JUnit Test Execution Order Example
Introduction
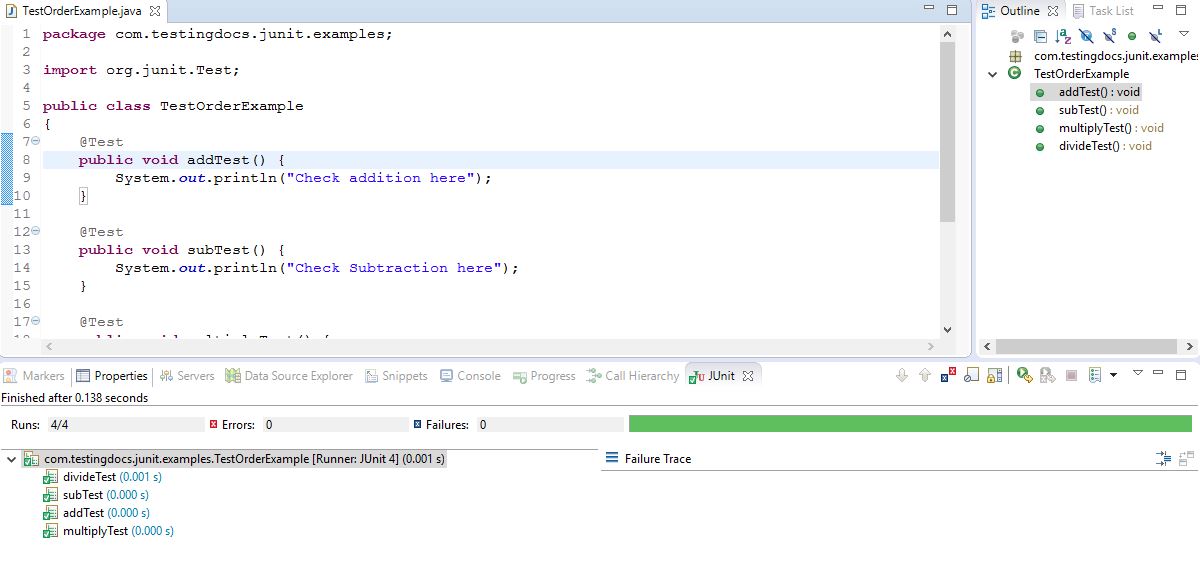
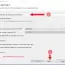
In this post, we will discuss the JUnit Test Execution Order Example. The test methods are simple calculator test cases. It is also not certain what order JUnit will run the test cases. The order may change on a different JVM or platform. By design, JUnit does not specify the execution order of test method invocations. However, relying on the JVM is not wise enough. As a matter of guidelines while writing unit tests, do not assume the order of execution.
Sample example code:
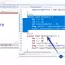
package com.testingdocs.junit.examples;
import org.junit.Test;
public class TestOrderExample
{
@Test
public void addTest() {
System.out.println("Check addition here");
}
@Test
public void subTest() {
System.out.println("Check Subtraction here");
}
@Test
public void multiplyTest() {
System.out.println("Check multiplication here");
}
@Test
public void divideTest() {
System.out.println("Check division here");
}
}
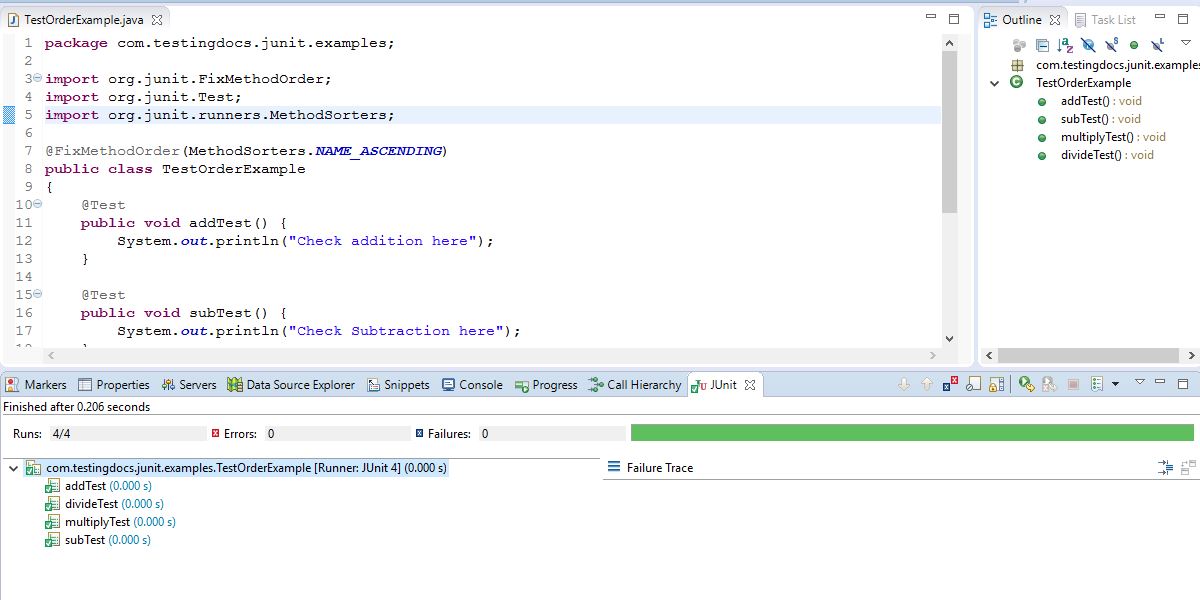
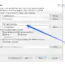
@FixMethodOrder
The default order of execution of JUnit tests within a class is deterministic but not predictable. Sometimes, if we need to specify the order of execution of test methods within a class we can use @FixMethodOrder.
Sort the methods into a specified execution order. Using MethodSorter.NAME_ASCENDING, sorts the test methods by the method name, in lexicographic order.
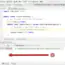
@FixMethodOrder(MethodSorters.NAME_ASCENDING)
public class TestOrderExample
{
@Test
public void addTest() {
System.out.println("Check addition here");
}
@Test
public void subTest() {
System.out.println("Check Subtraction here");
}
@Test
public void multiplyTest() {
System.out.println("Check multiplication here");
}
@Test
public void divideTest() {
System.out.println("Check division here");
}
}