MySQL MEMORY Storage Engine
Overview
In this tutorial, we will learn about the MEMORY storage engine in MySQL. MEMORY storage engine tables are temporary in the sense that their contents disappear when the server terminates. The tables still exists when the server restarts, but will be empty.
MEMORY Storage Engine
MEMORY storage engine uses tables that are stored in memory and that have fixed-length rows. The MEMORY storage engine manages tables that have the following characteristics:
- Table data and indexes area stored in memory
- In-memory storage results in fast performance
- Table data is lost if the server shuts down. Table structure survives server restart.
- MySQL manages query contention using table-level locking. Deadlocks cannot occur.
- Memory tables cannot contain TEXT or BLOB columns.
ENGINE=MEMORY
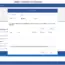
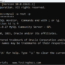
We can create tables using the ENGINE=MEMORY option to use the MEMORY storage engine in the CREATE TABLE statement.
mysql> CREATE TABLE temptable (
-> id INT NOT NULL,
-> name CHAR(40) NOT NULL
-> )
-> ENGINE = MEMORY;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
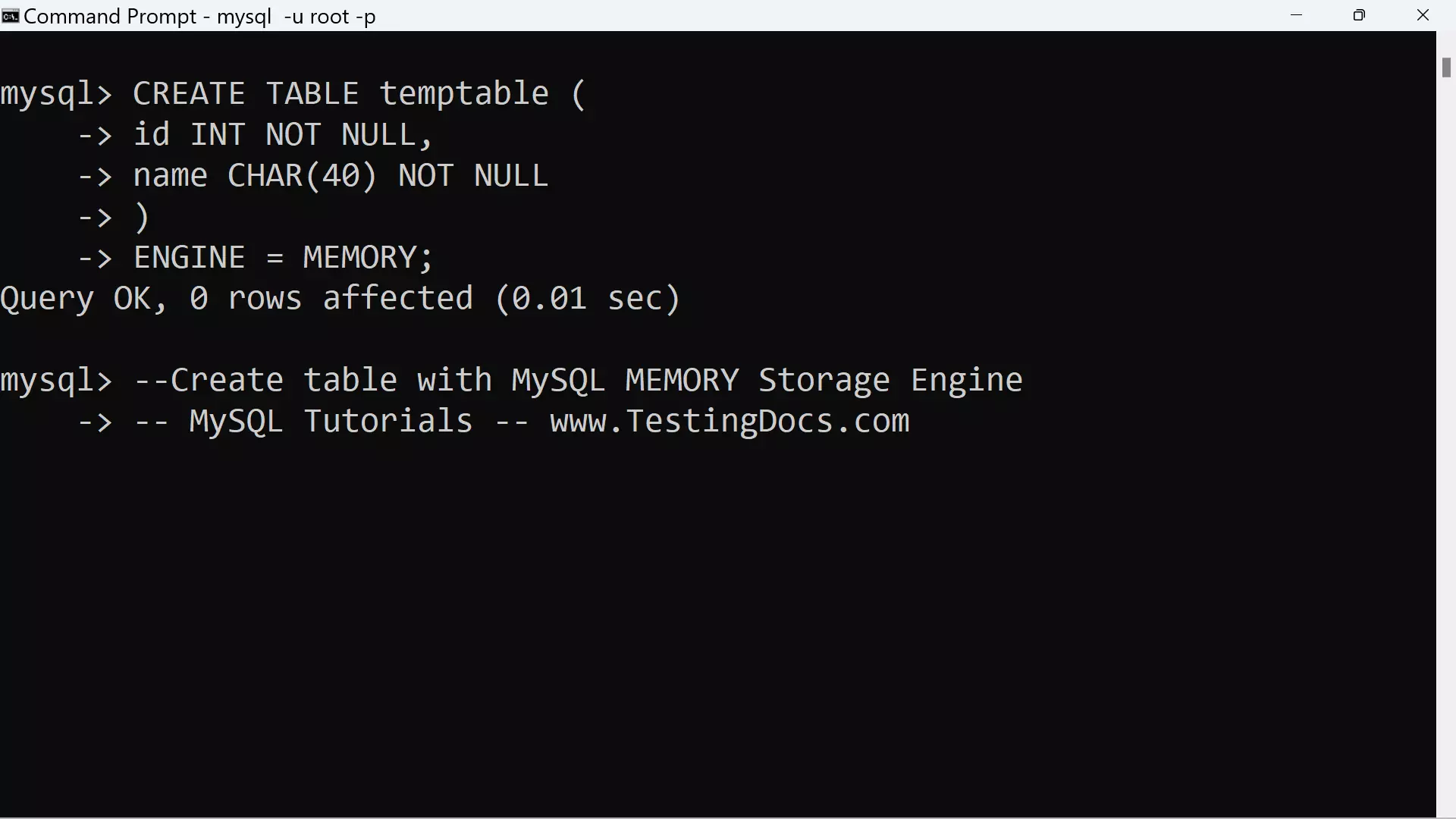
Memory storage table contents do not survive a restart of the server. However, the table structure remains with no rows.
The MEMORY storage engine was formerly called the HEAP engine. We might still use the HEAP option in older SQL code, and MySQL Server recognizes for backward compatibility.
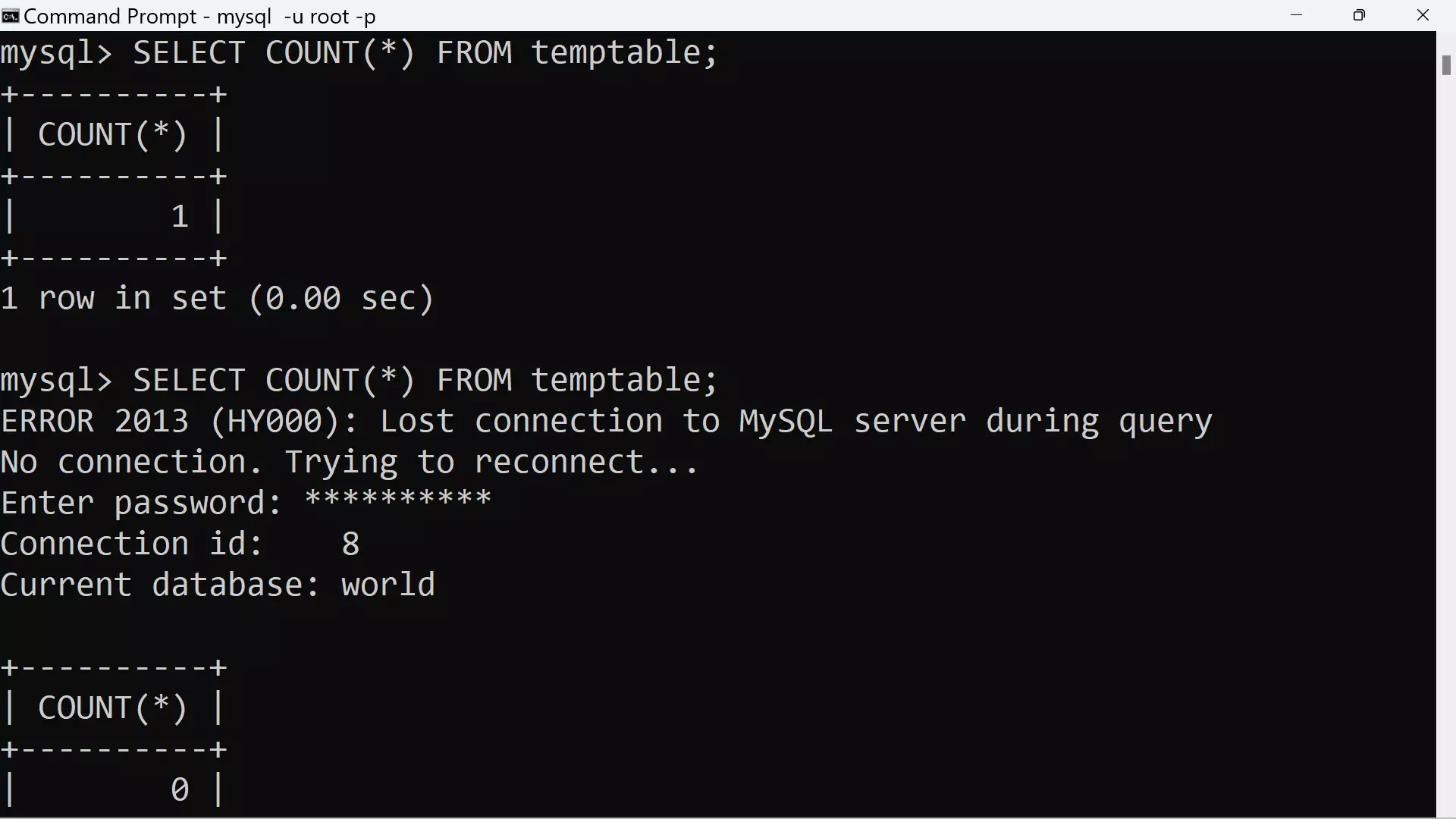
MEMORY storage engine tables are limited by max_heap_table_size so they do not get too large.
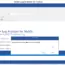
mysql> SHOW VARIABLES LIKE ‘%max_heap_table%’;
+———————+———-+
| Variable_name | Value |
+———————+———-+
| max_heap_table_size | 16777216 |
+———————+———-+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)
—
MySQL Tutorials
MySQL Tutorials on this website:
https://www.testingdocs.com/mysql-tutorials-for-beginners/
For more information on MySQL Database: