JUnit @RunWith Annotation
Introduction
In this post, we will discuss @RunWith Annotation. When a class is annotated with @RunWith or extends a class annotated with it, JUnit will invoke the class that it references to run the tests in that class instead of the runner built with JUnit.
What is a Runner?
A Runner runs tests and notifies a RunNotifier of significant events as it does so. We can also use custom runners if we want by extending the Runner class. When creating a custom runner, in addition to implementing the abstract methods you must also provide a constructor that takes as an argument the Class containing the tests. For example, Eclipse has a built-in a graphical runner.
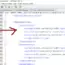
In order to use @RunWith annotation, we need to pass a class that is extended from Runner.
Class<? extends Runner>

We can run JBehave stories using this annotation. For example, we can use AnnotatedEmbedderRunner with this annotation.
@RunWith(value=AnnotatedEmbedderRunner.class) @UsingEmbedder(embedder=Embedder.class)
AnnotatedEmbedderRunner is a JUnit Runner that uses the AnnotationBuilder to create an embeddable test instance.
Another example we can run JBehave stories using Serenity by extending from SerenityStories class.
SerentiyStories class uses SerenityReportingRunner
@RunWith(SerenityReportingRunner.class)
SerenityStories is a JUnit-runnable test case designed to run a set of JBehave stories in a given package.