MySQL Architecture
MySQL Architecture
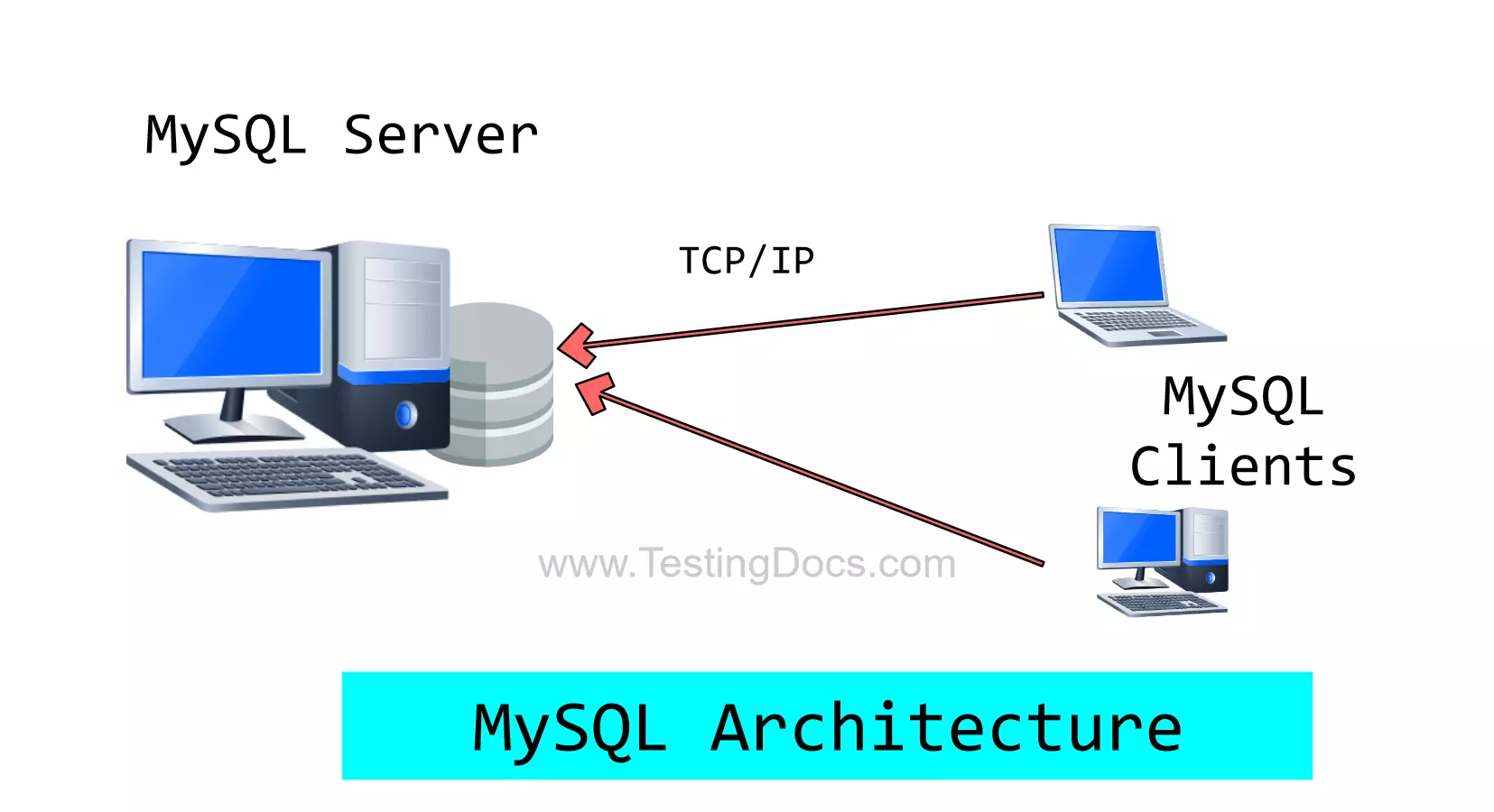
This tutorial provides a high-level overview of MySQL architecture. MySQL RDBMS operates as a client/server architecture model. The key components in the model are as follows:
- MySQL Server
- MySQL Client
MySQL Server
MySQL server is the central software program that manages the database objects, data, etc. The MySQL Server(mysqld) listens on a specific network port for incoming connection requests from clients. Clients can connect to the server to access or modify data in the database. The default port of the MySQL Server is 3306.
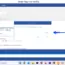
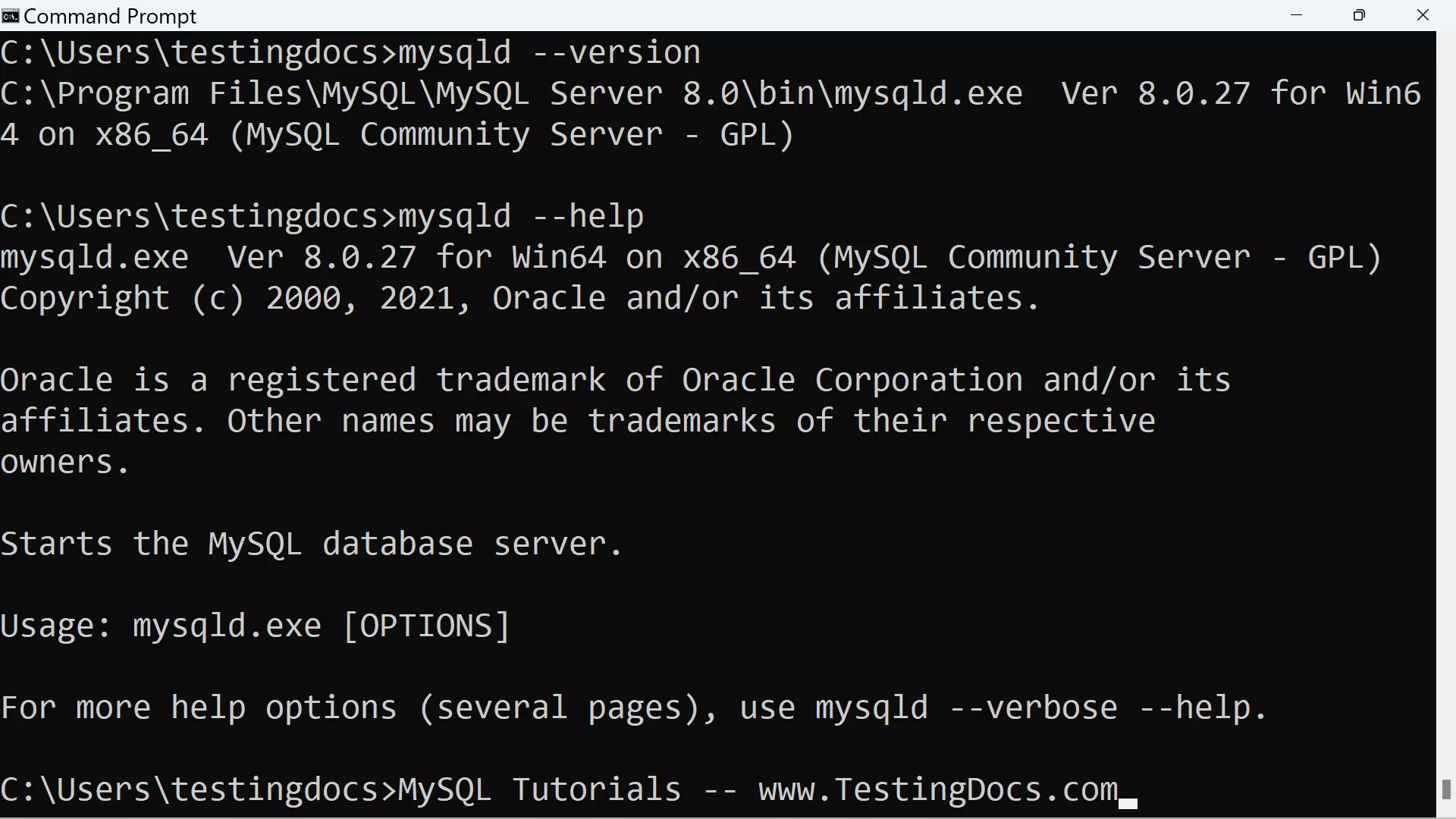
On the Windows operating system, we can know the MySQL server version by the following command:
Change working directory to MYSQL HOME\bin directory.
> mysqld –version
MySQL Client
MySQL clients are applications that sends requests to the database server. MySQL clients are software applications that connect to the server to access and manipulate the data in the database. In order for the clients to access data, the MySQL server must be running.
The client connects to the server, sends requests to the server. The server handles the requests and processes the requests. The client receives the response and disconnects from the server. MySQL Server can handle multiple database client connections at once.
MySQL clients can be
- Local – local clients run on the same machine where the MySQL Server runs.
- Remote – remote clients run on a different remote machine.
Remote clients connect to the MySQL Server using the TCP/IP network communication protocol. Local connections can use shared pipe, socket file(Unix) or TCP/IP.
https://www.testingdocs.com/mysql-command-line-client/
MySQL Server and Client
The MySQL Server process is started by default during the MySQL installation. We can also opt to create a Windows service during the standard installation. A MySQL client can establish a connection to the MySQL server to interact with the database. We can use the client to send SQL queries to the server. The server responds with the query results to the client.
Some of the things we can perform are as follows:
- Create database
- show database structure
- Create tables
- Create Views
- Insert and retrieve data
- Update data
- Delete data
- Drop tables
- Drop databases
- Create indexes
- Perform Backup and Restore
- etc.
—
MySQL Tutorials
MySQL Tutorials on this website:
https://www.testingdocs.com/mysql-tutorials-for-beginners/
For more information on MySQL Database: