Regression Testing Vs Re-Testing
Introduction
In this post, we will learn about Re-Testing and Regression testing. Mostly, the concepts stated on this page are from a manual testing standpoint. However, from a continuous delivery testing standpoint, most of the things done in the regression cycle can be automated.
Regression Testing
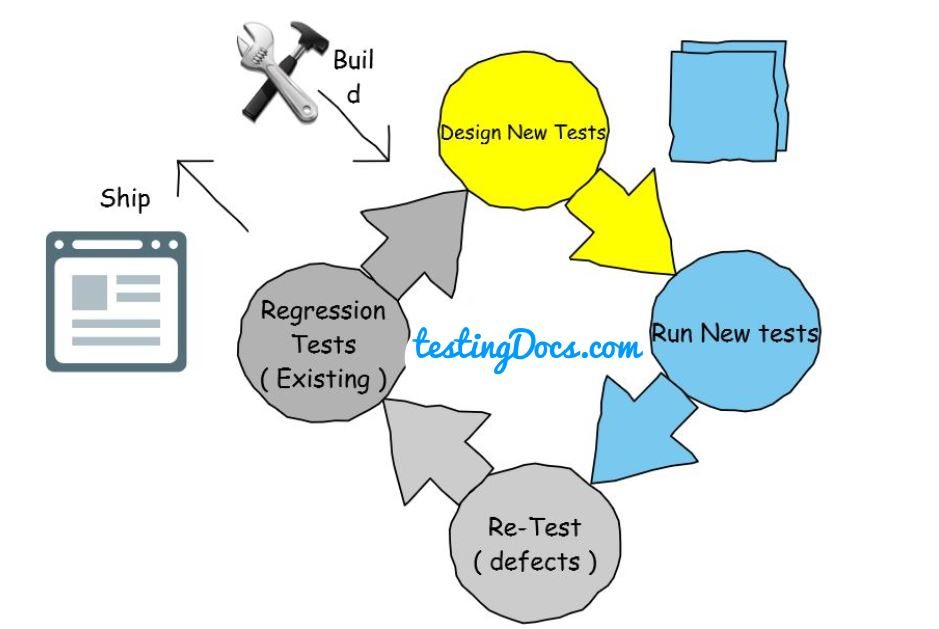
Regression is the re-execution of the test cases for unchanged parts to see whether the unchanged functionality is working fine are not. (This exercise is usually done as a cycle )
Regression testing is done to ensure that change in one part of the software has no side effects on other parts of the application.
When a defect is reported, the Dev team will fix the defect. It is likely that the change made in the code may lead to side effects that may not be visible immediately. So, whenever a change is made to the source code, the QA team has to ensure that there are no side effects of the change to other parts of the AUT.
Re-Testing
Retesting is done to make sure that the bug is fixed and the failed functionality is working fine or not, This is a kind of verification method followed in the Testing field for the fixed bugs.
Re-testing is done to ensure that the bug is fixed by running the same test case repeatedly. It is run on the same code where the change has been made. Also, it does not involve testing of other parts of the software. Furthermore, Re-testing means we are testing only a specific part of an application again. We do not consider how it will affect the other parts of the whole application.
Retesting is only done for failed Test cases. When there is little time Re-testing takes precedence over regression testing.