MySQL GROUP BY HAVING clause
Overview
In this tutorial, we will learn MySQL GROUP BY HAVING clause. We can filter the aggregate information using the HAVING clause.
HAVING clause
The HAVING modifier can be used to require that the groups produced by a GROUP BY clause satisfy particular condition.The HAVING condition can refer to aggregate functions. The HAVING clause is applied after GROUP BY and allows us to filter on the aggregate data that is not available to the WHERE clause.
WHERE vs HAVING
The WHERE clause is used to filter rows based on single row data. HAVING clause is used to filter based on aggregate data with GROUP BY clause.
The HAVING clause is evaluated after the grouping implied by the GROUP BY clause.
Syntax
The general syntax for the HAVING clause is as follows:
mysql> SELECT column_list, aggregate_function(column)
FROM <table_name>
GROUP BY grouping_column
HAVING <aggregate_condition> ;
Example
In this example, we will use the Continent table from the world MySQL database.
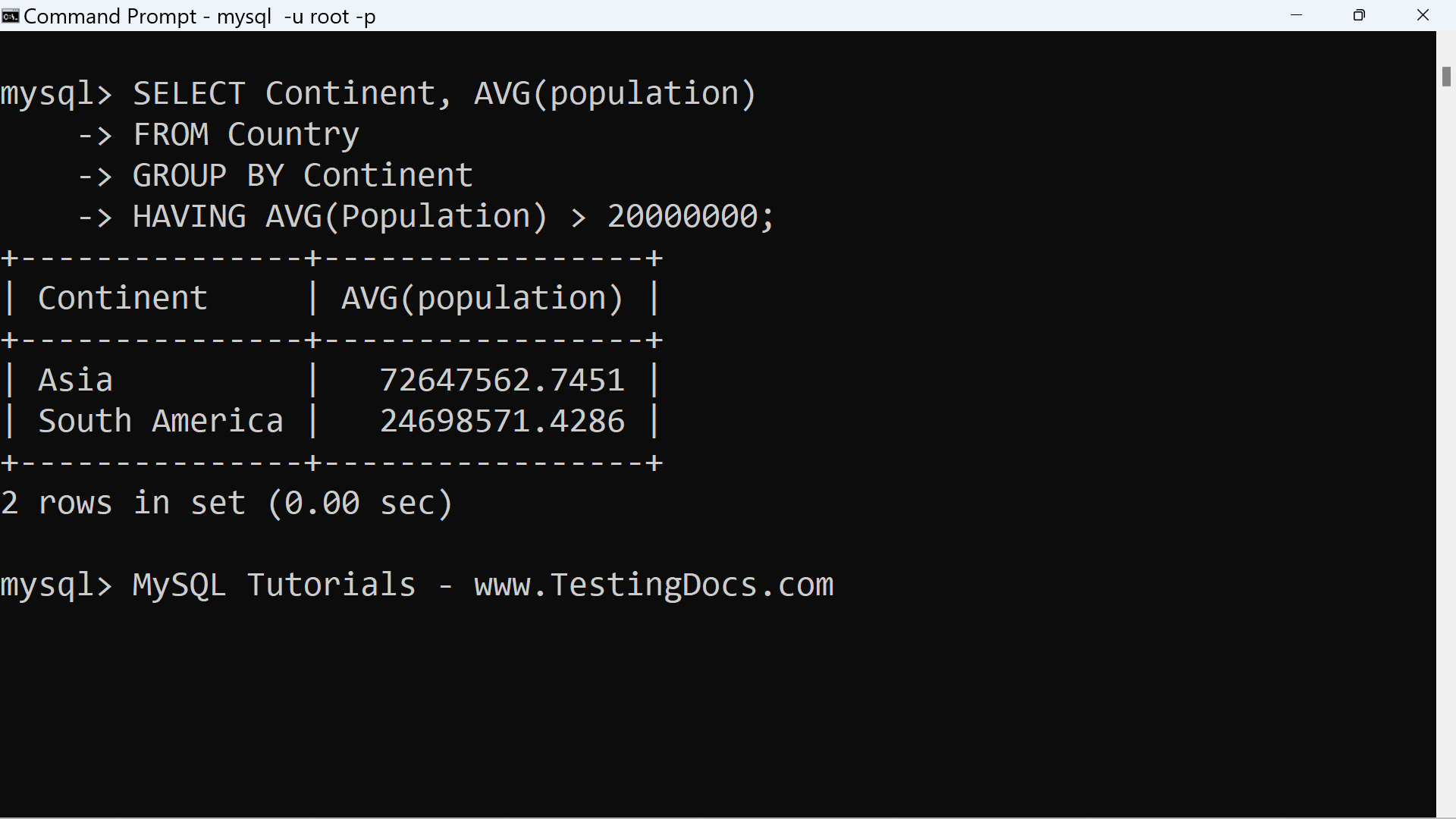
The following SQL query results in a list of the continents whose average of country population
is greater than 20,000,000.
We will the AVG() aggregate function to compute the average population.
mysql> SELECT Continent, AVG(population)
->FROM Country
->GROUP BY Continent
->HAVING AVG(Population) > 20000000;
+—————+—————–+
| Continent | AVG(population) |
+—————+—————–+
| Asia | 72647562.7451 |
| South America | 24698571.4286 |
+—————+—————–+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
—
MySQL Tutorials
MySQL Tutorials on this website:
https://www.testingdocs.com/mysql-tutorials-for-beginners/
For more information on MySQL Database: