Cloud Service Models
Cloud Service Models
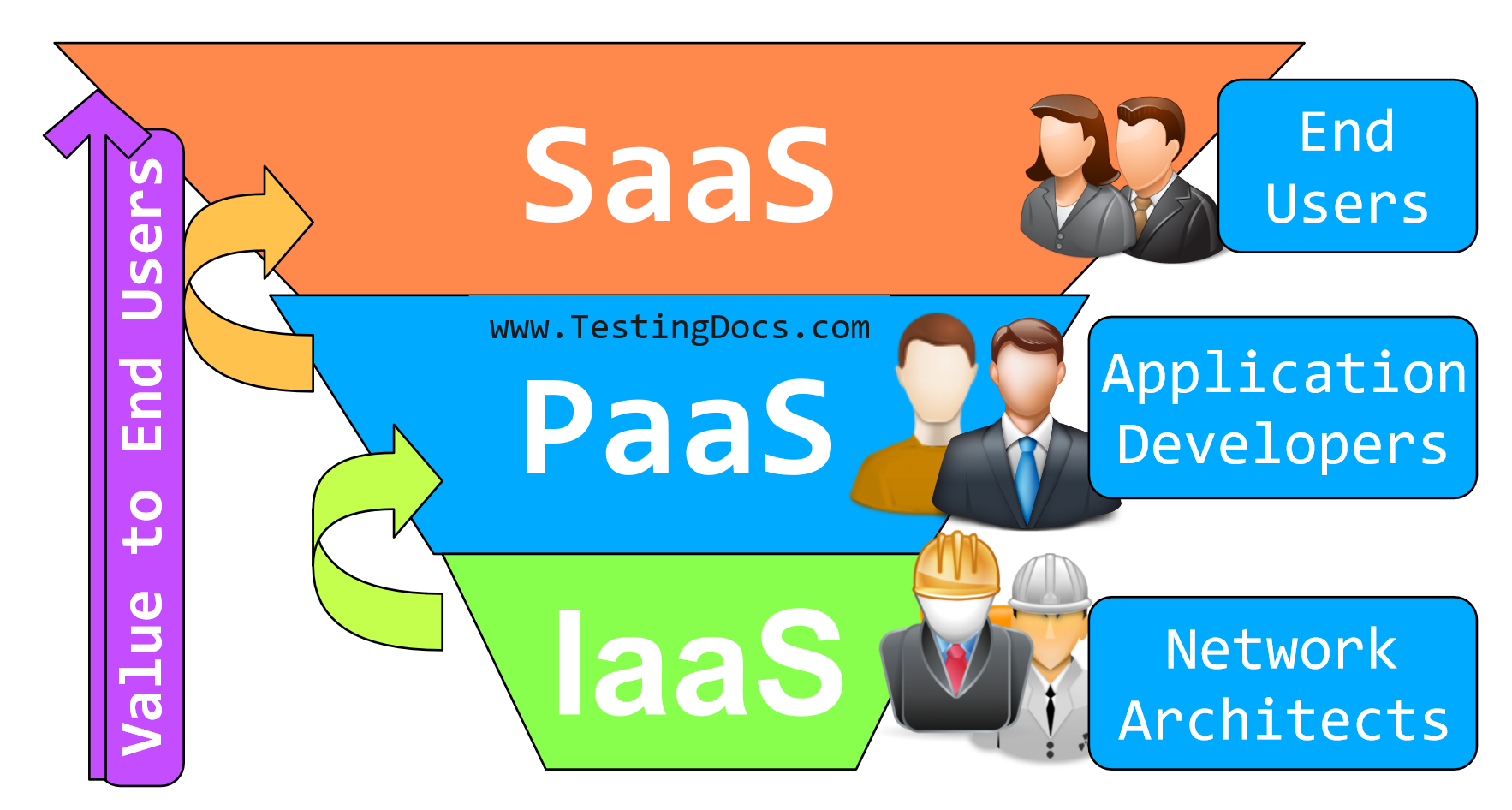
In this tutorial, we will learn about different Cloud Service Models in Cloud computing. Cloud Service Model describes how different types of resources are offered as a service to the end users by the cloud provider. The various cloud service models are as follows:
- IaaS(Infrastructure as a Service)
- PaaS( Platform as a Service)
- SaaS( Software as a Service)
IaaS
IaaS stands for Infrastructure as a Service. IaaS provides the Infrastructure to the clients. It defines renting Infrastructure to clients with facilities. In this model, basic computing resources like storage, computing, and network infrastructure are available to the users.
Users have a choice of deploying software and can install their own operating system and software applications on the infrastructure. Users will be charged as per use of storage space, CPU usage, and bandwidth of the network or charged as per the subscription they are signed up for the service. Users have to take care of the scaling and elasticity as the service provider is not responsible for this.
An example of IaaS is Amazon EC2 ( Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud). EC2 consumers have control to create, launch, use, and terminate EC2 server instances on demand. EC2 instances come in various sizes small, medium, and large depending on their computational power and platform resources. The VMs supports various Operating systems.EC2 uses a hypervisor to run various OSes.
PaaS
PaaS stands for Platform as a Service. In this model, the application is built using tools supported by the cloud provider. This model is typically meant for developers, who develop software applications over the cloud computing service provider’s platform and test it, deploying it over there. But they can’t take the software away from the said platform. Cloud Computing Services utilize the facilities offered within PaaS. Development, deployment, and debugging applications over the service provider’s platform are what a client gets.
Users do not manage the underlying infrastructure like network, servers, OS, storage, etc. Users don’t need to worry about the hardware, software, or scalability of services, as the cloud computing service provider is responsible to maintain these things.
Examples of PaaS are:
- Google App Engine
- Microsoft Azure
SaaS
SaaS stands for Software as a Service. In this model, users get software that is useful for them and use it without installing them on their systems. All they need is a stable internet connection that allows them to access the software from anywhere around the world on their devices like desktop computers, laptops, tablets, mobile devices, etc.
This model offers ease and flexibility to the users. The client uses the software application running in the cloud. Maintaining software applications for the entire organization is a simple yet effective procedure when they use cloud computing. Maintenance, installation, patches, and upgrades are managed by the cloud provider.
The user has no control over the cloud infra, network, OS, server, storage, and even application.
Examples of SaaS applications are:
- Google Workspace
- ServiceNow
- Salesforce