Risk Management Process
Overview
Risk management is a crucial process in Project management that enables team members to identify, assess, and mitigate potential risks that may affect the project. A risk is an unwanted event that might occur with a certain probability. The risk management process consists of the following stages:
- Risk Identification
- Risk Analysis
- Risk Mitigation
- Risk Monitoring
Risk Identification
Risk identification is the initial stage of recognizing what risks might occur during the project. At this stage, the main priority is to ensure that as many risks are identified.
Risk Analysis
The aim of the risk analysis stage is to quantify the risks so that they can be ranked and prioritized. This stage is about getting more information about each risk that might occur. The risk levels of each risk are identified.
The risk level is defined as the product of the probability of a risk( or the likelihood of occurrence) occurring and the impact of the risk if it occurred. The impact is the loss to the project or the organization if the risk becomes reality.
Risk Level = P(event) * Impact
Example:
If a risk had a probability of 1/20 occurrence
Its impact would be a loss to the organization is $ 500
Risk level = 1/20 * 500 = 25 $
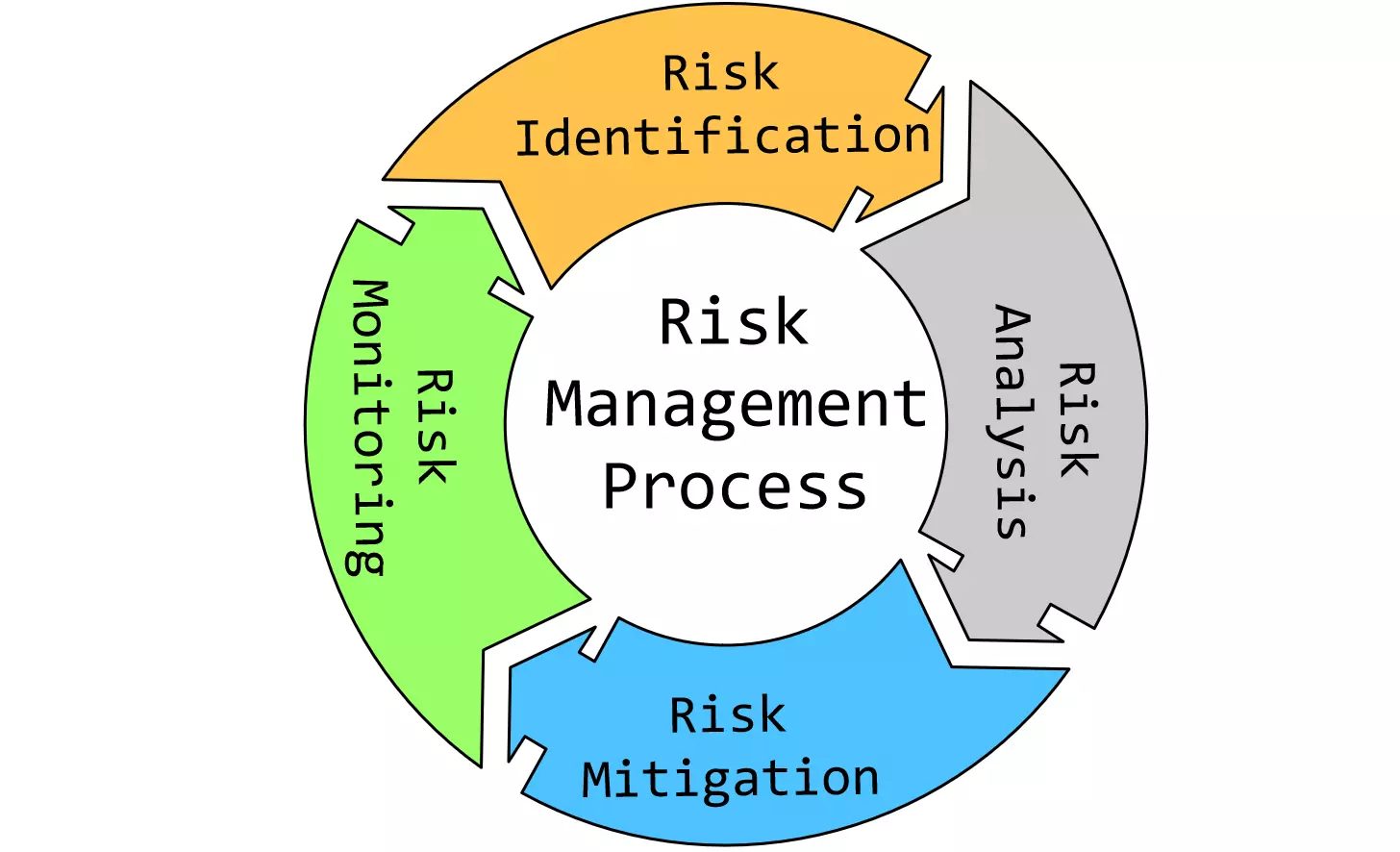
Risk Mitigation
Risk mitigation refers to the process of identifying, assessing, and reducing or eliminating the risks that may affect the project or organization. Risk mitigation is an essential part of risk management and involves taking steps to minimize the impact of each risk. It is the actions that the software team takes to tackle each risk.
Risk Monitoring
Risk monitoring refers to the continuous process of identifying, assessing, and tracking risks that may affect the project. It involves continuous observation, analysis, and evaluation of risks to ensure that appropriate measures are taken to mitigate or avoid them.