White Box Testing
Overview
In this tutorial, let’s learn about White box testing. White box testing is a software testing technique that examines an application or system’s internal structure, source code, program logic, and internal workings. White-box testing is a dynamic testing technique. Dynamic testing involves executing the Application Under Test (AUT). The other names of white box testing are as follows:
- Glass box testing
- Clear box testing
- Open box testing
- Path driven testing
- Logic driven testing
- Structural testing
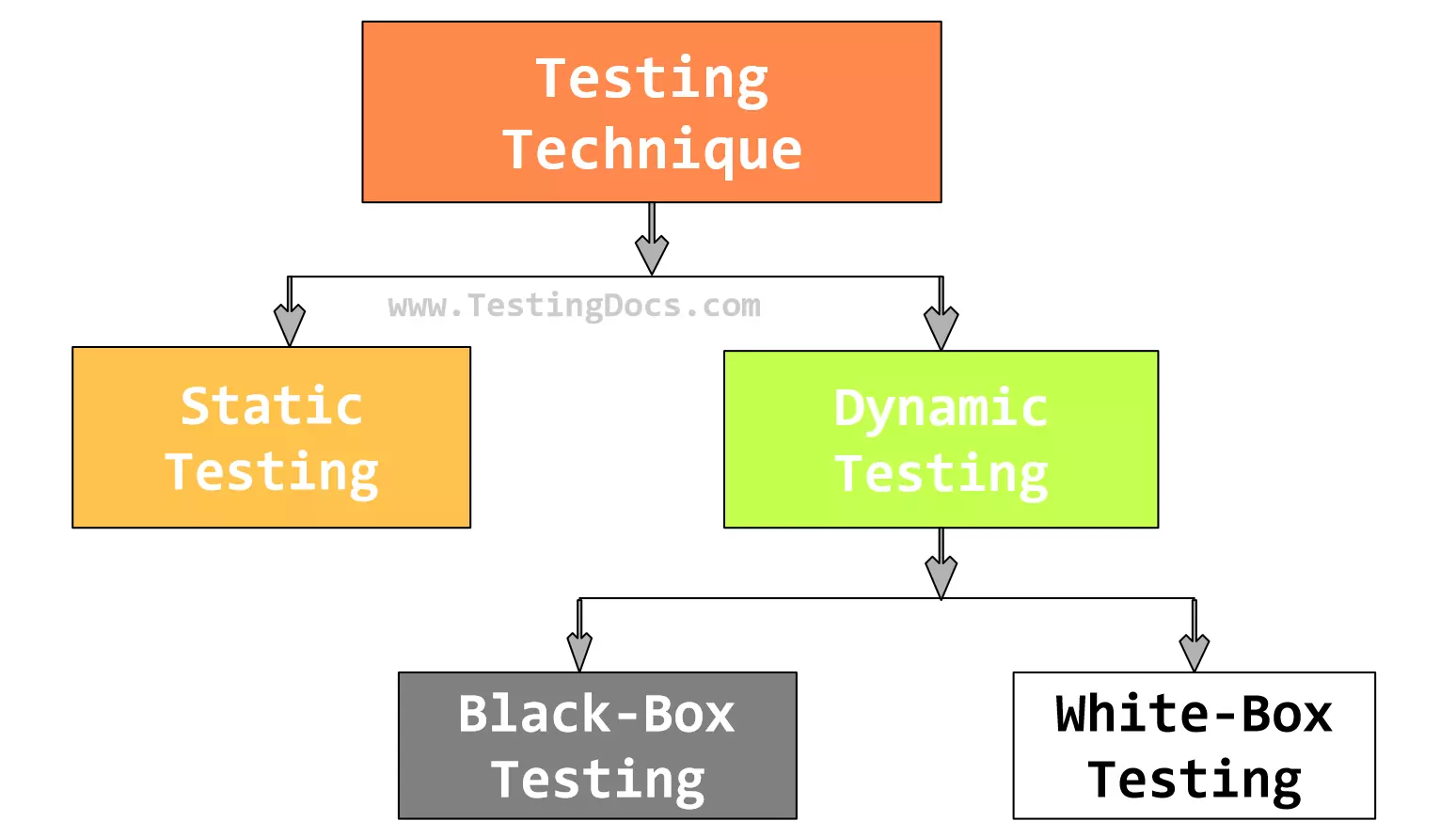
White Box Testing
White Box testing is based on the inner workings of an application. In most organizations, developers or testers with programming knowledge usually perform this type of testing. The tester has access to the software application’s source code and knows its internal workings. The tester uses this knowledge to design white box test cases that will exercise specific paths or conditions within the code to ensure it functions as intended.
- JUnit
- Google test
- EclEmma
White Box Testing Techniques
- Statement Coverage
- Branch Coverage
- Path Coverage
- Condition Coverage
- Multiple Condition Coverage
- Decision Coverage
- Control Flow Testing
- Data Flow Testing
Advantages of White Box Testing:
Some advantages of white box testing are as follows:
- Forces test developers to reason carefully about implementation.
- Reveal errors in “hidden” code.
- Spots the dead code or other issues with respect to best programming practices.
Disadvantages of White Box Testing:
Some disadvantages of White box testing are as follows:
- White box testing is expensive as one must spend time and money to perform it.
- The testing team should have in-depth knowledge of the programming language necessary for white box testing.
White box testing is helpful for detecting defects such as coding errors, logical errors, and security vulnerabilities that other testing techniques may miss.
—
Software Testing Tutorials: