CPU Clock Speed
Overview
CPU clock speed is also called CPU(Central Processing Unit) Clock Frequency or Clock Rate. Every computer system contains an internal clock that regulates the rate at which instructions are executed and synchronizes all the various computer components.
CPU Clock speed
The CPU clock speed is the speed at which a microprocessor executes instructions. Clock speed is a measure of how fast a computer system’s CPU can execute instructions.
The CPU requires a fixed number of clock ticks (or clock cycles) to execute each instruction. The faster the clock, the more instructions the CPU can execute per second.
Clock speeds are typically measured in Hertz (Hz). Some common processor speeds are:
- Mega Hertz (MHz)
- Giga Hertz (GHz)
Mega Hertz or MHz means 1 million cycles per second
Giga Hertz or GHz means 1 billion cycles per second
Clock Speed Examples
Some examples of CPU clock speeds of different processors are as follows:
16-bit Processor
- 8086 Microprocessor: 8MHz
32-bit Processor
- Intel 80386: 16MHz
64-bit Processor
- Intel i5 11th Gen: 3.2GHz
Windows Example
In this section, we will see how to check the CPU speed on the Windows operating system. There are multiple ways to check the speed of the processor on the Windows operating system.
The steps to check the CPU speed on Windows are:
- Open Task Manager.
- Click on the Performance tab.
- We can check the base speed under the CPU utilization graph.
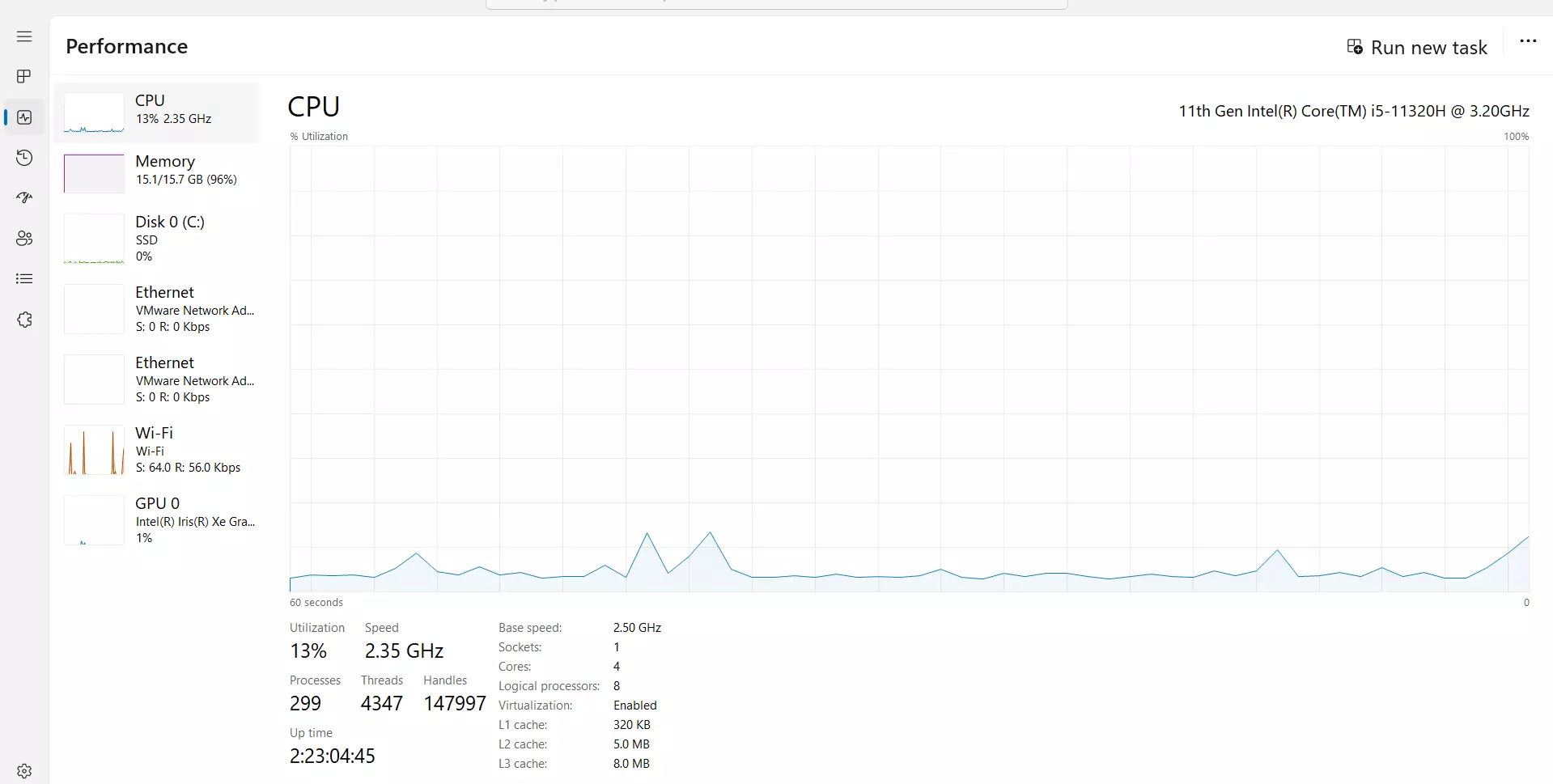
The CPU speed is 3.20 GHz. The base speed is 2.5 GHz.
That means the CPU speed is 3.20 GHz, i.e the CPU executes 3.2 billion cycles per second.

Notice that there are two frequencies displayed in the Windows system settings application. One frequency is the processor base frequency. The base frequency is the speed at that the processor is designed to run. The second frequency is computed by the Windows operating system.
Note that higher CPU clock speeds generally result in faster processing than lower clock speeds. However, other factors such as the CPU’s word length, Architecture, processor generation, number of cores, memory speed, etc play a significant role in determining overall CPU performance.