SQLite UPDATE Statement
Overview
The SQLite UPDATE Statement is used to modify the existing data in a table. We can use the WHERE clause to identify the row(s) and update the respective columns with new data.
SQLite UPDATE Statement
Syntax
The general syntax of the UPDATE statement is as follows:
To update a single column:
UPDATE table_name
SET column1 = value1
WHERE <condition>;
To update multiple columns:
UPDATE table_name
SET column1 = value1, column2 = value2…., columnN = valueN
WHERE <condition>;
Example
Example to update a single column:
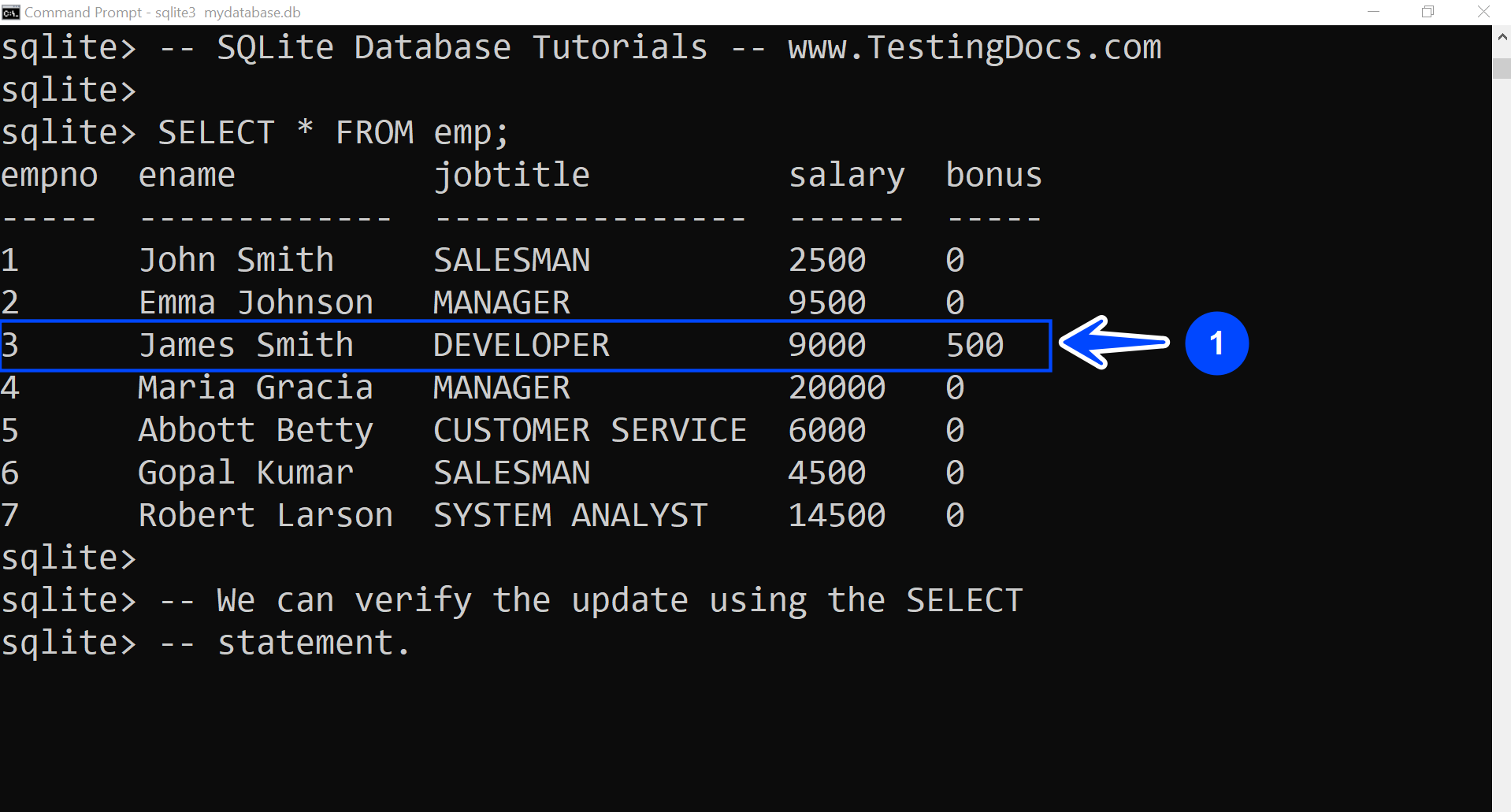
In this example, we will modify James Smith’s bonus to $500 using the UPDATE statement.
sqlite> UPDATE emp
…> SET bonus=500
…> WHERE empno = 3;
sqlite>
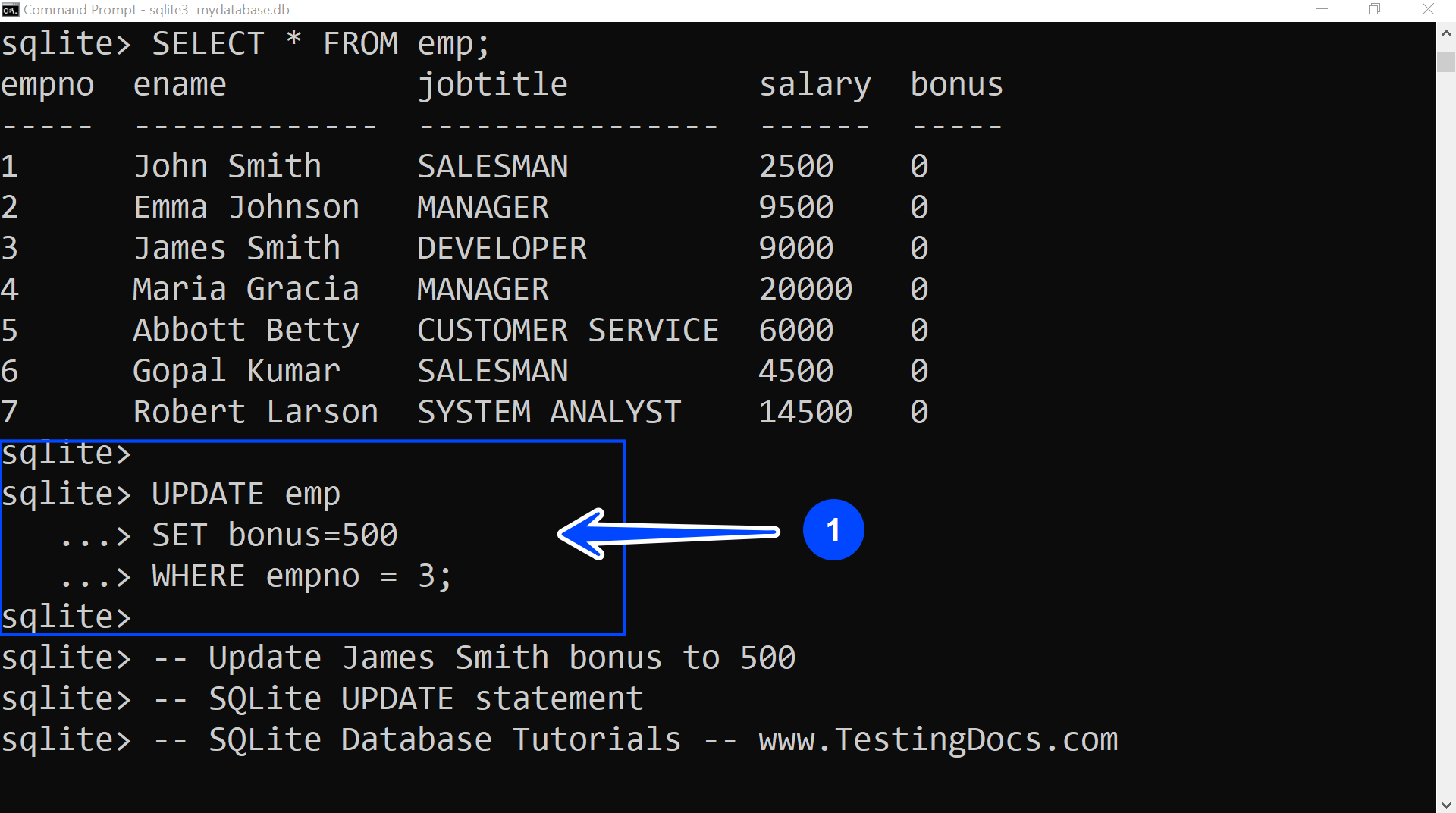
We used the table’s PRIMARY KEY empno to identify the employee record uniquely. James Smith’s empno is 3 in the emp table.
We can verify the modification using the SELECT statement.
Example to update multiple columns:
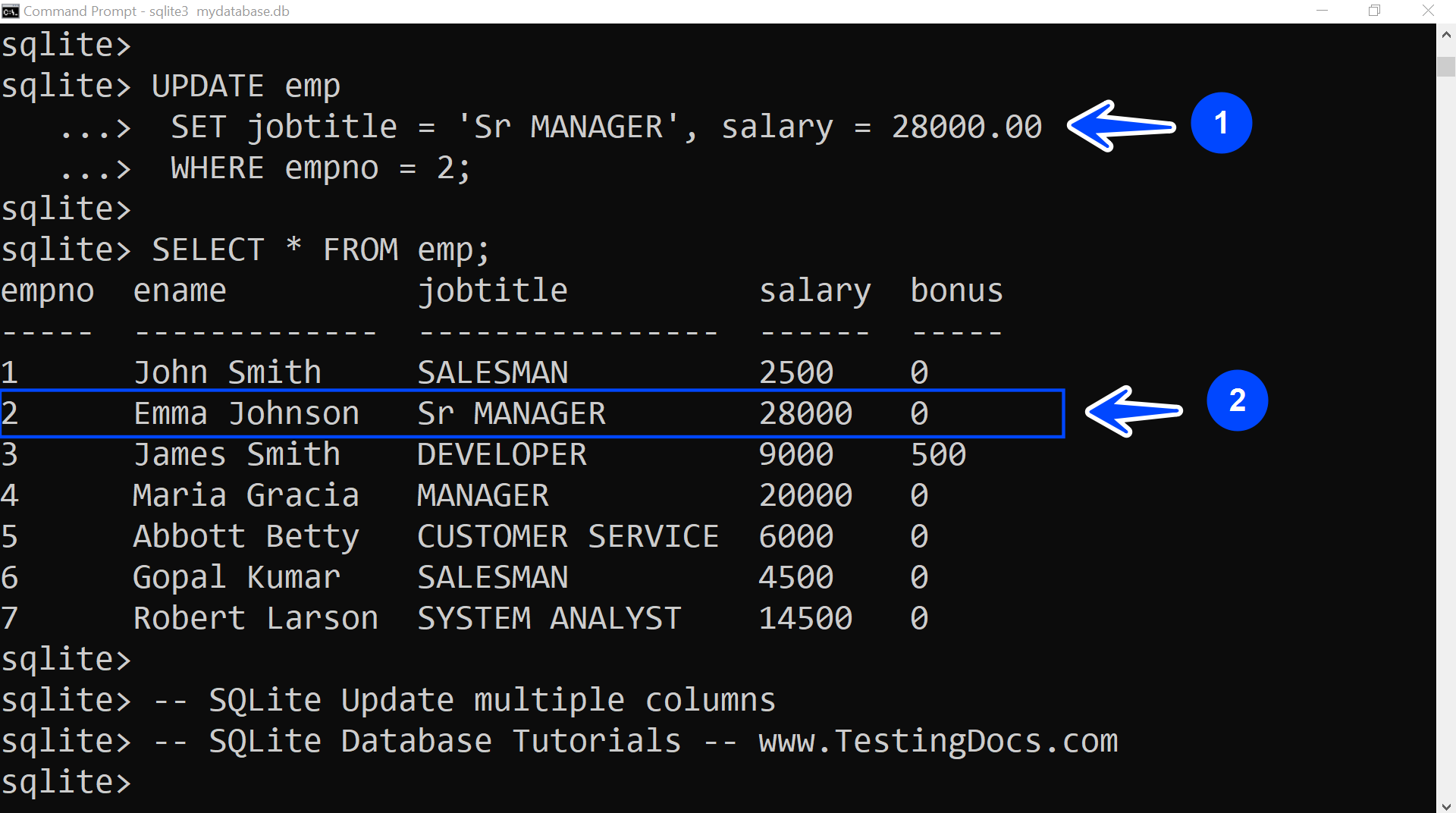
In this example, we will update Emma Johnson’s new role and salary after promotion. Her new role is Sr. Manager, and her new salary is $ 28,000.
sqlite> UPDATE emp
…> SET jobtitle = ‘Sr MANAGER’, salary = 28000.00
…> WHERE empno = 2;
sqlite>
The next example is to update a single column and all table rows.
Write the update statement to update the bonus of all the employees in the emp table to $ 1000.
sqlite> UPDATE emp
…> SET bonus=1000;
All rows will be updated when we omit the WHERE clause in the UPDATE statement. We can also specify the obvious true condition in the WHERE clause.
sqlite> UPDATE emp
…> SET bonus=1000
…> WHERE 1 = 1;
—
SQLite Tutorials
SQLite tutorials on this website:
https://www.testingdocs.com/sqlite-database-tutorials/
For more information on SQLite, visit the official website: