Classification of Computers
Overview
Let’s learn about the classification of computers. Computers are classified into various types depending on their purpose, type, operation, and size.
- Based on the type of electronics
- Based on Size
- Based on Usage/Purpose
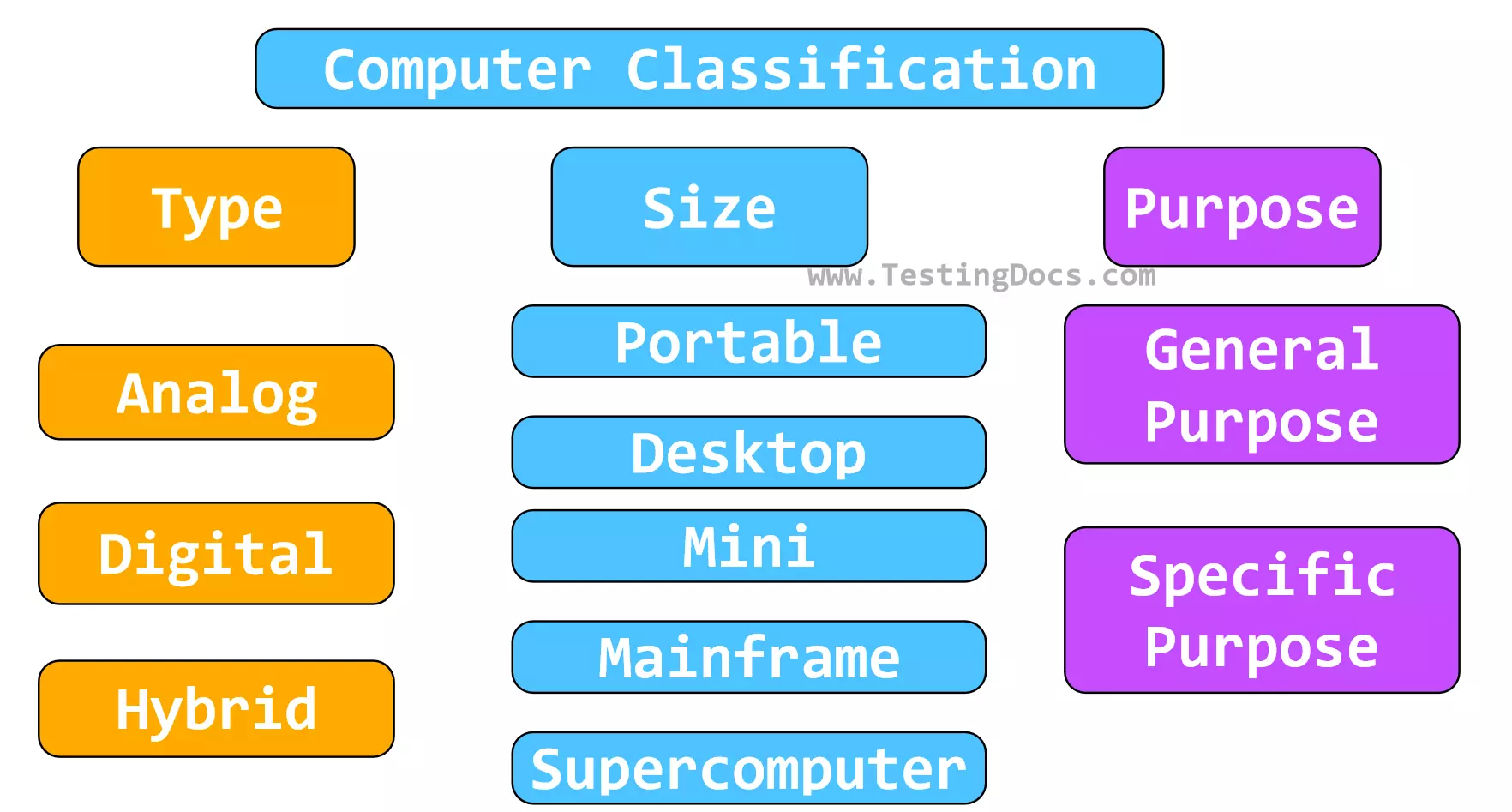
Type
Based on the electronics type, computers can be classified into:
- Analog computer
- Digital computer
- Hybrid computer
Analog computer
Analog computer operates on data that is represented by continuously varying electrical voltage. They are mainly used in scientific design environments.
Digital computer
Digital computer stores and process data in the form of discrete digits, or “binary bits.”
The bits are represented as binary digits (0 and 1). Data on digital computers is represented as a series of 0s and 1s bits. These are analogous to the ON state and the OFF state. Digital computers are accurate and much faster than Analog computers.
Hybrid computer
A hybrid computer combines the features of both the analog computer and the digital computer.
Usage
Based on the purpose of use, computers can be classified into:
- Special purpose computer
- General purpose computer
Special purpose computer
A special-purpose computer is designed to perform a specific task. It is specifically made to run a particular application. These computers are usually used for those purposes which are critical and need high performance and accuracy. For example, computers that are used for satellite launches, weather forecasting, etc.
General purpose computer
The general-purpose computer is designed to cater to the needs of many different software applications. These computers can be used for any type of software application.
Size
Based on the size, computers can be classified into:
- Portable computer
- Desktop computer
- Mini computer
- Mainframe computer
- Supercomputer
Portable computer
A portable computer is a very small computer. It can be easily carried anywhere from one location to another. Examples of portable computers are pen-based computers, hand-held computers, laptops, notebook computers, etc. Software employees, business executives, students, etc use portable computers to perform their duties.
Desktop computer
Desktop computers are also known as personal computers or PCs. They are normally assembled, installed, and configured on a desktop and hence the name desktop computer or tabletop computers. These are used in organizations as workstation machines.
Mini computer
A minicomputer is a computer that has all the features of a large-size computer but it’s less expensive, and less powerful than a mainframe or supercomputer. This computer can support several users at a time, with a multi-terminal time-sharing system. These are used in business organizations, universities, government offices, etc.
Mainframe computer
Mainframe computers are high-performance computers with large amounts of memory and processors that process bulk calculations and transactions in real time.
Supercomputer
Supercomputers are extremely powerful computers. They have large storage capacities and high computing speeds that are faster than that of other computers. Supercomputers are used in scientific, military, engineering, electronics, medicine, etc.