MySQL INFORMATION_SCHEMA Database
Overview
In this tutorial, we will learn about MySQL INFORMATION_SCHEMA database. The INFORMATION_SCHEMA is an information database, the place that stores information about all the
other databases that the MySQL database server maintains.
INFORMATION_SCHEMA is a special database. It contains several read-only system views. The server doesn’t create a database directory with the name. The schema contains system views and not base tables, so there are no associated database files. It is possible to only to read the contents of the schema. We cannot insert data or delete from the database.
INFORMATION_SCHEMA
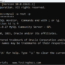
We can select the INFORMATION_SCHEMA database with a USE statement.
mysql> SHOW DATABASES;
+——————–+
| Database |
+——————–+
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| sakila |
| sys |
| world |
+——————–+
6 rows in set (0.02 sec)
mysql> USE information_schema;
Database changed
INFORMATION_SCHEMA Tables
In INFORMATION_SCHEMA there are several read-only tables. These are system views, not base tables,
so there are no files associated with them. It is possible only to read the contents of tables. We cannot insert, update , or delete from the tables.
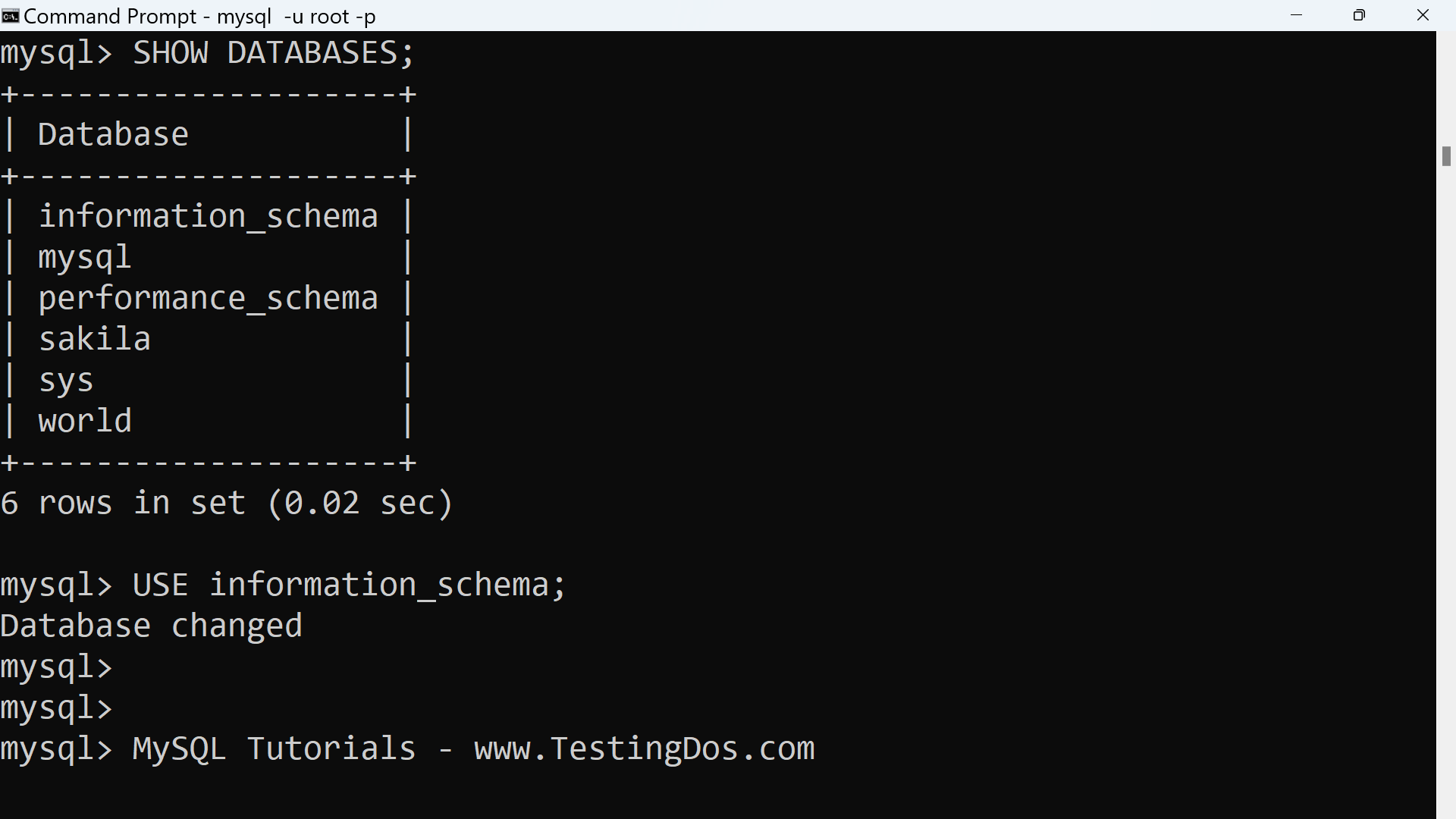
The following is the list of the available tables in the INFORMATION_SCHEMA:
mysql> SHOW TABLES;
+—————————————+
| Tables_in_information_schema |
+—————————————+
| ADMINISTRABLE_ROLE_AUTHORIZATIONS |
| APPLICABLE_ROLES |
| CHARACTER_SETS |
| CHECK_CONSTRAINTS |
| COLLATION_CHARACTER_SET_APPLICABILITY |
| COLLATIONS |
| COLUMN_PRIVILEGES |
| COLUMN_STATISTICS |
| COLUMNS |
| COLUMNS_EXTENSIONS |
| ENABLED_ROLES |
| ENGINES |
| EVENTS |
| FILES |
| INNODB_BUFFER_PAGE |
| INNODB_BUFFER_PAGE_LRU |
| INNODB_BUFFER_POOL_STATS |
| INNODB_CACHED_INDEXES |
| INNODB_CMP |
| INNODB_CMP_PER_INDEX |
| INNODB_CMP_PER_INDEX_RESET |
| INNODB_CMP_RESET |
| INNODB_CMPMEM |
| INNODB_CMPMEM_RESET |
| INNODB_COLUMNS |
| INNODB_DATAFILES |
| INNODB_FIELDS |
| INNODB_FOREIGN |
| INNODB_FOREIGN_COLS |
| INNODB_FT_BEING_DELETED |
| INNODB_FT_CONFIG |
| INNODB_FT_DEFAULT_STOPWORD |
| INNODB_FT_DELETED |
| INNODB_FT_INDEX_CACHE |
| INNODB_FT_INDEX_TABLE |
| INNODB_INDEXES |
| INNODB_METRICS |
| INNODB_SESSION_TEMP_TABLESPACES |
| INNODB_TABLES |
| INNODB_TABLESPACES |
| INNODB_TABLESPACES_BRIEF |
| INNODB_TABLESTATS |
| INNODB_TEMP_TABLE_INFO |
| INNODB_TRX |
| INNODB_VIRTUAL |
| KEY_COLUMN_USAGE |
| KEYWORDS |
| OPTIMIZER_TRACE |
| PARAMETERS |
| PARTITIONS |
| PLUGINS |
| PROCESSLIST |
| PROFILING |
| REFERENTIAL_CONSTRAINTS |
| RESOURCE_GROUPS |
| ROLE_COLUMN_GRANTS |
| ROLE_ROUTINE_GRANTS |
| ROLE_TABLE_GRANTS |
| ROUTINES |
| SCHEMA_PRIVILEGES |
| SCHEMATA |
| SCHEMATA_EXTENSIONS |
| ST_GEOMETRY_COLUMNS |
| ST_SPATIAL_REFERENCE_SYSTEMS |
| ST_UNITS_OF_MEASURE |
| STATISTICS |
| TABLE_CONSTRAINTS |
| TABLE_CONSTRAINTS_EXTENSIONS |
| TABLE_PRIVILEGES |
| TABLES |
| TABLES_EXTENSIONS |
| TABLESPACES |
| TABLESPACES_EXTENSIONS |
| TRIGGERS |
| USER_ATTRIBUTES |
| USER_PRIVILEGES |
| VIEW_ROUTINE_USAGE |
| VIEW_TABLE_USAGE |
| VIEWS |
+—————————————+
Some tables descriptions are as follows:
| INFORMATION_SCHEMA Table | Description |
| SCHEMATA | Information about databases |
| TABLES | Information about database Tables |
| COLUMNS | Information about Columns in database tables |
| ROUTINES | Information about Stored procedures and Functions |
| TRIGGERS | Information about Triggers |
| VIEWS | Information about Views |
| TABLE_CONSTRAINTS | Information about Constraints on database tables |
| TABLE_PRIVILEGES | Information about Table privileges held by MySQL users |
|
USER_PRIVILEGES |
Information about Global privileges held by MySQL users |
| CHARACTER_SETS | Information about available Character sets |
Example
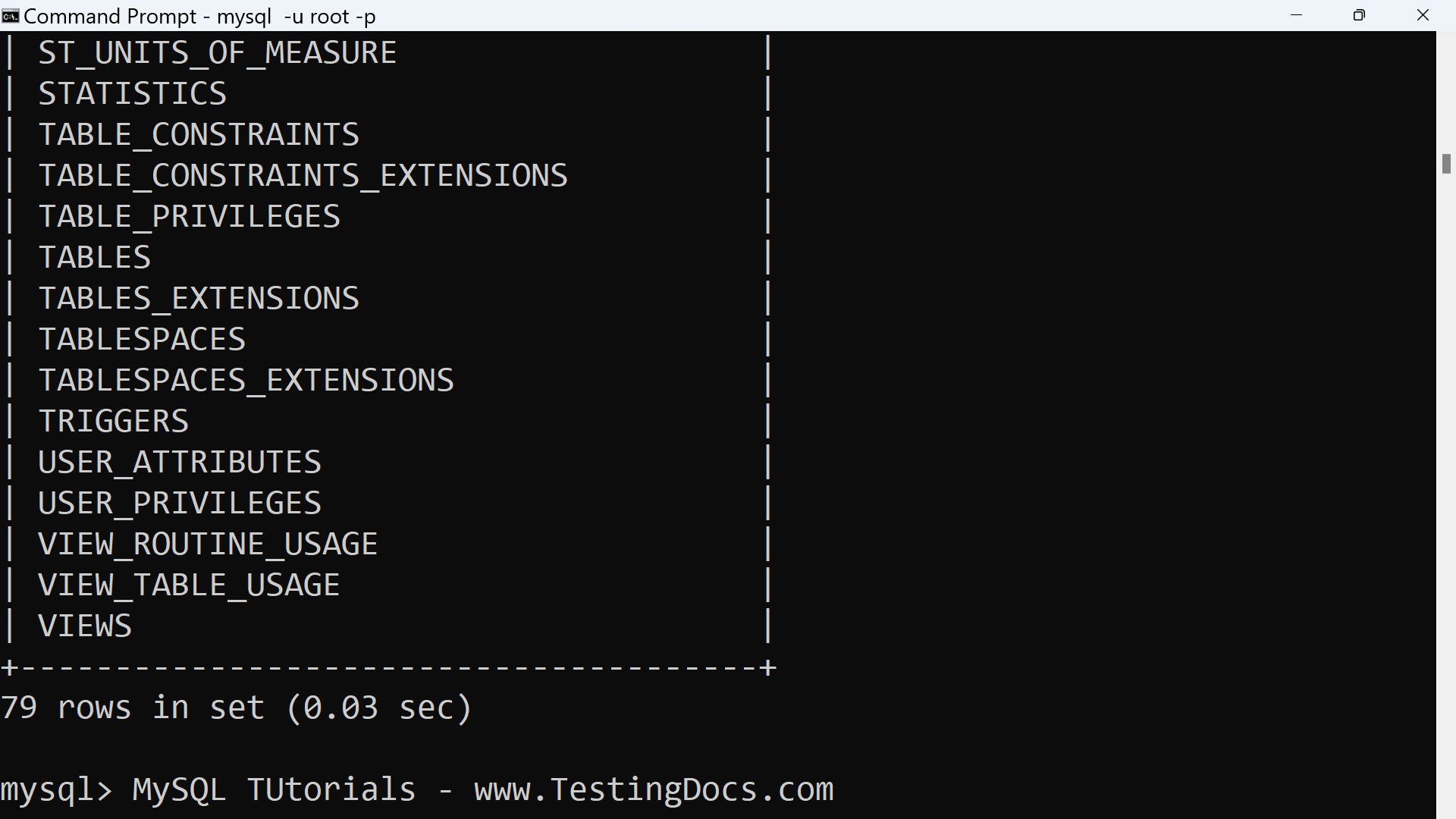
Here is an example of a statement that retrieves metadata information:
mysql> SELECT Table_name, Table_type, Engine
-> FROM Information_Schema.Tables
-> WHERE Table_schema= ‘world’;
+—————–+————+——–+
| TABLE_NAME | TABLE_TYPE | ENGINE |
+—————–+————+——–+
| city | BASE TABLE | InnoDB |
| country | BASE TABLE | InnoDB |
| countrylanguage | BASE TABLE | InnoDB |
| v_city | VIEW | NULL |
+—————–+————+——–+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
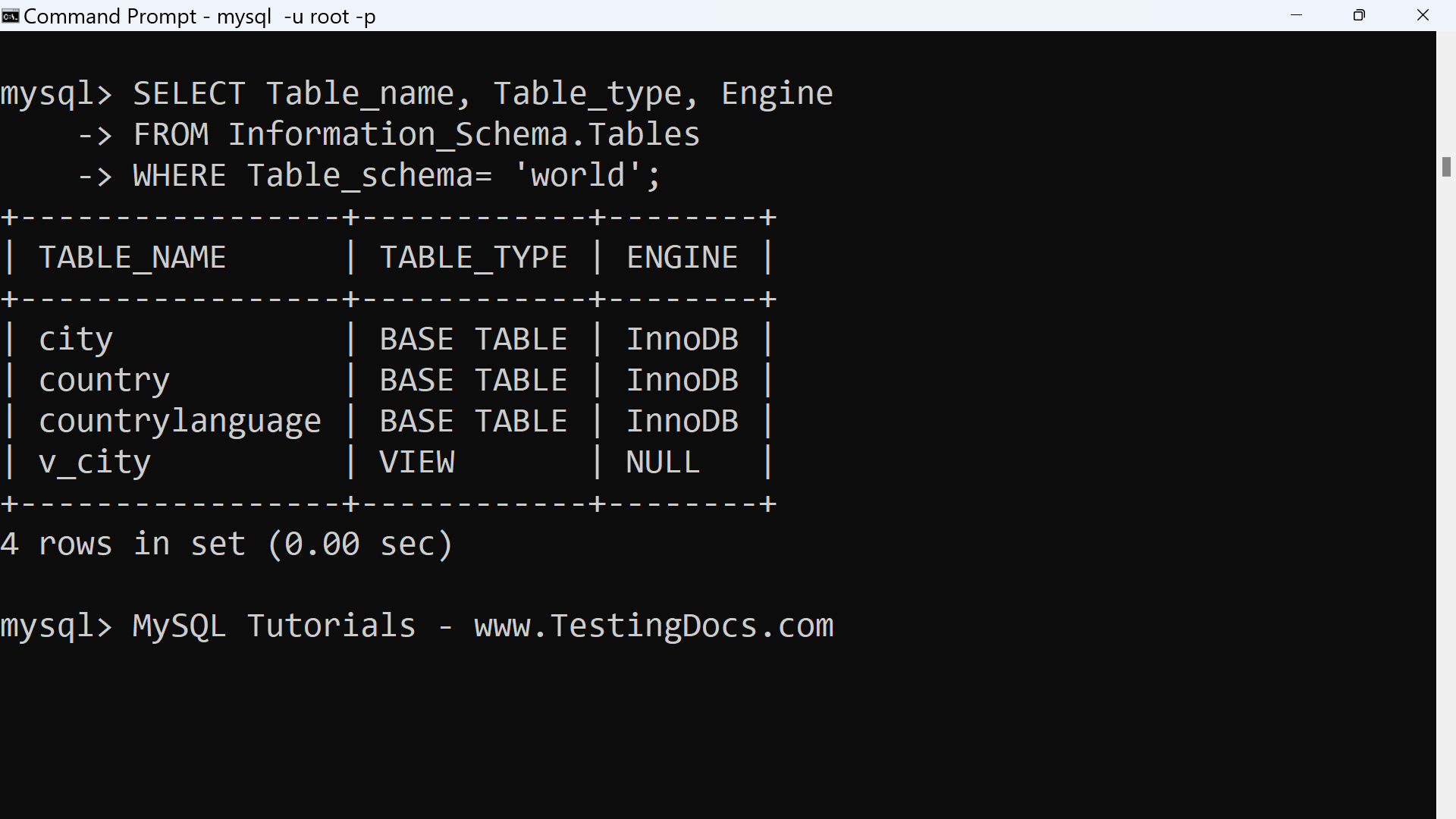
Each MySQL user has the right to access these tables, but can see only the rows in the tables
that correspond to objects for which the user has the proper access privileges. The above statement gets the list of all the tables in the world database
The columns show:
- The name of the Table
- Table type
- Table Storage engine
—
MySQL Tutorials
MySQL Tutorials on this website:
https://www.testingdocs.com/mysql-tutorials-for-beginners/
For more information on MySQL Database: