Java Servlet Lifecycle
Overview
The Java Servlet interface defines Servlet lifecycle methods to initialize the servlet service requests and remove the servlet from the server container.
Servlet Life Cycle
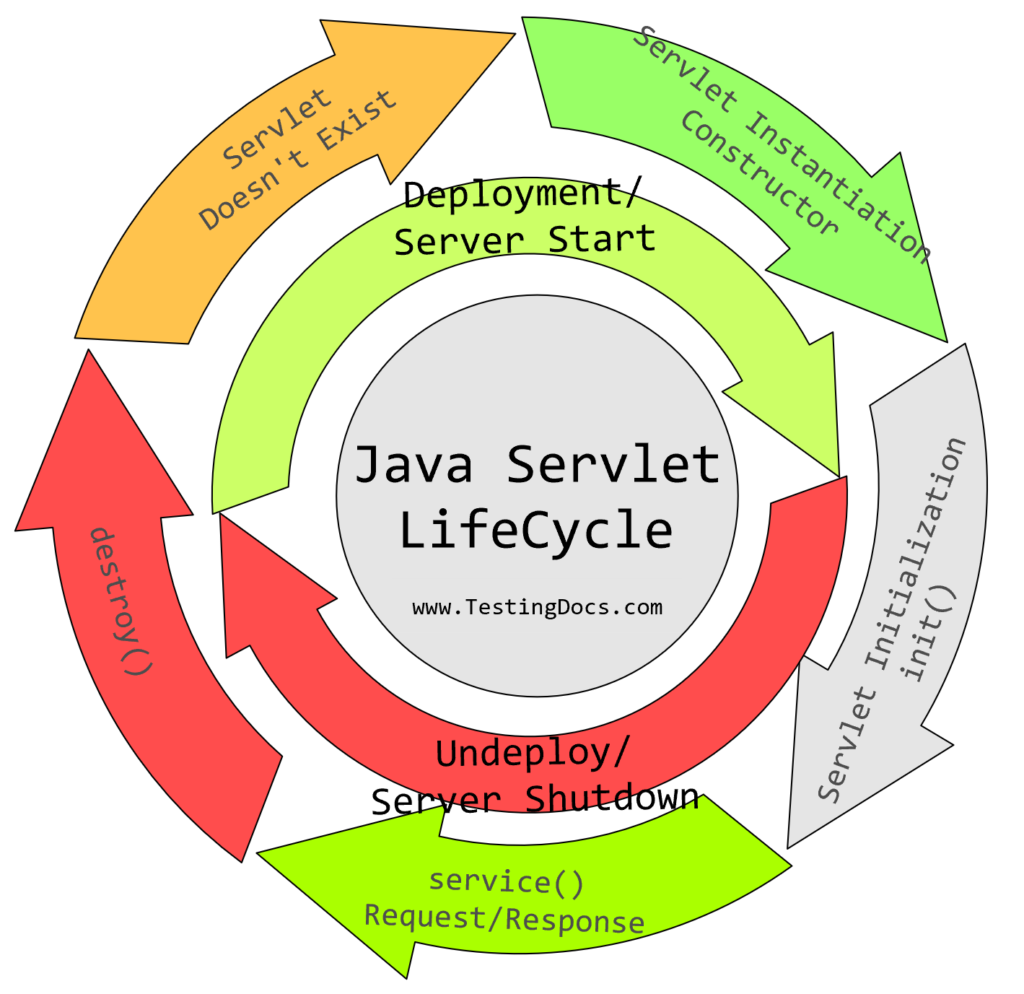
A Java Servlet has a life cycle that defines the steps in the whole processing of a servlet. The main steps are as follows:
- The Servlet loading and initialization.
- How does the servlet receive and respond to requests
- How a servlet is taken out of service.
The process of creating, servicing the request, and destroying a servlet is called the servlet life cycle. The servlet is just loaded once and remains in memory until it serves a request. The javax.The Servlet container uses a Servlet interface to manage a Servlet’s full life cycle. The ‘javax.Servlet’ interface must be implemented by every servlet you create, either directly or indirectly.
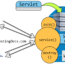
All servlet life cycle methods, such as init(), service(), and destroy(), are defined in the Servlet interface. These are invoked in the following sequence:
- init()
- service(req,res)
- destroy()
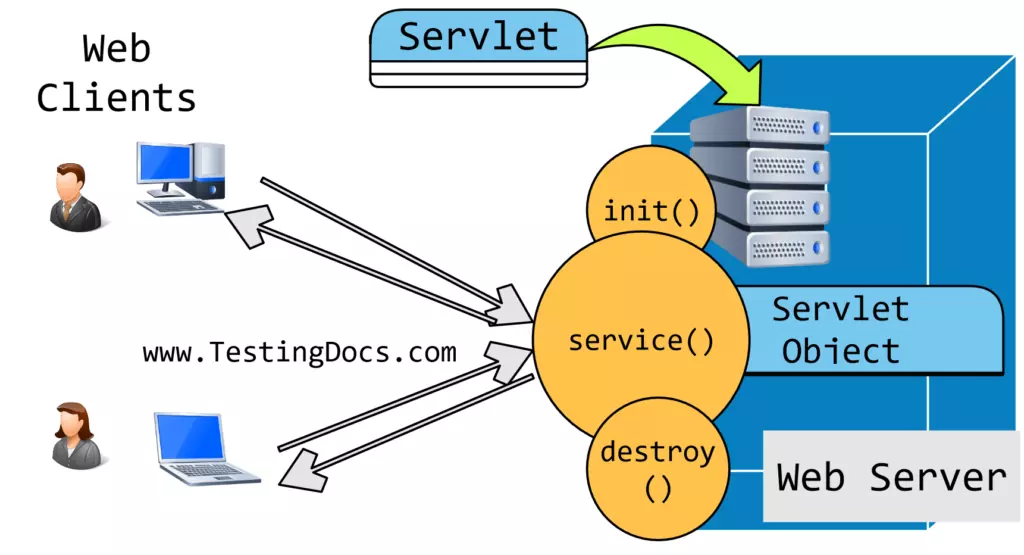
The first client request should wait until the web container creates and initializes the servlet object to handle the request. To avoid this, we can also instruct the servlet container to create the servlet object when the server starts.
When the servlet object is created, the container initializes the servlet object by invoking the constructor. After the constructor, the lifecycle init() method is invoked.
init()
The web container invokes the init() method to indicate that the servlet can handle service requests. The signature of the init method is as follows:
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException
This method is called after instantiating the servlet. The servlet is created and then initialized with the init() method. The web container creates the servlet object whenever the first request is given to the servlet.
service()
The servlet container invokes the service method that allows the servlet to accept the request and respond with a response. The method signature of the service method is as follows:
public void service(ServletRequest req,ServletResponse res)
throws ServletException, IOException
Once the servlet is initialized, it can process the client’s request. The response is provided back to the client after processing the request. The service() method would be executed for each client request.
Servlets that run under the multithreaded web containers can handle multiple service requests simultaneously. Any calls from the clients to the service() method are handled.
destroy()
When the servlet’s processing is complete and it is nearing the conclusion of its life cycle, the destruct() method is called. This method will be called when your application is halted, or the servlet container is shut down.
The servlet is then destroyed with the destroy() method and sent for garbage collection. The method signature of the destroy method is as follows:
public void destroy()
The init() and destroy() methods are executed only once during the lifecycle of the Servlet. The container invokes the destroy () method whenever the server is shut down or when the servlet is removed( servlet undeploy) from the servlet. Any resource produced in the init() method will be cleared up; shared resources are closed before the servlet is removed from the service.
—
Java Tutorials
Java Tutorial on this website:
https://www.testingdocs.com/java-tutorial/
For more information on Java, visit the official website :