Software Testing Goals
Software Testing Goals
Software Testing goals specify what we want to achieve through software testing. They can be classified as Primary or secondary. The primary goal of software testing is to find defects in the software program. The secondary goal of the software is to build confidence that the system is working as expected when there are no defects.
When the goals are met, software testing ensures quality, enhances reliability and performance, reduces costs, and improves customer satisfaction.
When we consider the time factor, software testing goals can be classified into:
- Short-term Goals
- Long-term Goals
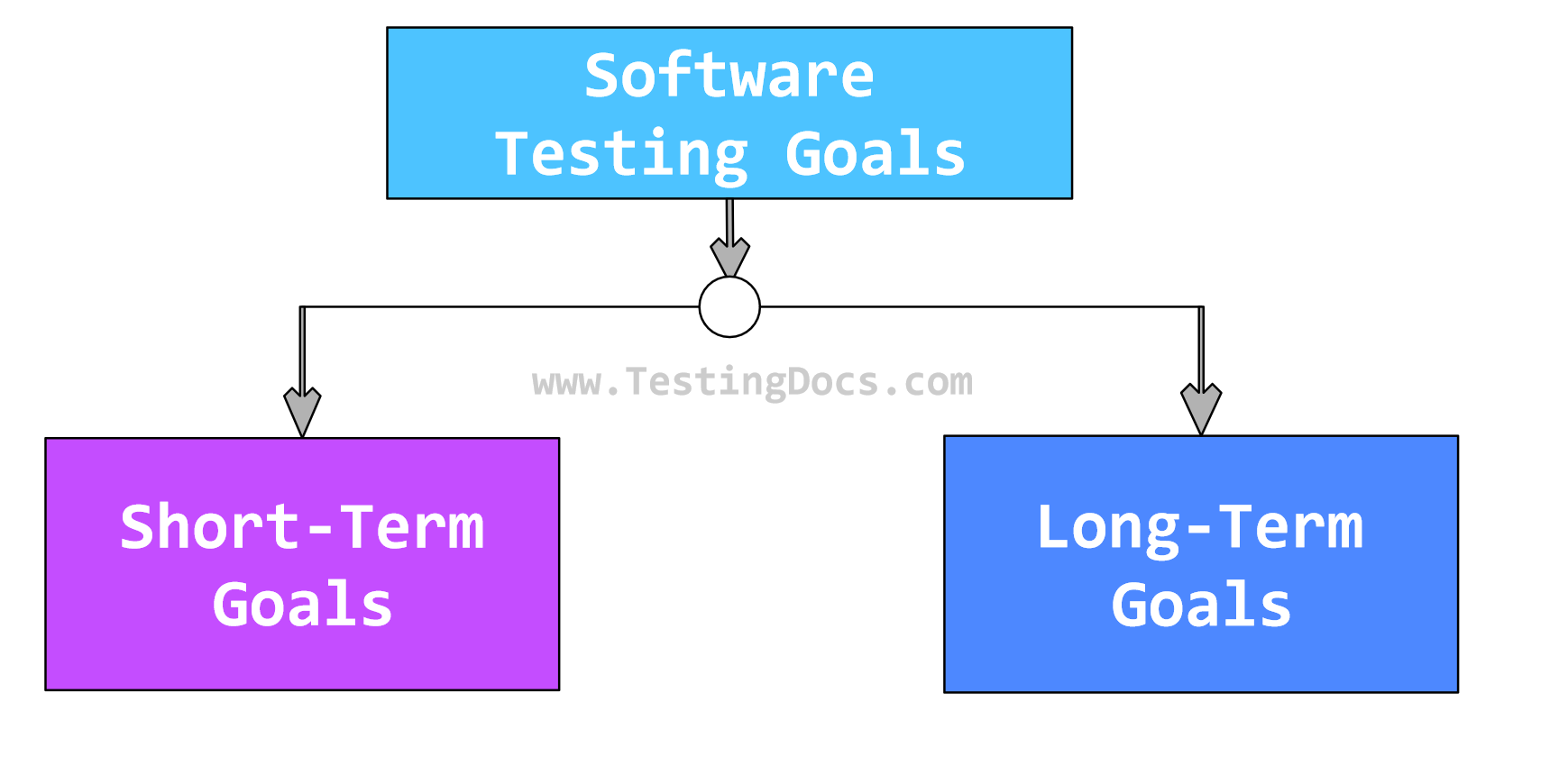
Short-term Goals
Short-term goals are known as immediate goals because the results of these are immediate after performing software testing. These goals are set in the individual phases of SDLC.
Finding bugs
Software testing helps identify defects and bugs in the software, which can be fixed before the software is released to the market. It is very important to have good test coverage to test the software application entirely and ensure it’s performing well and per the specifications.
Verification and Validation
Testing ensures the software works as expected and meets the business and technical requirements guiding its design and development. To ensure that it satisfies the product specifications. A product specification refers to a detailed description of the technical and functional requirements of the product. Product specifications are documented using the following documents:
- Business Requirement Specification (BRS)
- System Requirement Specifications (SRS)
Long-term Goals
Long-term goals are also known as ultimate goals. These goals affect the software quality of the product in the long run. Long-term goals should focus on reducing overall costs while improving the quality of the software, reducing risks, and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Reducing costs
Testing helps reduce costs by identifying and fixing defects early in the software development process. This reduces the cost of fixing defects later in the process or after the software has been released.
Enhance customer satisfaction
Testing ensures software meets user’s needs. It makes sure that the end product meets the business and user requirements. A product with minimal defects that meets user’s needs receives positive feedback and enhances customer satisfaction.
—
Software Testing Tutorials: