MySQL Transaction Statements
Overview
In this tutorial, we will learn about MySQL Transaction statements. Transaction statements allow multiple statements to run as a single unit so that all or none of the database statements succeed.
Transactions
A transaction executes one or more SQL statements as a single unit of work so that either all the statements succeed or none will execute in case of an error.
If all the statements succeed, the transaction is committed, and the changes are recorded in the database permanently. If an error occurs during the transaction, all the changes made by the transaction are undone and ignored. The database is left in the state it was before the failed transaction started.
Transaction Statements
Transaction statements and the description are as follows:
| Transaction Statements | Description |
|---|---|
| START TRANSACTION | This statement begins a new transaction. |
| COMMIT | This statement commits the current transaction and makes the changes permanent to the database. We can use COMMIT to store the changes to the disk. |
| ROLLBACK | This statement rollbacks the current transaction and cancels the changes. We can use ROLLBACK to ignore the changes made by the transaction. |
| SET AUTOCOMMIT | This statement is used to disable/enable the default auto-commit mode for the current database connection. |
AUTOCOMMIT mode
By default, the MySQL server runs with autocommit mode enabled. When this mode is set, as soon as we execute an SQL statement that updates a table, MYSQL stores the updates on the disk. i.e., each statement is considered a transaction.
To disable auto-commit mode for a series of SQL statements, we can use the START TRANSACTION statement.
START TRANSACTION
— SQL statement1
— SQL statement2
…
COMMIT
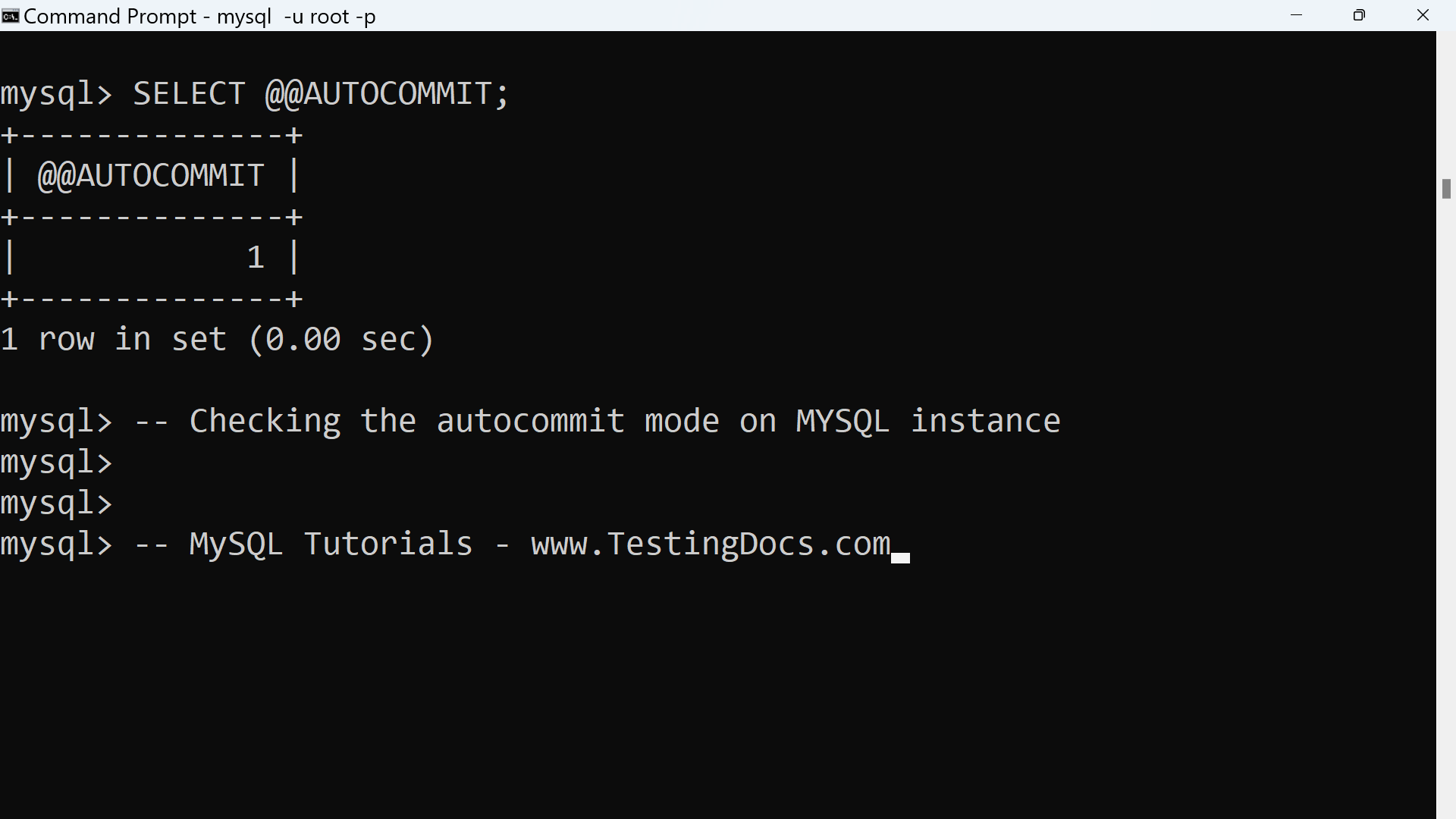
The autocommit mode remains disabled until you end the transaction with either COMMIT or ROLLBACK. We can check the current setting by using the SELECT statement as follows:
mysql> SELECT @@AUTOCOMMIT;
+————–+
| @@AUTOCOMMIT |
+————–+
| 1 |
+————–+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Example
Let’s look at a simple transaction example: a transfer of $500 from customer A’s savings account to customer B’s account.
A successful transaction should do the following things :
- Check for sufficient balance in customer’s account of A.
- Withdraw $500 from the account A.
- Deposit $500 into account B.
Pseudocode for the transaction:
START TRANSACTION
Check for sufficient balance in account A
If balance > 500
Withdraw money from the Account A.
Deposit money into Account B.
COMMIT — if no errors make changes permanent
ROLLBACK — if something went wrong or insufficient balance.
— end transaction
Disable AUTOCOMMIT
With transactional-safe storage engine like InnoDB we can disable autocommit with the following command:
SET AUTOCOMMIT=0
In this mode, we must use the COMMIT to make the changes permanent after a successful transaction or ROLLBACK to ignore the changes made since the start of the failed transaction.
—
MySQL Tutorials
MySQL Tutorials on this website:
https://www.testingdocs.com/mysql-tutorials-for-beginners/
For more information on MySQL Database: