Python Lists
Overview
In this tutorial, we will learn about Python Lists. A list is a compound data type that stores an ordered sequence of items of varying data types.
Python Lists
The basic characteristics of Python Lists are as follows:
- Ordered: Lists are ordered in sequence. The order in which items are added to a list is maintained.
- Mutable: Lists are mutable. Lists can be changed after creating, adding, removing, or modifying items.
- Dynamic: Lists are dynamic. Lists can grow or shrink in size as needed.
- Heterogeneous: A list can contain items of different data types, including numbers, strings, other lists, etc.
Declaration
A list contains items separated by commas and enclosed within square brackets[].
>>> l = [1,2,3.14] # Declare a list
>>>
>>> type(l) # Know the type
<class ‘list’>
>>>
>>> print(l) # Prints the list to the console
[1, 2, 3.14]
>>>
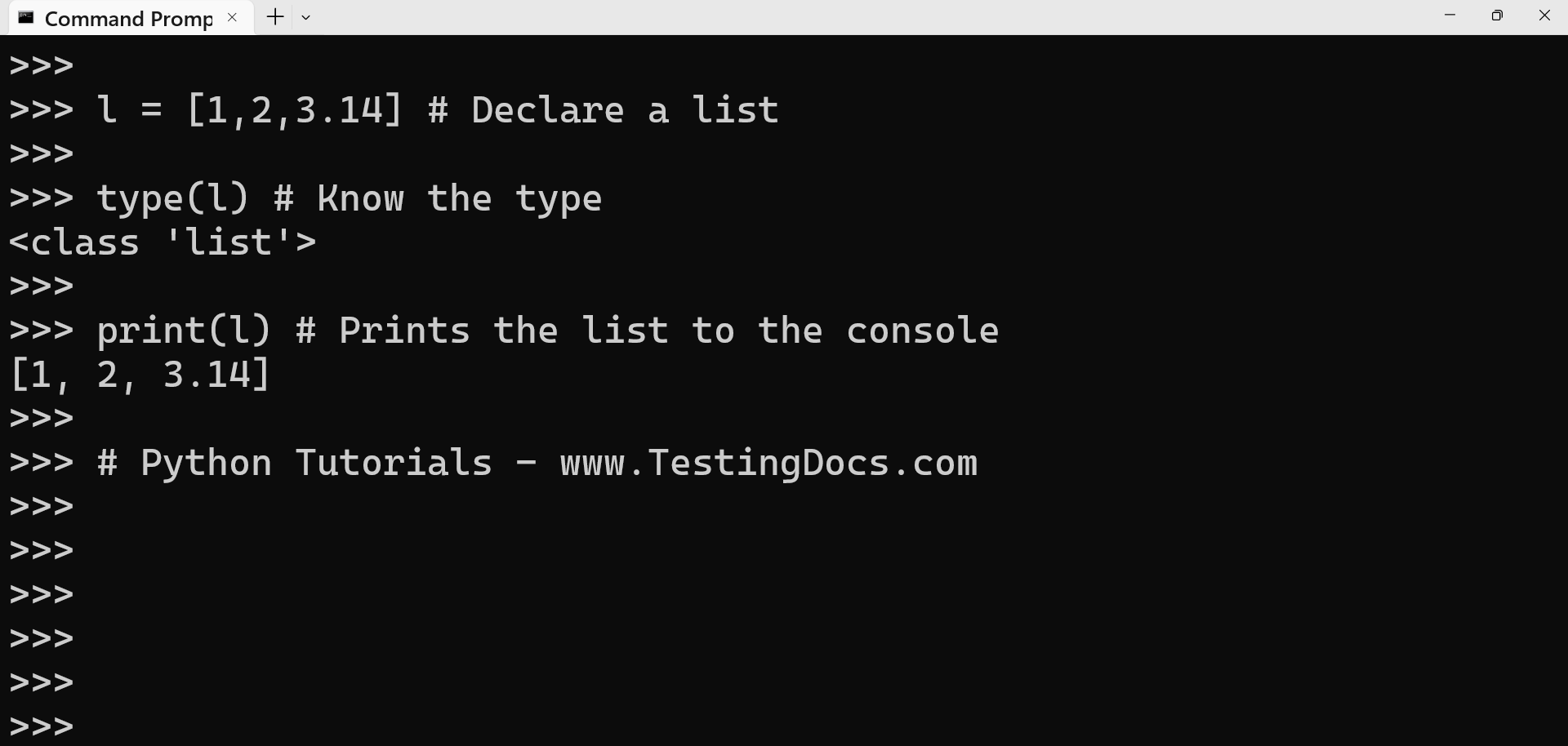
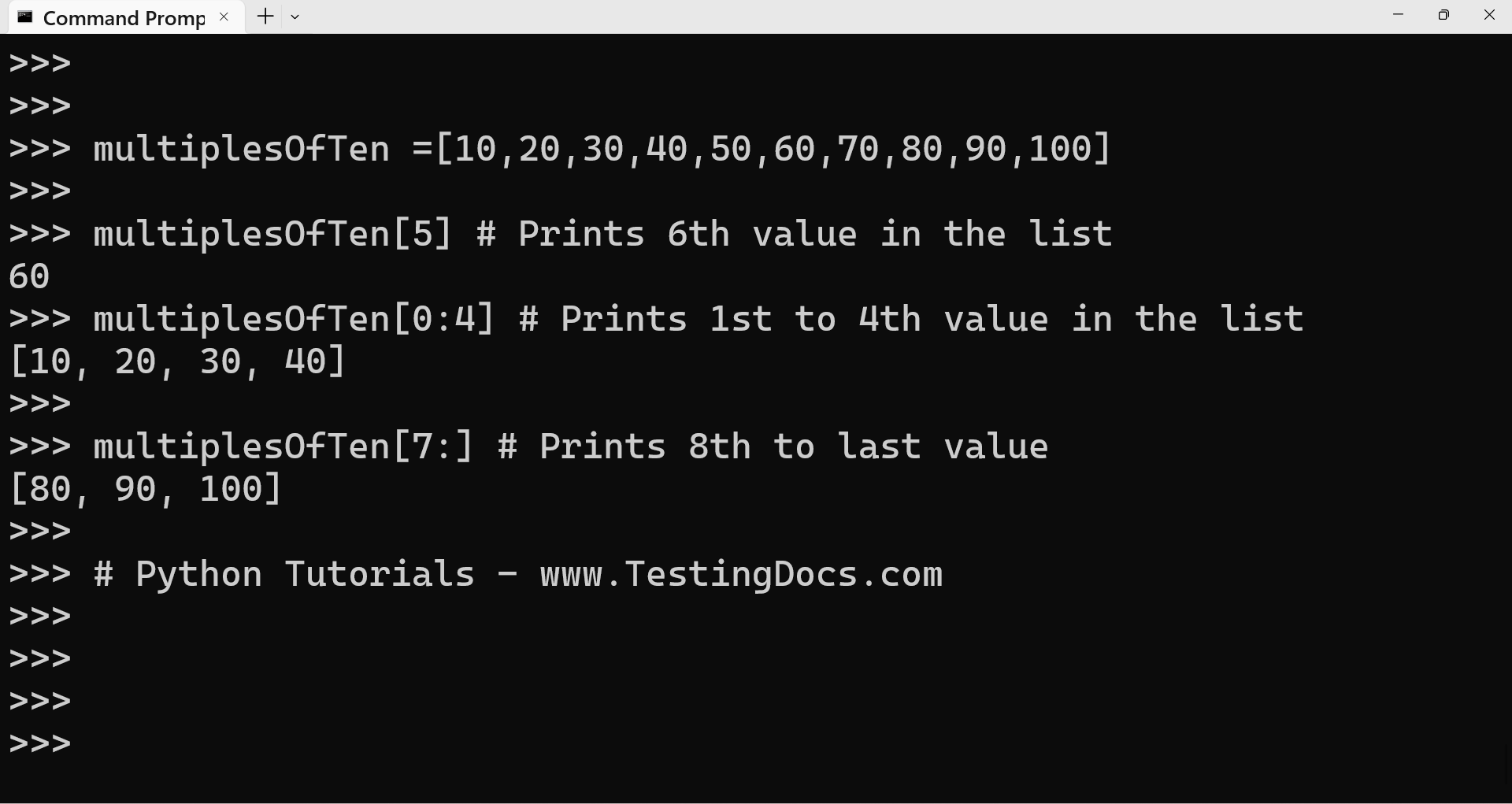
A slicing operator [] can be used to extract an item or a range of items from a list. The list index starts from 0 in Python. The use of the slicing operator.
Illustration of slicing operator
>>> multiplesOfTen =[10,20,30,40,50,60,70,80,90,100]
>>>
>>> multiplesOfTen[5] # Prints 6th value in the list
60
>>> multiplesOfTen[0:4] # Prints 1st to 4th value in the list
[10, 20, 30, 40]
>>>
>>> multiplesOfTen[7:] # Prints 8th to last value
[80, 90, 100]
>>>
The plus sign(+) is used for concatenation, and the asterisk(*) is the repetition operator. Lists can contain other lists. This feature allows the creation of multi-dimensional arrays.
—
Python Tutorials
Python Tutorial on this website can be found at:
https://www.testingdocs.com/python-tutorials/
More information on Python is available at the official website: