Python Assignment Operator
Overview
Python Assignment operator assigns a result of an expression or constant value to a variable. The symbol = is known as an assignment operator in Python language.
Assignment operators assign the values generated after evaluating the right-hand operand to the left-hand operand. There are two types of assignment operators as follows:
- Simple Assignment Operator
- Compound Assignment Operator
Simple Assignment Operator
The simple assignment is performed using the equal sign (=). The value of the right operand is assigned to the variable on the left.
For example:
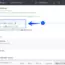
>>>year=2017 # This will assign a value of 2017 to the variable year.
Example
The following program code represents the assignment statement.
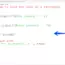
# Python assignment operator demo
# Python tutorials - www.TestingDocs.com
num = 79 # integer value 79 is assigned to num
print('The number assigned = ',num) # prints the variable num
Explanation
In the above code, num=79 is an assignment statement that uses the assignment = operator that assigns the value 79 on the right-hand side to the variable num on the left-hand side.
Compound Operators
There are various compound operators in Python language. These operators are also called shorthand operators.
—
Python Tutorials
Python Tutorial on this website can be found at:
https://www.testingdocs.com/python-tutorials/
More information on Python is available at the official website: