Beta Testing
Overview
Beta Testing is also known as Field testing. Beta testing can be considered “pre-release testing. Beta is the second letter of the Greek alphabet. The term alpha test initially meant the first testing phase in a software development process.
Beta Testing
Beta testing is testing a software product or service in a real-world environment and working conditions before its official release. It is an essential step in the software development lifecycle as it helps identify bugs and errors that may have been missed during the development process.
During beta testing, the software is made available to a selected group of users willing to test the product and provide feedback to the developers. The beta testers typically use the software in various ways, attempting to find any issues, bugs, or usability problems. They then provide feedback on their experience, reporting any issues or suggestions encountered. The developers use this feedback to improve the software, fix bugs, and enhance its functionality, making it more user-friendly and robust.
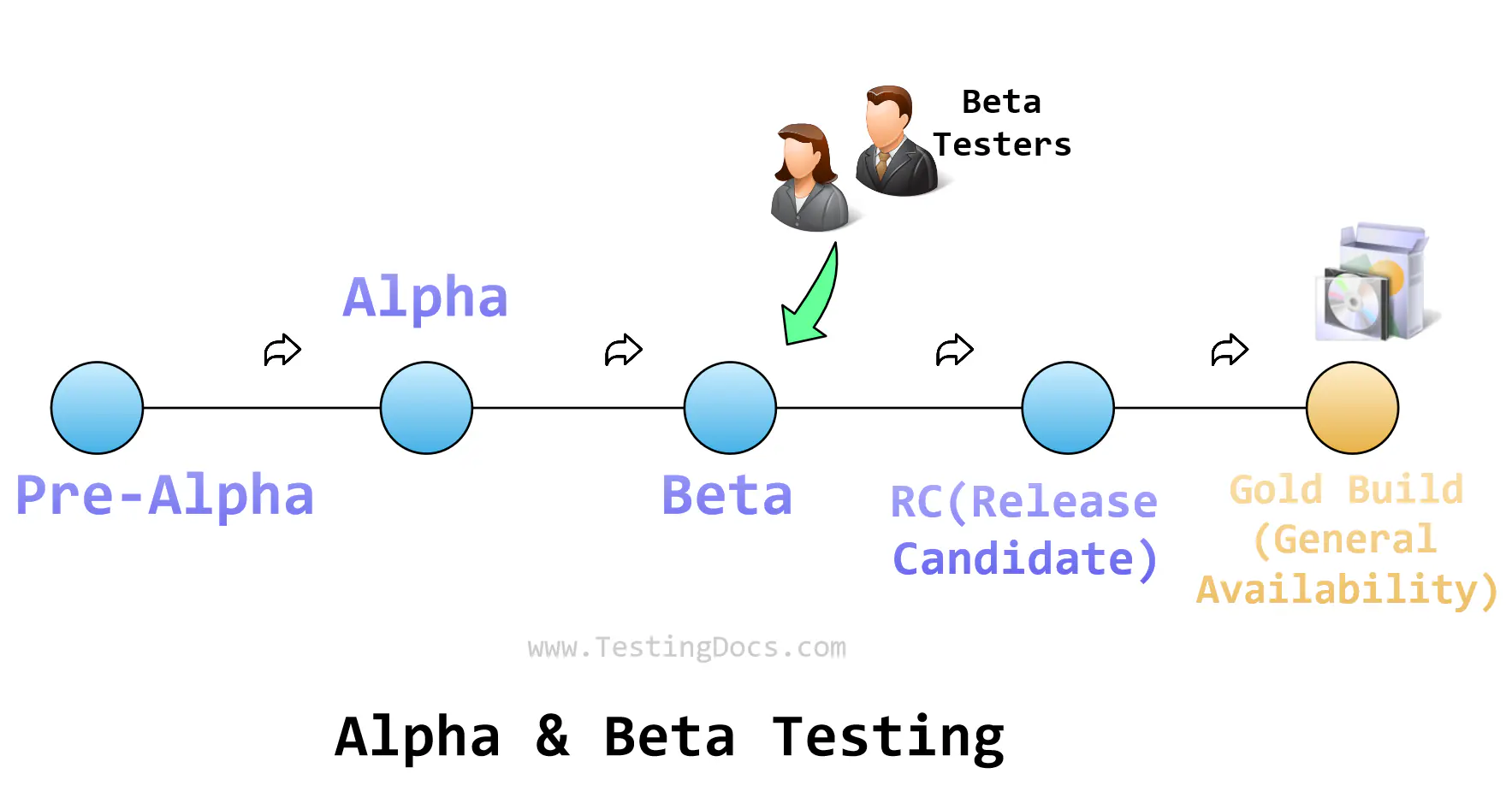
A beta test is the second phase of software testing in which a sampling of the intended audience tries the product out. Beta testing comes after Alpha testing and before the commercial software release. Issues reported are tried to be fixed before the public launch.
Types of Beta Testing
There are different types of beta testing, depending on the purpose and scope of the test. Some of the types are as follows:
- Closed Beta
- Open Beta
Closed beta
Closed beta versions are released to select individuals for a user test and are invitation-only. This is when the software is tested by a limited number of users invited by the developers or selected through an application process. The users are usually required to sign a non-disclosure agreement (NDA) and follow certain guidelines for testing and reporting. Closed beta testing is often used to test sensitive or complex software requiring more control and security.
Open beta
This is when the software is tested by anyone who wants to participate. The users can download or access the software from a public website or platform and provide feedback through various channels, such as forums, surveys, or social media. Open beta testing is often used to test popular or mass-market software requiring more exposure and feedback. Open betas are from a larger group to the general public and anyone interested. The testers report any bugs they find and sometimes suggest additional features they think should be available in the final version.
The goal of beta testing is to place your application in the hands of real users outside of your engineering team to discover any flaws or issues from the user’s perspective that you would not want to have in your final, released version.
Beta testing allows regular end users to evaluate software functions, usability, and stability, providing feedback directly to the engineering teams before full market release.
In conclusion, beta testing is a vital part of the software development lifecycle that helps ensure a successful product launch. By testing the software with real users in real environments, developers can identify and fix bugs, improve functionality, evaluate performance, collect feedback, and increase user satisfaction.
—
See Also: