Arrays in Flowgorithm Flowchart
Overview
In this tutorial, we will learn Arrays in Flowgorithm flowchart. The main advantages of an array are its flexibility and ease of storing elements of the same type.
What is an Array?
An Array is a data structure that holds elements of the same data type in contiguous memory locations. We can store and access the array elements using the index or subscript.
For example, to store five elements, we can declare one array variable of size 5. We must declare five different variables to store the elements without using arrays. It is quite difficult for the programmer to remember and use variables as the number of elements increases.
Array Types in Flowgorithm
https://www.testingdocs.com/flowgorithm-array-types/
Using Arrays in Flowgorithm
The main steps involved in working with arrays in the Flowgorithm flowchart are as follows:
- Create and Declare an Array
- Initialize Array Elements
- Process Array Elements
- Output Results
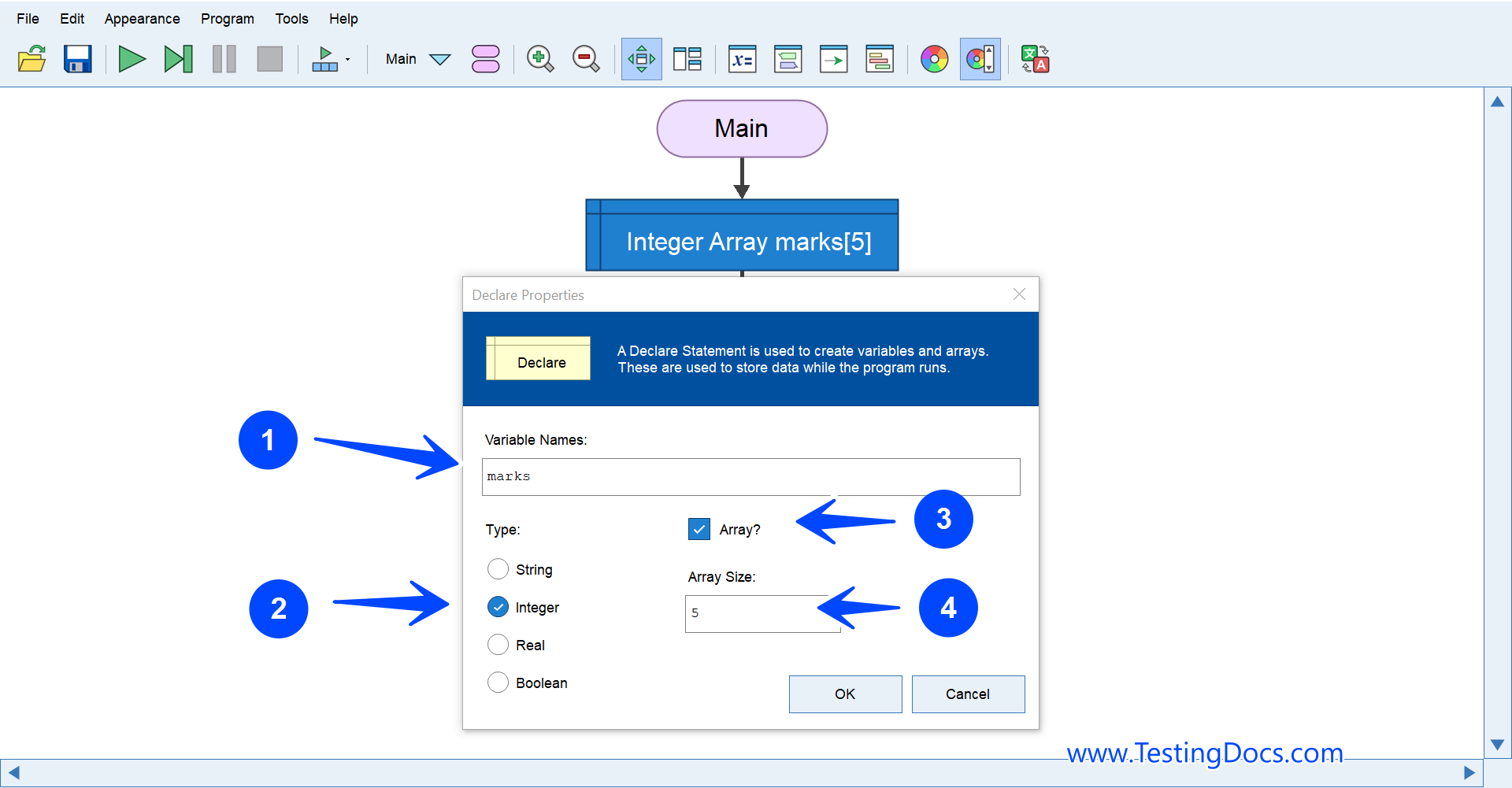
Declare an Array
A Declare statement or symbol creates and declares an array in the Flowgorithm flowchart.
Let’s declare an integer array of size 5. An integer array of size five can store five integers.
- Array variable name: marks
- Data type it can store: Integer
- Check the box Array? to indicate the variable is an Array.
- Specify the Array size: 5
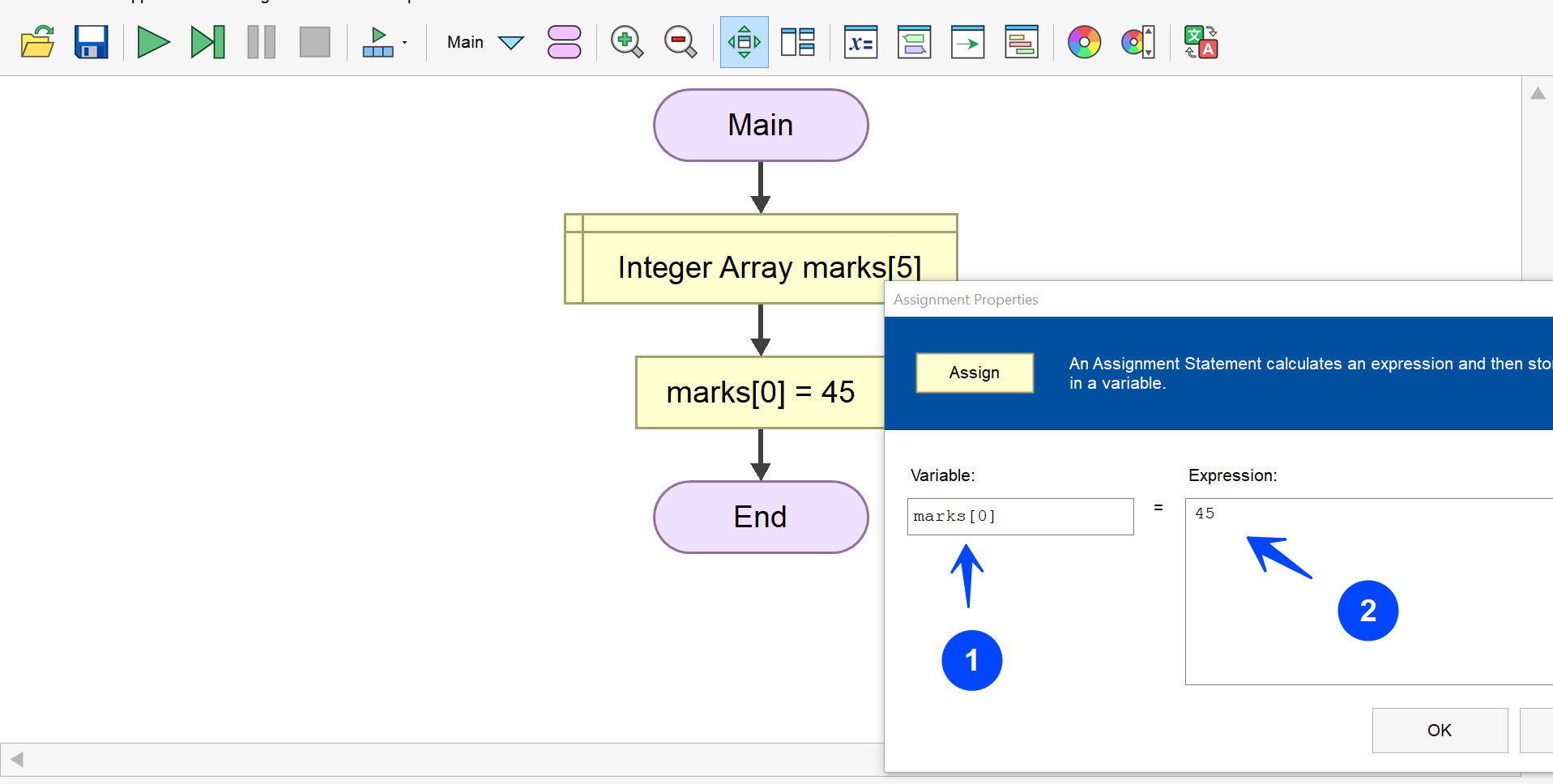
Initialize Array Elements
Initializing array elements is storing the array elements in the array. We can store and retrieve individual array elements using the array index. In the Flowgorithm flowchart, the index starts with 0.
For example: marks[i]
In the Flowgorithm, the index variable is called the subscript variable.
Array index or subscript
For example, we can use zero as the index to store and access the first array element. Similarly, we can use two as the index to store and access the third array element.
marks[0] = 45
In this example, we have initialized the first array element of the marks array to 45.
Process Array Elements
To process and perform calculations, we need to retrieve the array elements. We can use the array index variable to retrieve the array elements and process the calculations.
For example, to retrieve the second array element in the marks array, we can use:
marks[1]
Array Example
In this example, we use the ‘fruits’ array variable. The ‘fruits’ is an array variable that stores different fruit names. The data type is String. The size of the array is 5.
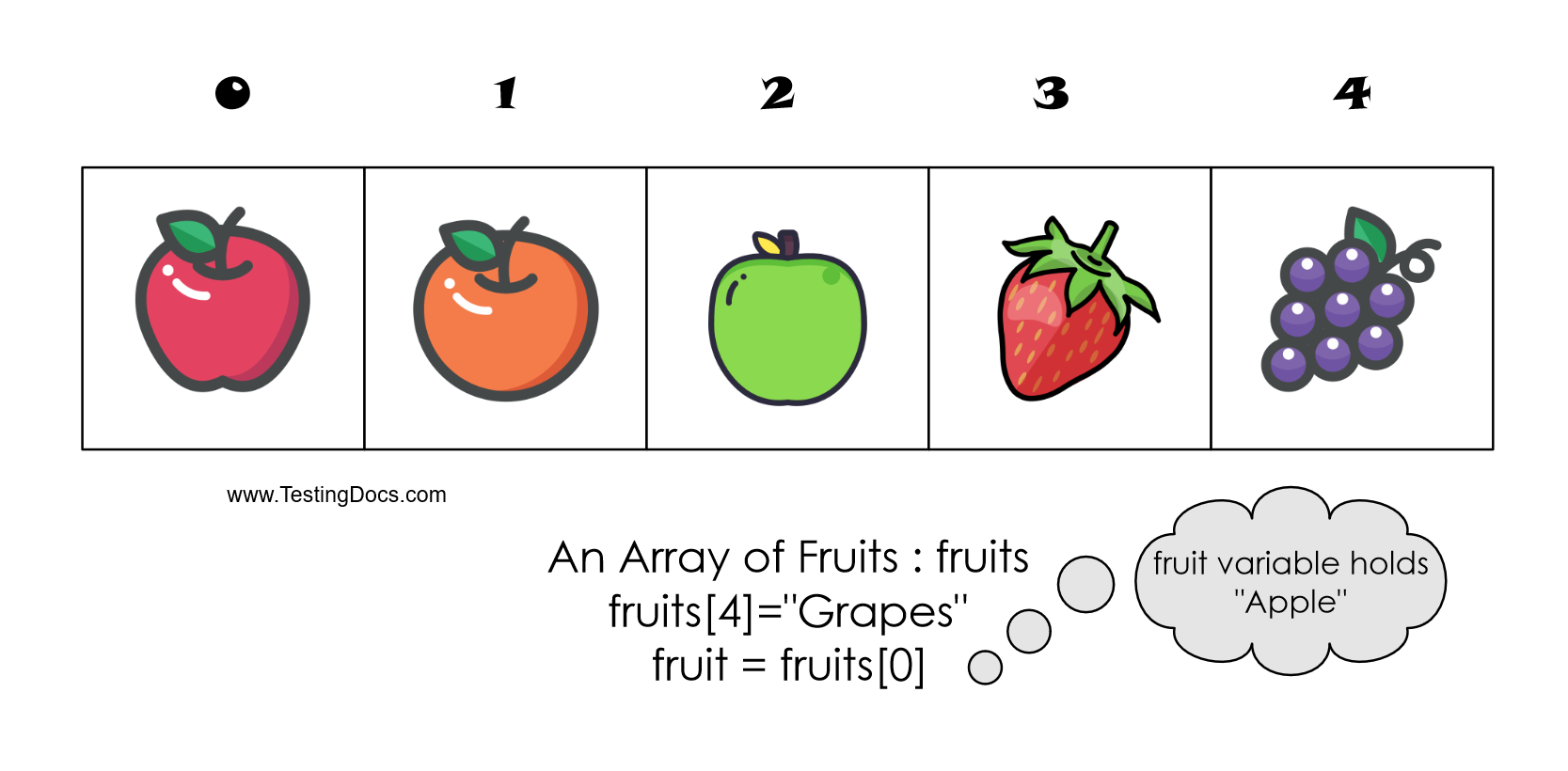
Note that the array stores the names of the fruit names and not the fruit objects. The data type of the array elements is String.
The fifth fruit name is stored in array index 4. For example,
fruits[4] = “Grapes”
For an Array of size 5, the valid range of the subscript is from 0 to 4. Generally, for an array of size n, the valid range of the subscript range is from o to n-1.
Under any circumstances, if we try to allot values to an array subscript that is outside the valid range, we would get an error Bad Subscript. In Java programming language, we call this exception an ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException.
Declare fruits array variable:
- Give a variable a name and check the checkbox Array? to make it an array variable.
- Specify the array elements data type in the Type: drop-down.
- Specify the array size in the Array Size: textbox.
- The Declare symbol would look like this:
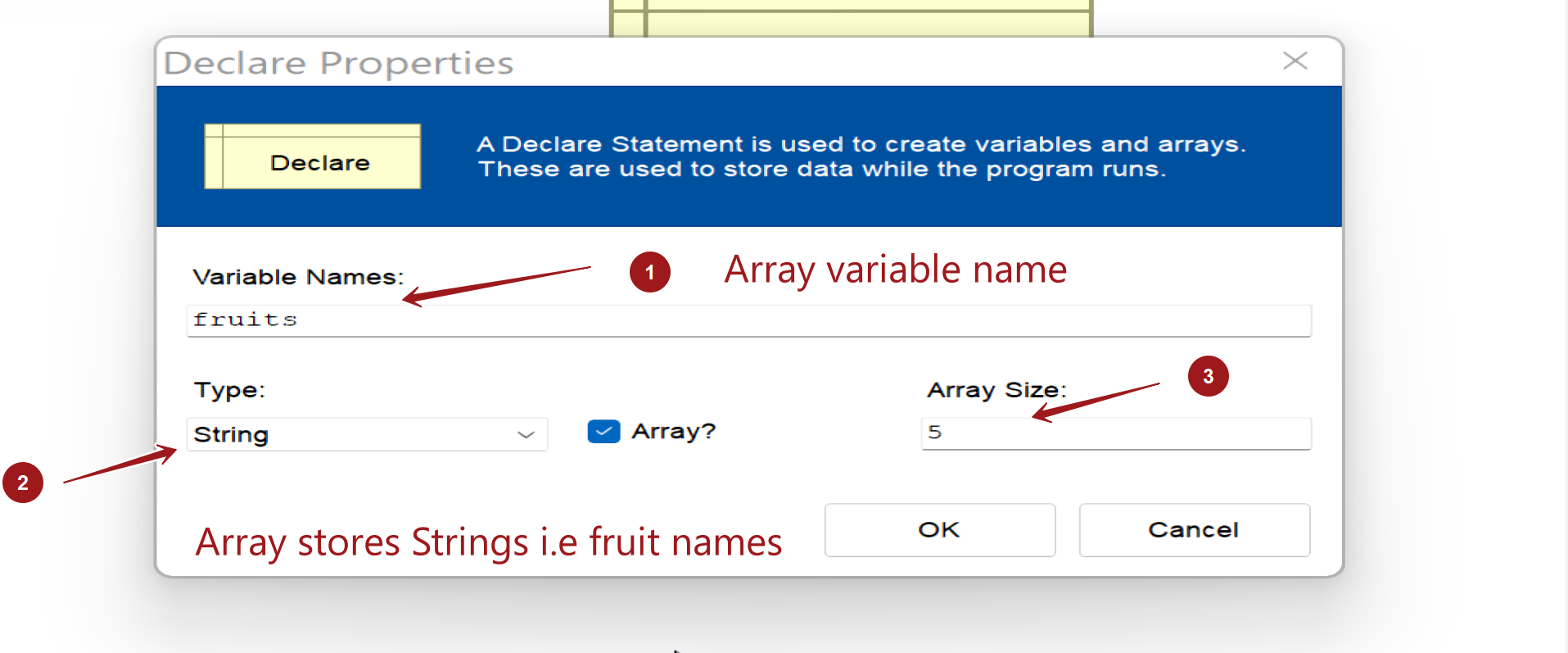
String Array fruits[5]
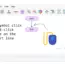
Let’s create a sample flowchart to declare the array variable and store the elements in the array.
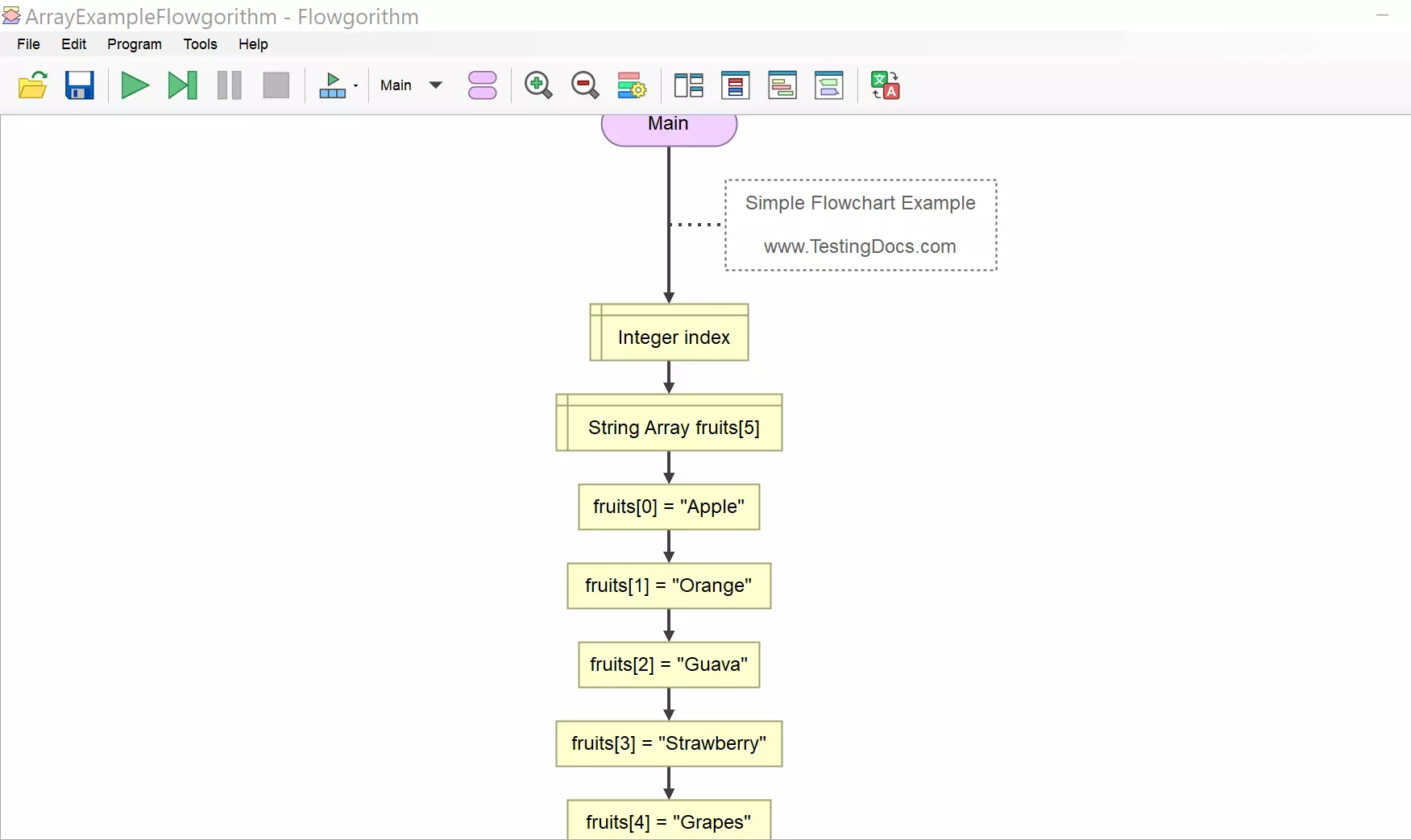
We have hard-coded the array values using the Assign statements. The array elements do not change and are fixed every time the flowchart runs. In the next article, we will see how to populate the array using a loop statement and take input from the user.
Array elements with User Input
Populate Array with User Input
Parallel Arrays
Flowgorithm only supports one-dimensional arrays. To store interrelated information, we can use multiple arrays called Parallel Arrays.
—