Computer Programming Languages
Overview
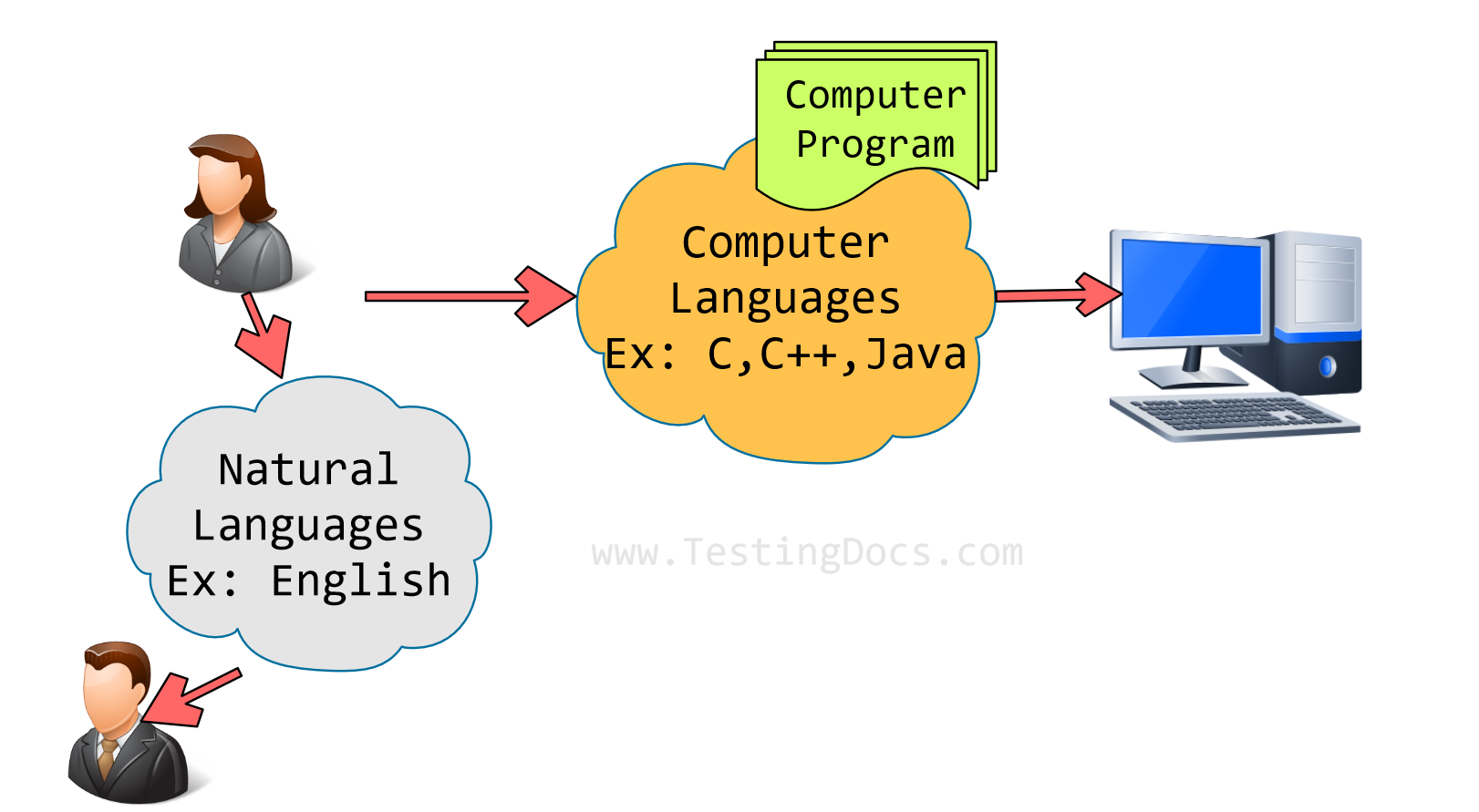
This tutorial will teach us about computer programming languages and their classifications. Humans speak and communicate using a natural language such as English, Russian, French, German, Spanish, Japanese, Hindi, Chinese, Tamil, etc. Natural language is referred to as Human Language.
Programming Language
Computer languages provide the means of communication with the computer machine.
A computer programming language is a set of rules, commands, instructions, symbols, and syntax that allows programmers to write code and create software programs or applications like desktop applications, websites, computer games, etc.
Computer Programming Languages
Computer Languages are broadly classified into the following categories:
- Low-level Languages
- High-level Languages
Programming languages that software developers, used to write source code are called High-Level Languages. This source code can be compiled into a Low-level Language, which is recognized by the computer machine hardware.
Low-Level Languages
Low-level languages are close to the language that the computer machine understands. They are highly dependent on the machine and its hardware components. The low-level languages are further classified into the following:
- Machine Language
- Assembly Language
Machine Language
Machine Language(ML) is in the form of 0’s and 1’s, called binary numbers or bits. A digital computer only stores and understands information in bits.
Machine language is a collection of machine instructions. It is machine-dependent and is challenging to learn and write programs in Machine Language.
Example: Intel Machine Language.
Assembly Language
The next step in early programming languages was to use symbols or mnemonics to denote low-level machine instructions. The machine instructions comprising of 0’sand 1’s are substituted by symbols (mnemonics) to improve their understanding. These languages are known as symbolic languages.
The symbolic languages had to be translated and assembled into machine languages. Hence, symbolic languages are also known as Assembly languages( AL). The program that translates the assembly language program to machine language is known as the assembler.
Example: x86 Intel assembly language, MIPS assembly language
High-level Languages
Assembly language programming is more straightforward and less time-consuming than machine-level programming. However, the programmers must have knowledge of the machine architecture/processor on which the program will run.
High-level languages are close to the language that humans understand. The high-level languages hide the inner details and implementation of the machine and its hardware design from the programmer. For example, the high-level programmer is least concerned about how many CPU registers store data inside the microprocessor.
The programmer need not worry about the target computers and can concentrate on the problem, algorithm, and source code of the computer program. This process of hiding implementation details is known as abstraction. Programs written in high-level languages are portable to many computers.
Examples: FORTRAN, C, C++, Java, Python
The top ten programming languages list can be found here:
https://www.testingdocs.com/top-10-programming-languages-2023/