MySQL Table Aliases
Overview
In this tutorial, we will learn about MySQL table aliases. A table alias is used to give a database table a temporary name. Table aliases enable qualified column references to be simple and more readable.
Syntax
Table aliases are not case-sensitive on Windows but not on the Linux operating system.
The general syntax is as follows:
SELECT col_list FROM table_name <table_alias_name>
A table alias is also created with the AS keyword.
SELECT col_list FROM table_name AS <table_alias_name>
Examples
Table aliases are used in JOIN statements. For example,
mysql>SELECT t1.* FROM table1 AS t1
INNER JOIN table2 AS t2
ON t1.col = t2.col ;
t1 and t2 are table aliases in the example.
Usage in correlated subquery
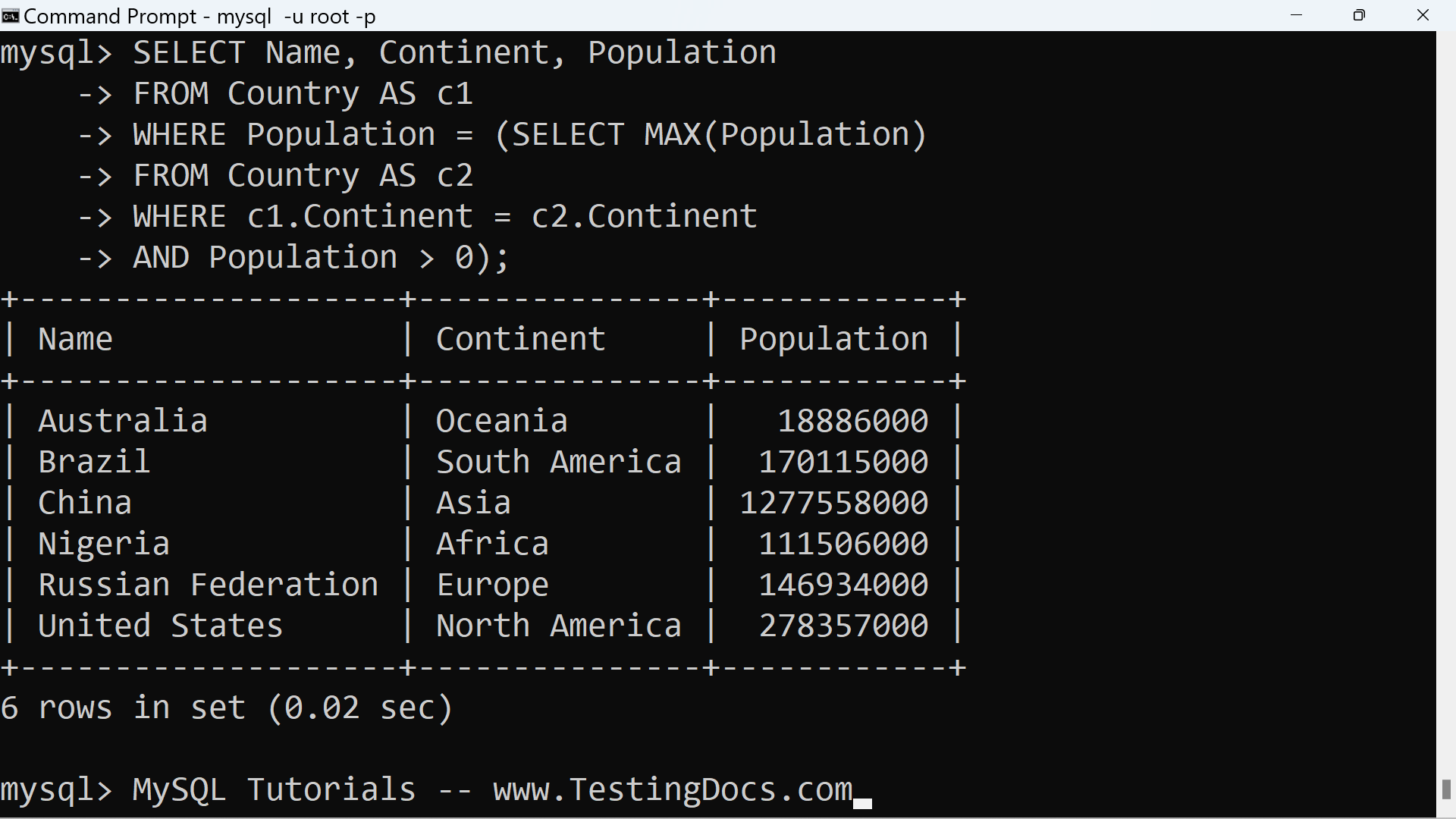
We can use the table name aliases in the subqueries. In this example we will use two table name aliases c1 and c2 to reference the same table Country.
mysql> SELECT Name, Continent, Population
-> FROM Country AS c1
-> WHERE Population = (SELECT MAX(Population)
-> FROM Country AS c2
-> WHERE c1.Continent = c2.Continent
-> AND Population > 0);
+——————–+—————+————+
| Name | Continent | Population |
+——————–+—————+————+
| Australia | Oceania | 18886000 |
| Brazil | South America | 170115000 |
| China | Asia | 1277558000 |
| Nigeria | Africa | 111506000 |
| Russian Federation | Europe | 146934000 |
| United States | North America | 278357000 |
+——————–+—————+————+
The table aliases c1 and c2 are used in the example. This is necessary because the columns that are used to correlate values from the inner and outer queries come from different references to the same table and thus have the same name.
—
MySQL Tutorials
MySQL Tutorials on this website:
https://www.testingdocs.com/mysql-tutorials-for-beginners/
For more information on MySQL Database: