C Logical Operators
Overview
In this tutorial, we will learn about C logical operators. Logical operators are used to combine multiple logical expressions and evaluate them to a single logical value i.e true or false
C Logical Operators
C language has three logical operators, they are as follows:
| C Logical
Operator |
Operator Symbol | Description |
| and Operator | && | The and operator is a binary operator. It requires two boolean conditional expressions that should be evaluated to be either True or False.
The and returns True If both the conditions are True. Otherwise, it will return False. |
| or Operator | || | The or operator is also a binary operator. It requires two boolean conditional expressions that should be evaluated to be either True or False.
The or returns False If both the conditions are False. Otherwise, it will return True. |
| not Operator | ! | The not operator is a unary operator. It requires only one boolean conditional expression. The not negates the given condition. It will return True if the condition is False. It will return False if the condition is True. |
Example
The Boolean data type is declared in the stdbool.h header file. We need to include the header file to work with the bool data type and boolean constants like true, and false.
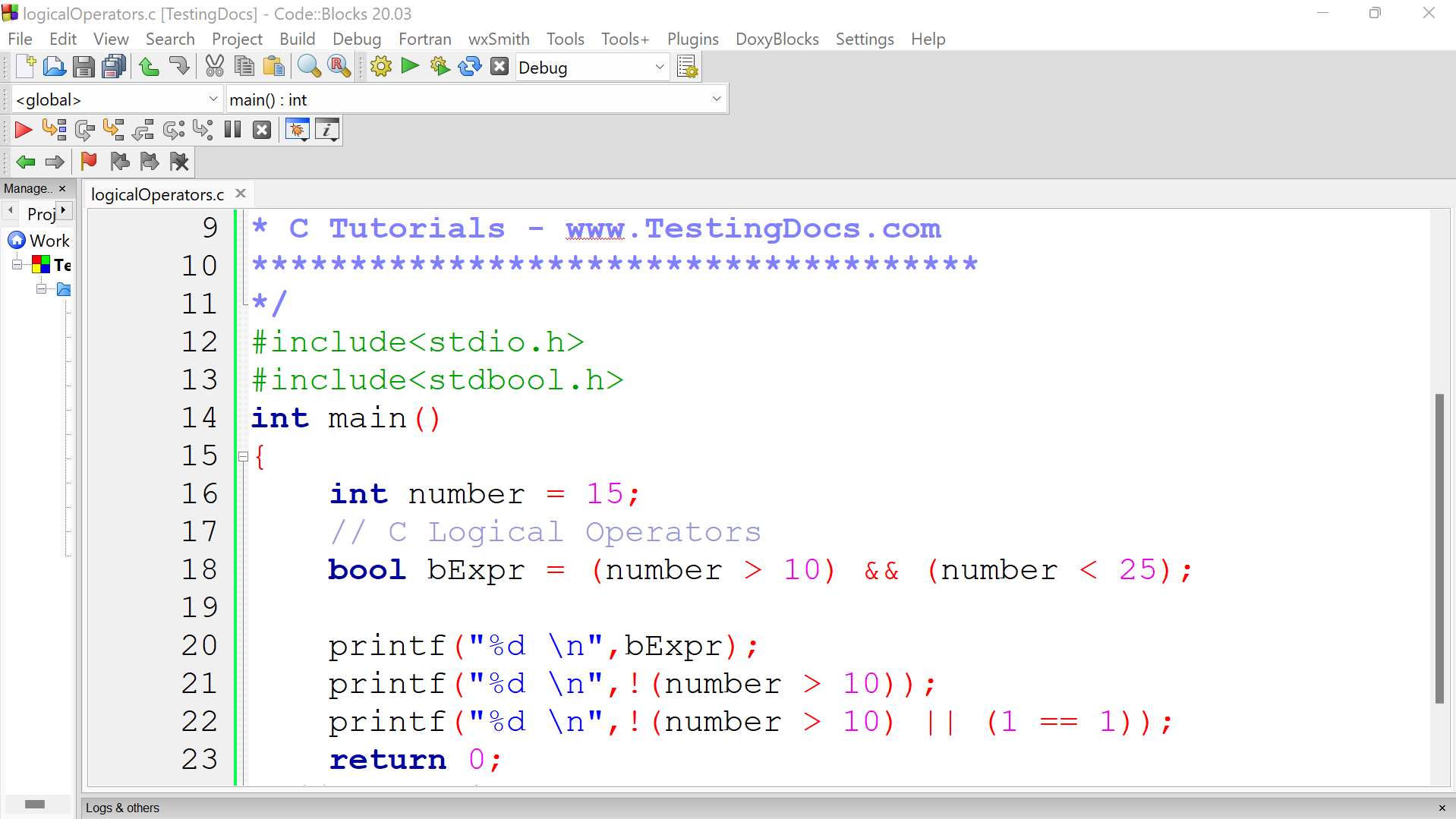
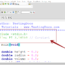
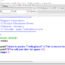
/**
**********************************
* Program Description:
* C Logical Operators
* Filename : logicalOperators.c
* C Tutorials – www.TestingDocs.com
*************************************
*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
int main()
{
int number = 15;
// C Logical Operators
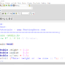
bool bExpr = (number > 10) && (number < 25);
printf(“%d \n”,bExpr);
printf(“%d \n”,!(number > 10));
printf(“%d \n”,!(number > 10) || (1 == 1));
return 0;
} // end main