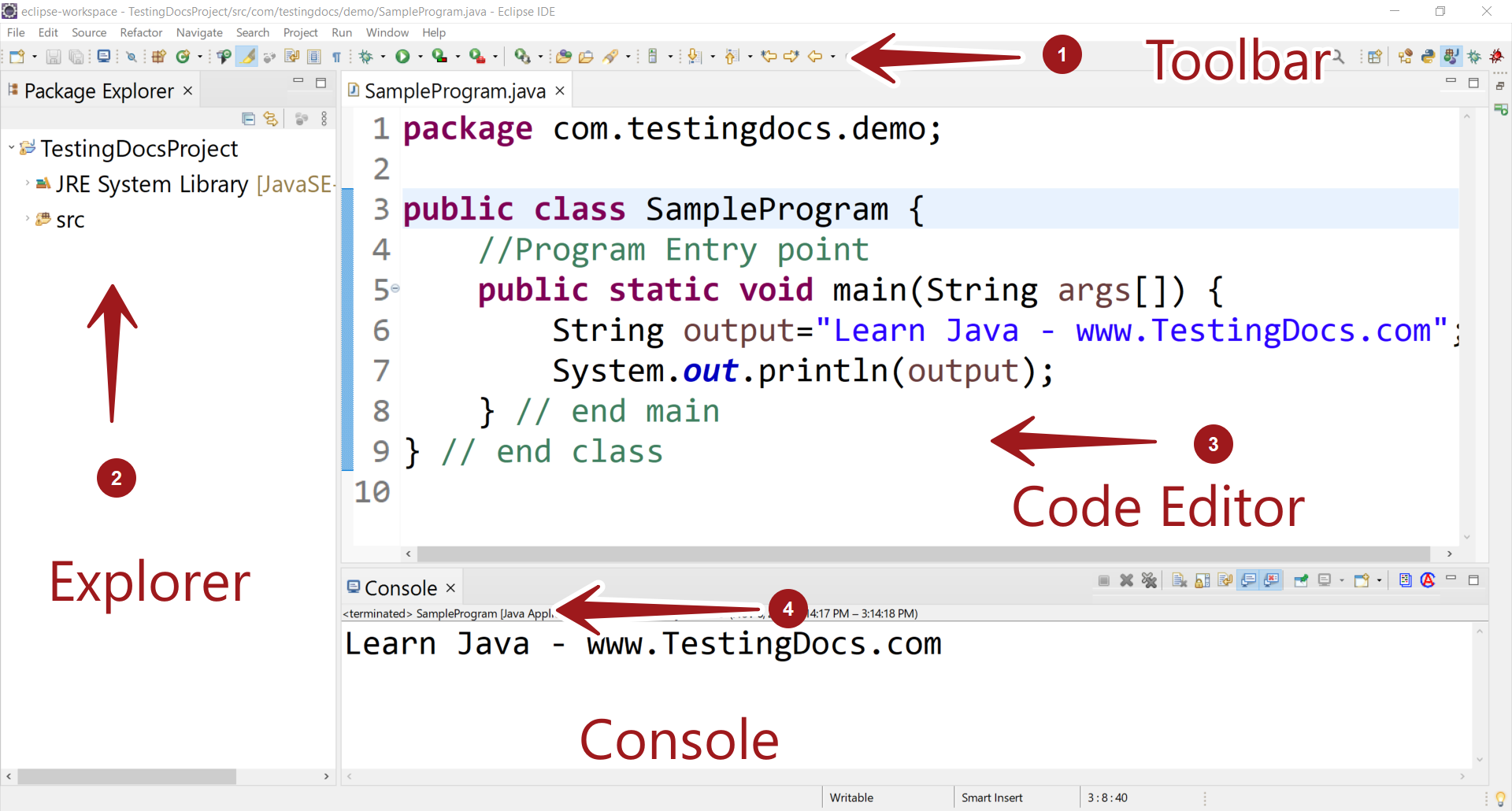
Project Explorer
We can explore the project contents using Project explorer. We can browse project packages, files, Java source code, folders, properties and configuration, Maven dependencies, etc.
In the Project Explorer view, make sure the project and the source folder are expanded so you can see the packages. Expand the package to see the Java files contained in the package.
—
Eclipse Tutorials
Eclipse Tutorials on this website can be found at:

