Java List Interface Example
Java List Interface Example
In Java, the List Interface is part of the java.util package and is used to store an ordered collection of elements. It is one of the most commonly used interfaces in the Java Collections Framework.
The List index starts with 0 like usual arrays in Java. The List interface allows the addition of duplicates and nulls to the list.
You can import the List using the following statement:
import java.util.List;
Features of Java List
The key features of Java list are as follows:
- Maintains insertion order
- Allows duplicate elements
- Elements can be accessed by index
- Supports null values (depends on implementation)
Common Implementations of List
Some of the common implementations are as follows:
- ArrayList – Resizable array, fast access
- LinkedList – Doubly-linked list, fast insertion/deletion
- Vector – Thread-safe, but slower
- Stack – A subclass of Vector that follows LIFO order
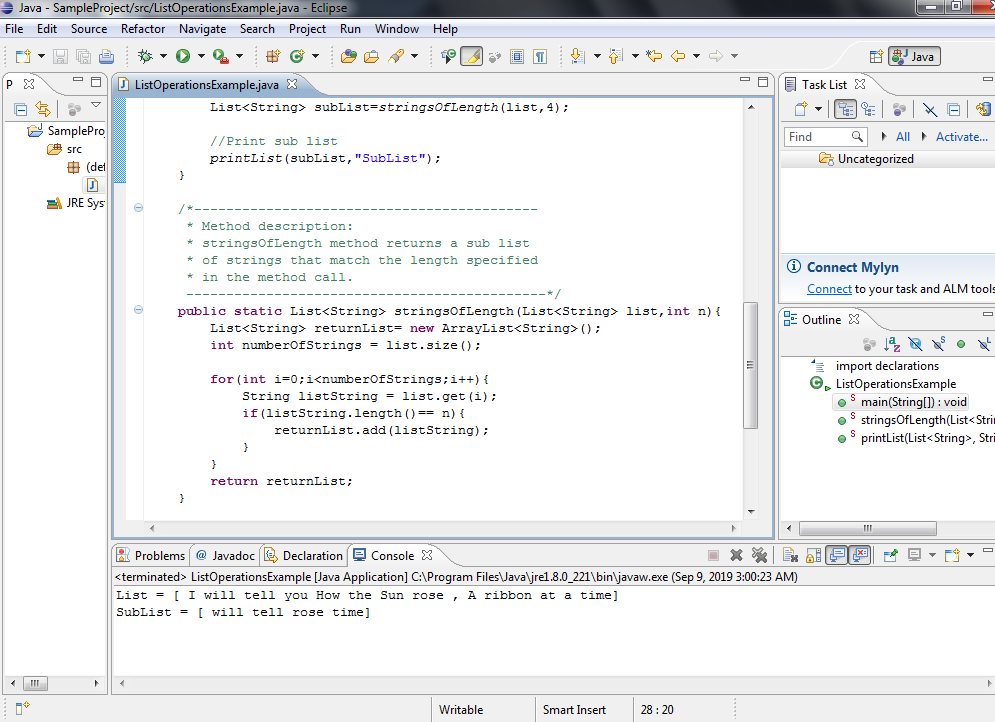
Sample Listing
Below is a sample java program to capture strings of some length in a list and return the list of strings to the main program.
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/*-------------------------------------------
* Program description:
* To learn how to write a java method that
* processes a list of strings and returns
* a sub list of string of specified length
*
---------------------------------------------*/
public class ListOperationsExample {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Emily Dickenson's poem two lines of
// first stanza....
List<String> list= new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("I");
list.add("will");
list.add("tell");
list.add("you");
list.add("How");
list.add("the");
list.add("Sun");
list.add("rose");
list.add(",");
list.add("A");
list.add("ribbon");
list.add("at");
list.add("a");
list.add("time");
//Print list
printList(list,"List");
//Find string of length 4 in the stanza
List<String> subList=stringsOfLength(list,4);
//Print sub list
printList(subList,"SubList");
}
/*-------------------------------------------
* Method description:
* stringsOfLength method returns a sub list
* of strings that match the length specified
* in the method call.
---------------------------------------------*/
public static List<String> stringsOfLength(List<String> list,int n){
List<String> returnList= new ArrayList<String>();
int numberOfStrings = list.size();
for(int i=0;i<numberOfStrings;i++){
String listString = list.get(i);
if(listString.length()== n){
returnList.add(listString);
}
}
return returnList;
}
/*-------------------------------------------
* Method description:
* printList method prints the list
---------------------------------------------*/
public static void printList(List<String> list,String name){
int numberOfStrings = list.size();
System.out.print(name + " = [");
for(int i=0;i<numberOfStrings;i++){
System.out.print(" " + list.get(i));
}
System.out.println("]");
}
}
Screenshot
—
Java Tutorials
Java Tutorial on this website: