Localization Testing
Overview
Localization Testing helps to ensure that software applications are functional, culturally, and linguistically suitable for the intended global audience. Localization involves modifying an application for a specific region, including language and cultural changes once the product is stable.
Localization Testing
Localization testing involves verifying that a software application or product has been successfully adapted for a specific target locale or cultural context. It ensures that the software’s user interface, content, and functionality align with the language, conventions, and expectations of the target audience.
Localization Testing is often abbreviated as “L10n Testing”. The term “L10n” represents the first letter L, followed by 10 characters, and ending with the letter n. This abbreviation is used to make discussions and documentation more concise when referring to localization testing in the software industry.
Locale
A “locale” refers to a specific geographical, cultural, or linguistic region. It encompasses various elements that characterize a particular place, such as language, customs, traditions, currency, date and time formats, and other cultural norms. Locales are important in the context of language and software development, as they help tailor content, user interfaces, and experiences to the preferences and expectations of specific audiences.
The main focus of L10n testing is on aspects such as language translation, date and time formats, numerical formats, currency symbols, cultural considerations, legal and regulatory compliance, and other locale-specific elements. Localization testing involves verifying that the software meets the following criteria in the target locale:
- Language
- Data Formats
- Keyboard Input
- Functional Testing
Example
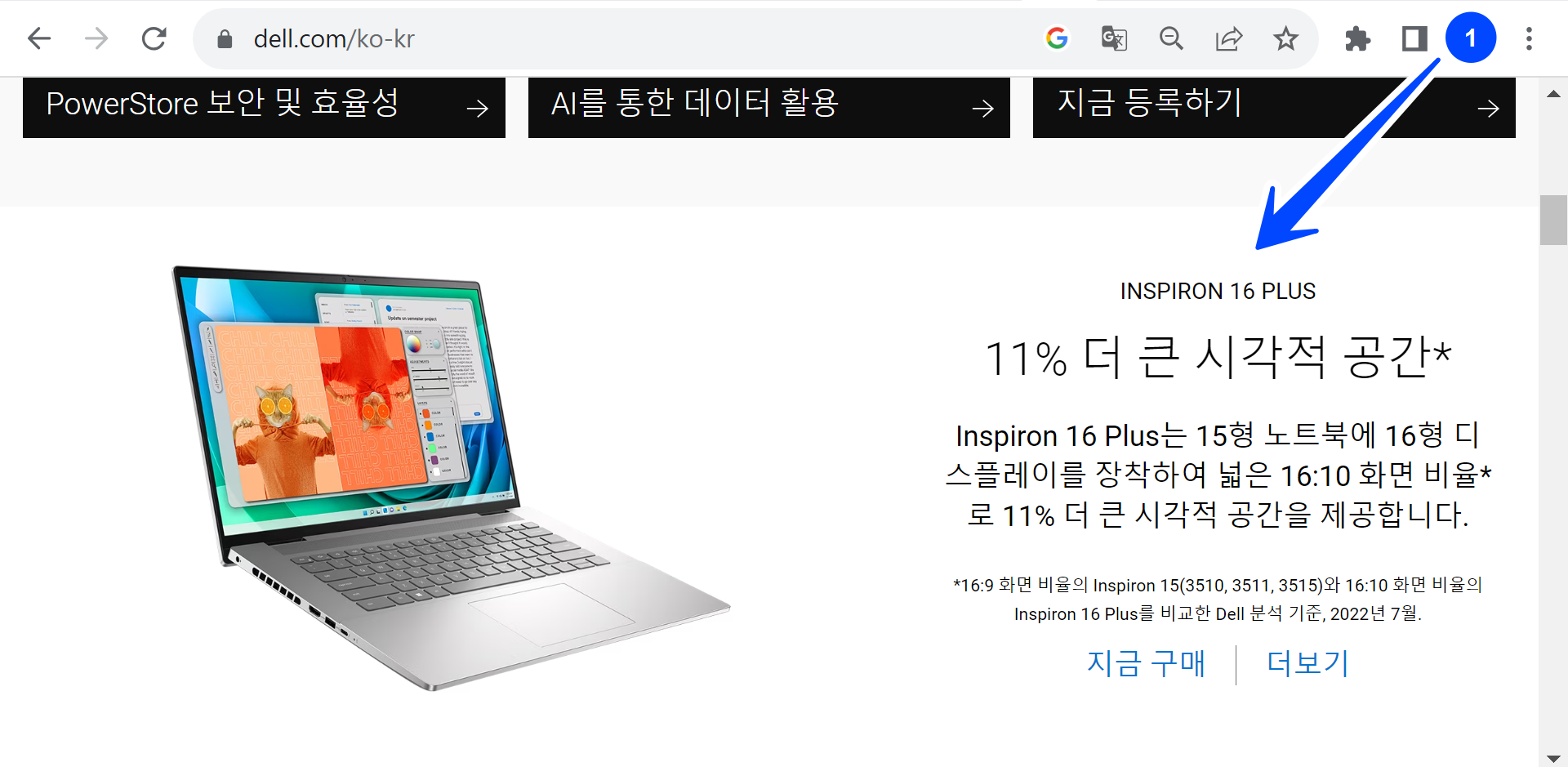
Example of Dell homepage localized for the Korean audience.
In this example, the software product( Dell web application) developed in English is being localized for the Korean market, localization testing would involve verifying that the software’s user interface, text content, dates, times, currency formats, and other elements are aligned with Korean and cultural norms.
Localization Testing is essential for ensuring that software products are suitable and functional for users in diverse global markets.
—
Software Testing Tutorials: