Introduction to C Language
Overview
The C Language is a standard computer programming language. C is a successor of the B language which was introduced in early 1970 by Ken Thompson and Dennis Ritchie.
C language was developed by Dennis Ritchie to program the Unix operating system at AT&T Bell Labs. C is one of the most widely used programming languages. C is a very popular language from which many other languages are derived.
Features
Some of the C language features are as follows:
- C was originally created for operating system programming like Unix. However, it has evolved into a general-purpose programming language.
- C is a medium-level language, efficient, and popular for writing system software.
- C is a cross-platform programming language. It is available on a wide variety of platforms. Most machine architectures support a C compiler.
- It is also commonly used in computer science education for teaching programming basics in schools. colleges and universities.
Uses of C
C was initially used for system development and Operating system programs. C produces code that runs nearly as fast as code written in assembly language.
C was adopted as a system development language. Some examples of the use of C language are as follows:
- Operating Systems
- Language Compilers
- Language Interpreters
- Assemblers
- Text Editors
- System Drivers
- System Utilities
Getting Started
To get started with C language programming download and install an IDE.
IDE stands for Integrated Development Environment. IDE software provides a variety of tools to assist C programmers to enhance productivity. They combine the language tools like compiler, linker, and loader.
IDE also provides a visual source code editor with source code syntax color highlighting, auto-completion of code, Debugger, etc. Most of the tutorials on this website use Code::Blocks IDE. Code::Blocks is an open-source, cross-platform IDE.
Download & Install Code::Blocks on Windows
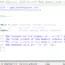
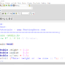
Hello World C program
The program prints out a “Hello World!!” message to the standard output, which is usually a terminal or computer screen display.
—
For more information on Code::Blocks IDE, visit the official website: