MySQL Scalar Subquery
Overview
In this tutorial, we will learn about Scalar Subquery with an example. Scalar subquery is the simplest form
of a subquery. A scalar subquery, as the name suggests, is a subquery that returns a scalar or single value. To know the scalar subquery placement in the SQL statement:
Example
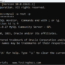
In this example, we will use the City table from the world MySQL table. The following example shows how to use a scalar subquery as part of a WHERE clause conditions.
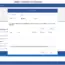
mysql> SELECT Name FROM City
-> WHERE Population >
-> (SELECT Population FROM City WHERE Name= ‘New York’);
+——————-+
| Name |
+——————-+
| São Paulo |
| Jakarta |
| Mumbai (Bombay) |
| Shanghai |
| Seoul |
| Ciudad de México |
| Karachi |
| Istanbul |
| Moscow |
+——————-+
9 rows in set (0.03 sec)
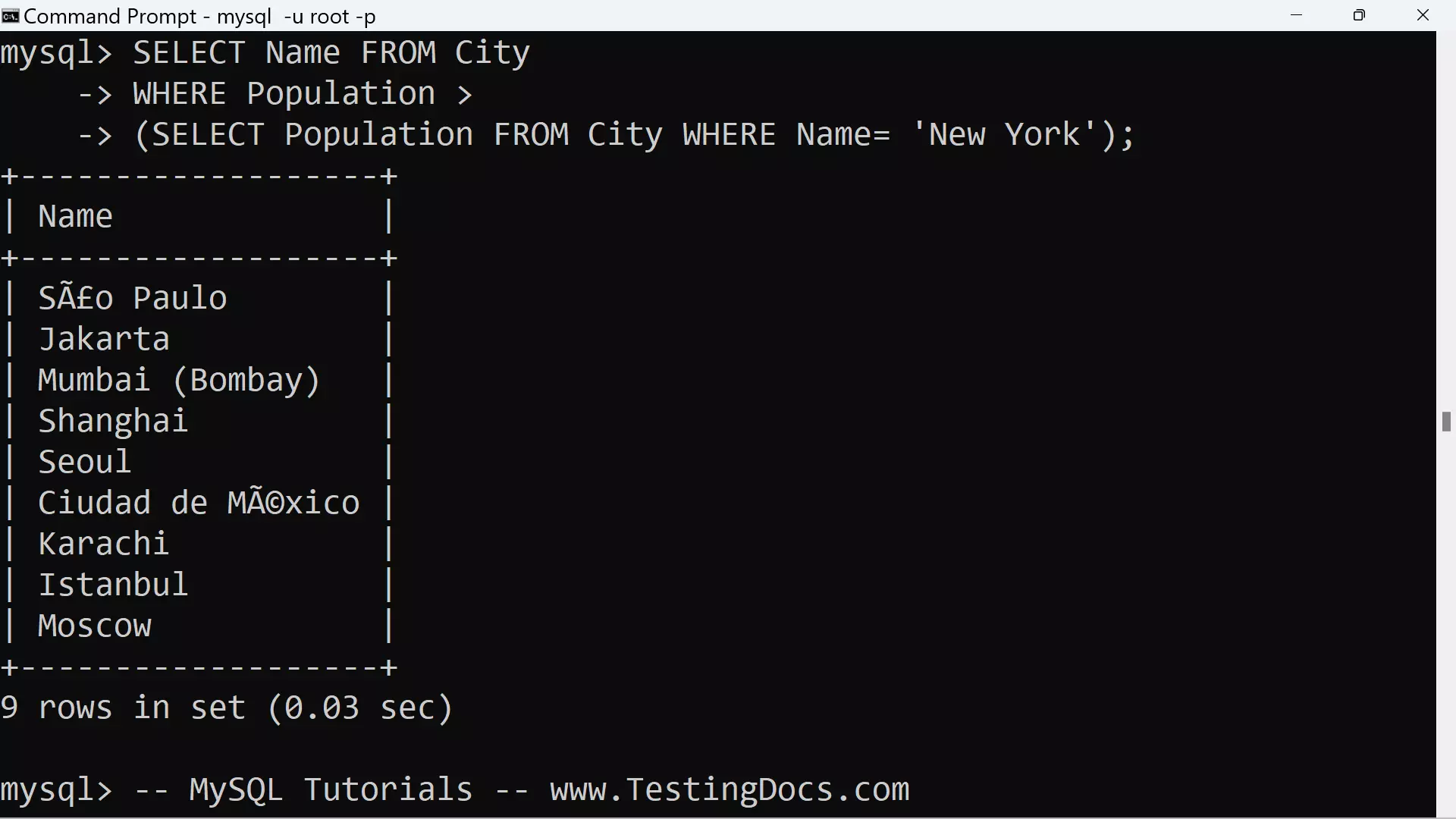
If we execute the subquery from the above example as a stand-alone statement, we will notice that the query yields a scalar/single value.
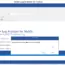
mysql> SELECT Population FROM City WHERE Name= ‘New York’;
+————+
| Population |
+————+
| 8009000 |
+————+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Scalar subqueries can appear almost anywhere that a scalar value is allowed by the SQL syntax.
This means that you can use subqueries as function parameters, use mathematical operators on subqueries
that evaluate to numeric values, etc.
—
MySQL Tutorials
MySQL Tutorials on this website:
https://www.testingdocs.com/mysql-tutorials-for-beginners/
For more information on MySQL Database: