Python Identity Operators
Python Identity Operators
Python identity operators compare the memory locations of two objects. They are different from equality operators. There are two identity operators in Python language. There are as follows:
| Python Operator |
Description | Example |
| is | The is operator evaluates to True if the variables on the other side of the Operator point to the same object and False otherwise | X is y, here in results in 1 if if(x) equal id(y) |
| is not | The is not operator evaluates to False if the variables on either side of the operator point to the same object and True otherwise | x is not y, here is not results in 1 if if(x) is not equal to id(y) |
It’s important to note that identity operators differ from the equality operators (== and !=), which compare the values of two objects.
Example
Sample program to illustrate the use of the identity operators:
# Python program Identity Operators
# Python Tutorials - www.TestingDocs.com
x = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
y = x # y is the same list as x
z = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] # z has same contents as x, but is a different object
# is operator
print('x is y? =', x is y) # True, x and y are same objects
print('x is z? =', x is z) # False,x and z are different objects
# is not operator
print('x is not z? = ', x is not z) # True, x and z are different objects
Output
x is y? = True
x is z? = False
x is not z? = True
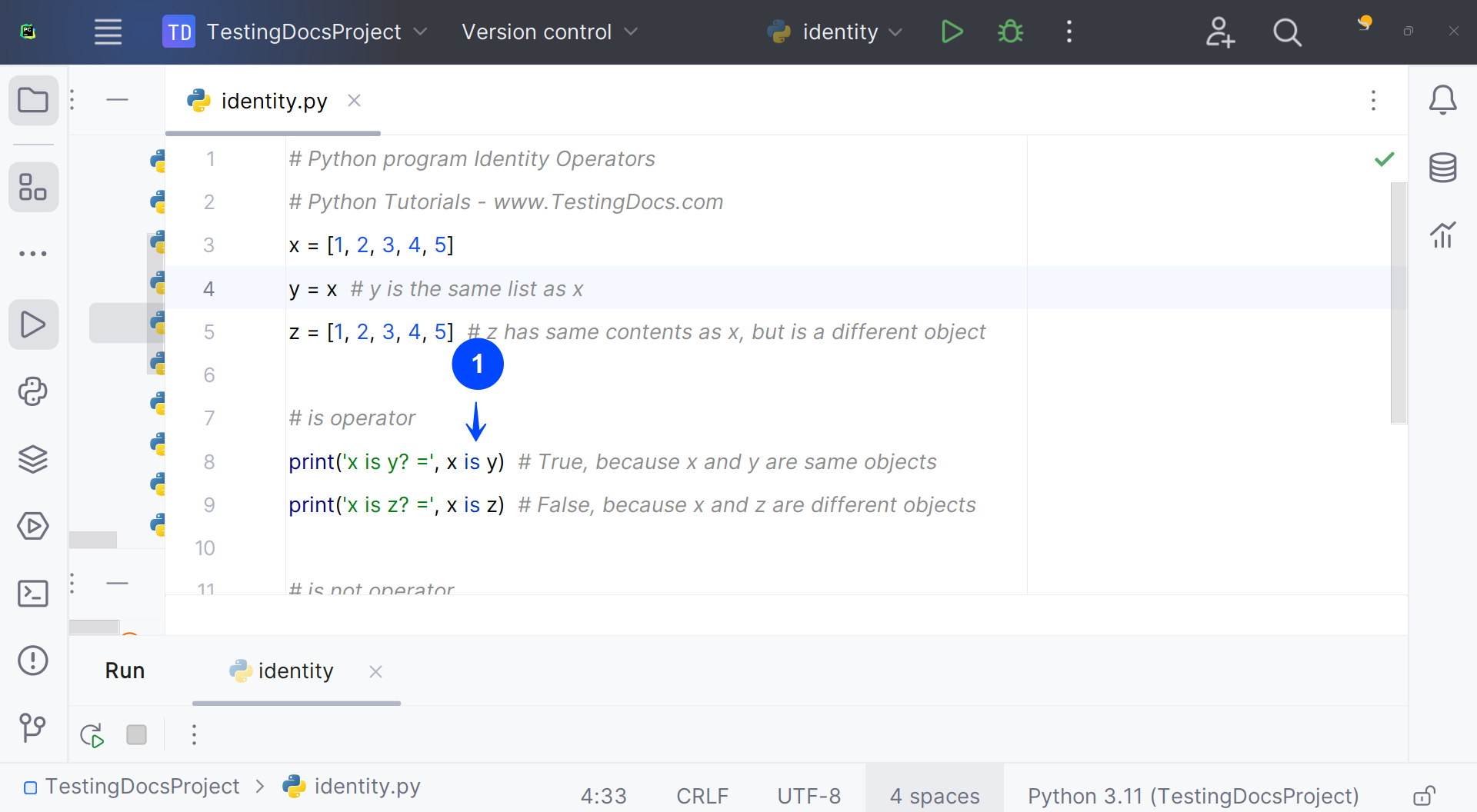
In the example, x and y refer to the same list object, so x is y is True.
However, z is a different list object that just happens to have the same values,
so x is z evaluates to False.
—
Python Tutorials
Python Tutorial on this website can be found at:
https://www.testingdocs.com/python-tutorials/
More information on Python is available at the official website: