SQL SubQuery
Overview
Subquery also called as inner query is used to return a value to the outer or the main query. There are two types of sub queries.
Nested Sub-query
Nested sub-query is executed first and its results are inserted in the WHERE clause of the outer main query. Sub queries can be single row or multiple row depending on the number of rows the query returns to the main query.
Let’s consider the problem on emp table.
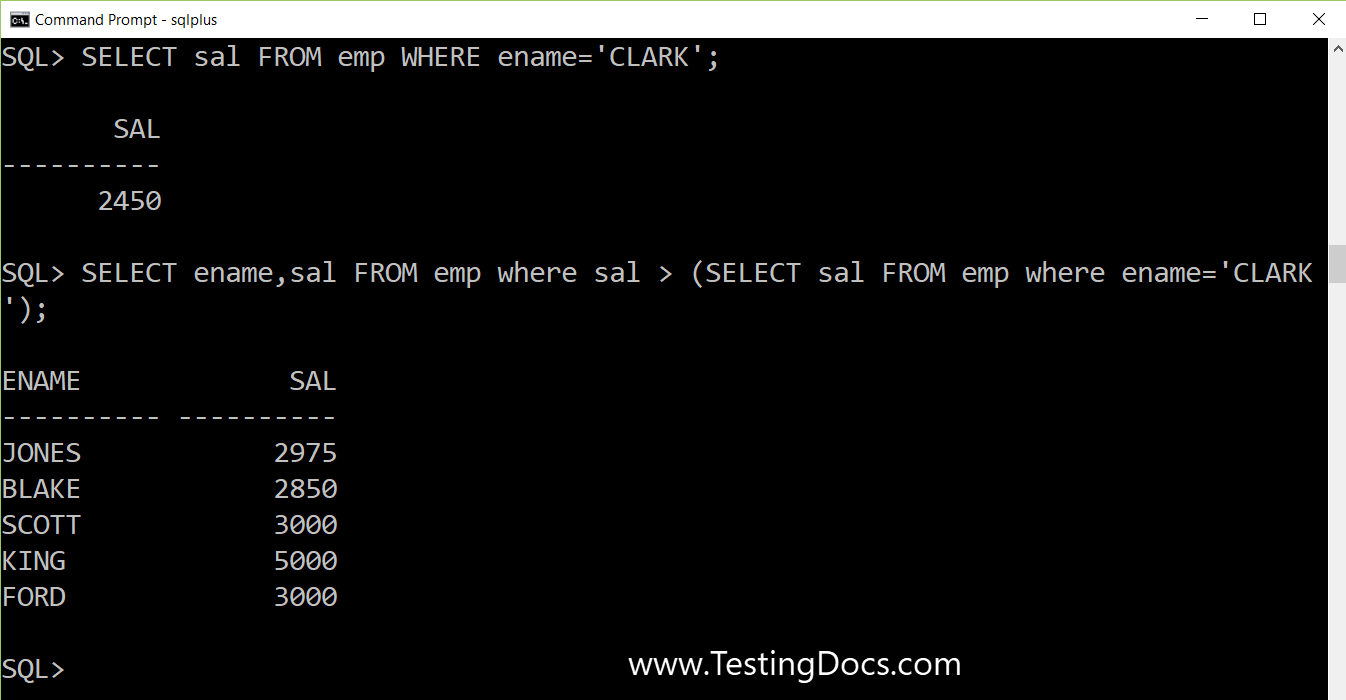
Who has salary greater than Clark’s salary?
SQL> SELECT sal FROM emp WHERE ename='CLARK'; SAL ---------- 2450
Now, we will write the main SQL query that uses the above one to find the employees who earn more than Clark.
SQL> SELECT ename,sal FROM emp where sal > (SELECT sal FROM emp where ename='CLARK'); ENAME SAL ---------- ---------- JONES 2975 BLAKE 2850 SCOTT 3000 KING 5000 FORD 3000
Correlated sub-query
Correlated subquery is one that is executed after the outer main query is executed. The correlated subquery depends on some variable that it receives from the main query.
Example:
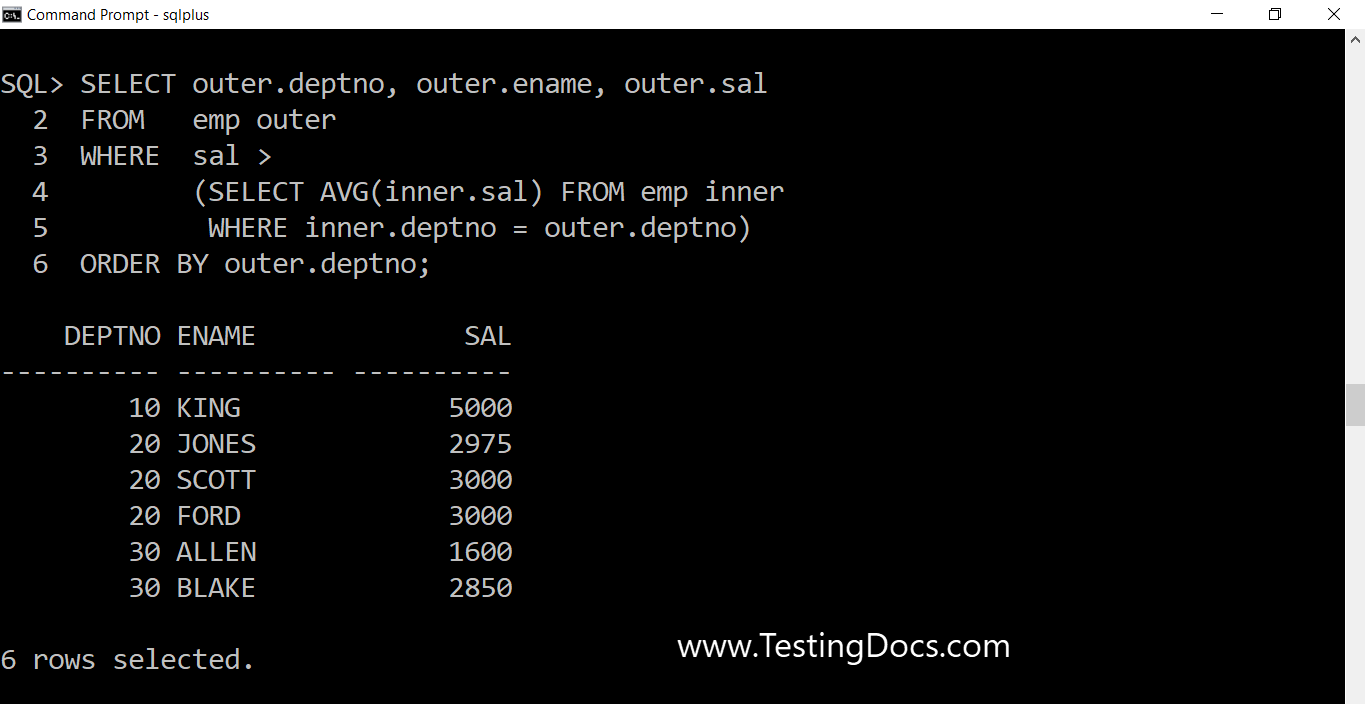
Find list of employees whose salary is more than their department’s average salary?
SQL> SELECT outer.deptno, outer.ename, outer.sal 2 FROM emp outer 3 WHERE sal > 4 (SELECT AVG(inner.sal) FROM emp inner 5 WHERE inner.deptno = outer.deptno) 6 ORDER BY outer.deptno; DEPTNO ENAME SAL ---------- ---------- ---------- 10 KING 5000 20 JONES 2975 20 SCOTT 3000 20 FORD 3000 30 ALLEN 1600 30 BLAKE 2850 6 rows selected. SQL> SELECT deptno, AVG(sal) FROM emp 2 GROUP BY deptno 3 ORDER BY deptno; DEPTNO AVG(SAL) ---------- ---------- 10 2916.66667 20 2175 30 1566.66667 SQL>