Dynamic Testing
Overview
Dynamic testing is a software testing technique in which the application is executed. Let’s learn about this technique and its differences in this tutorial.
Dynamic Testing
Testing software through executing the program is known as Dynamic Testing. Computer hardware understands a program only if it is coded in its machine language. Machine language is hard for human programmers to understand. Software programs are usually written in High-level programming languages like C, C++, Java, Python, Kotlin, etc.
Depending on the programming language, the general steps the software team takes are as follows:
- Writing and editing the program
- Compiling the program
- Linking the program with the required library modules
- Deploying the program on the environment
- Executing the program
Dynamic testing is performed in the last step, where the software program is run in a certain environment to verify the program output is as desired, and the results are recorded.
Types of Dynamic Testing
- Unit Testing: Focuses on testing individual units or components of the software in isolation.
- Integration Testing: This involves testing the interactions between different units or modules to ensure they work together correctly.
- System Testing: Tests the entire software system to verify that it meets the specified requirements.
- Acceptance Testing: Determines whether the software satisfies the business requirements and is ready for release.
Dynamic Techniques
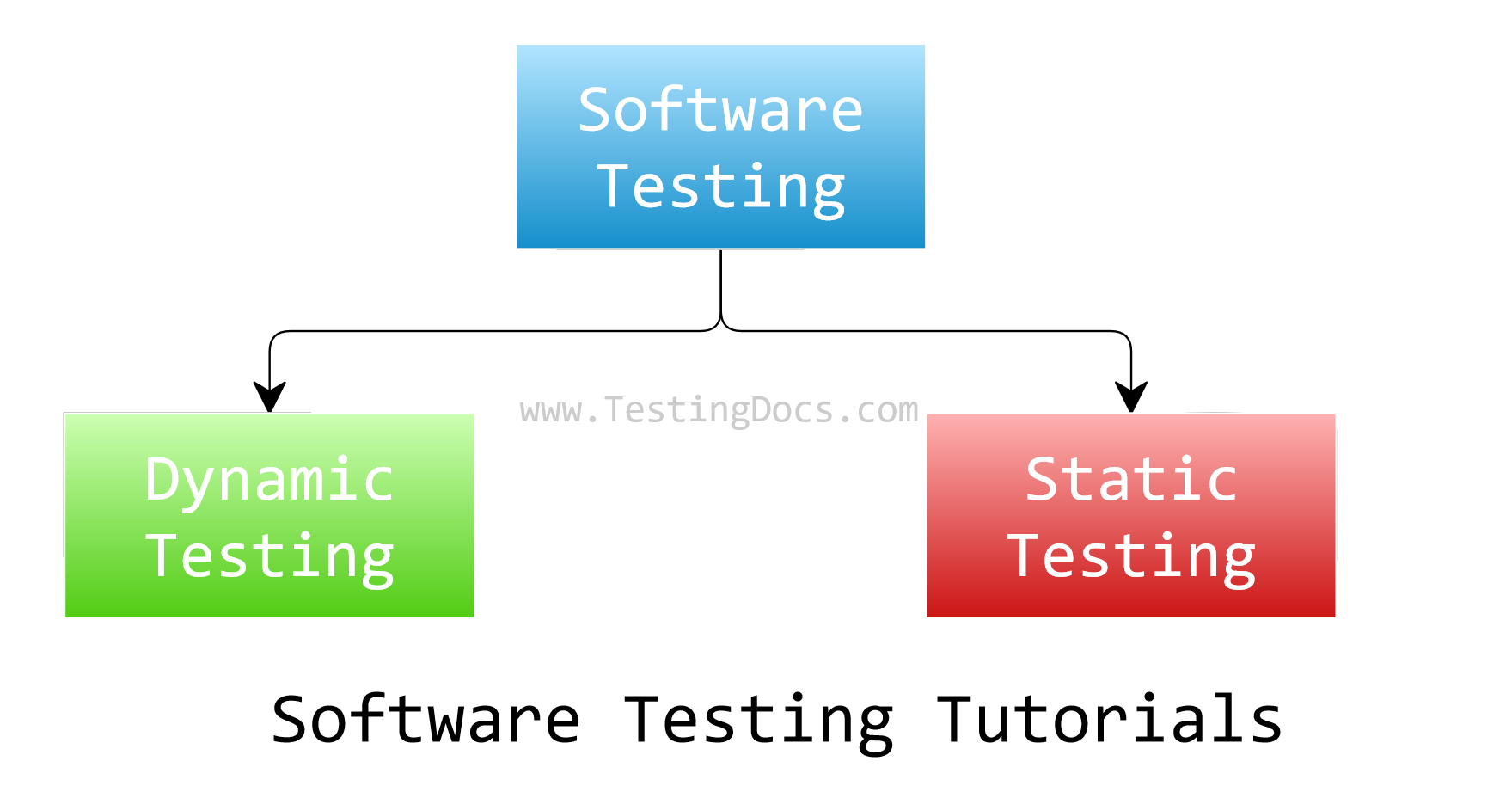
Static vs Dynamic
The following tutorial outlines the differences between Static testing and Dynamic Testing. Static testing involves reviewing the code or documentation without executing the software program.
The main objective of dynamic testing is to find errors in the code and ensure that the software behaves as expected. This type of testing involves the actual execution of the software.
Continuous Integration and Continuous Testing
In Agile and DevOps environments, dynamic testing is often integrated into continuous integration pipelines ( CI/CD pipeline tools like Jenkins, TravisCI, etc ) to ensure that new code changes are continuously tested.
—
Software Testing Tutorials: