MySQL Table Indexes
Overview
In this tutorial, we will learn about MySQL Table Indexes. An index will assist MySQL server to find rows more quickly and easily. Database index is much like an index found in the back of a textbook. Database indexes are used to locate rows in a table. Instead of containing all of the rows data, an index contains only the column(s) used to locate the rows. It also contains information describing where the rows are physically located. Mostly, we create all the indexes when we create tables.
MySQL Indexes
Most indexes are stored in B-Trees. A B-Tree index can be used for column comparisons in
that use the =,>, >=, <, <=, or BETWEEN operators. Indexes on spatial data types use R-trees, and MEMORY tables also support hash indexes.
When we insert a row into a table, the database server does not attempt to put the data in any particular location within the table. Instead, the server simply places the data in any available location within the table. Tables can be very large, and as a table gets bigger, retrievals from it become slower. This is due to the fact that the location of the data is unknown, so the server must at all the data in order to find the relevant row(s).
Indexes can be created on single columns or multiple columns (composite index). The following are commonly used indexes:
PRIMARY KEY
Only one PRIMARY KEY is allowed per table. PRIMARY KEY uniquely identifies a single row in the table.
No NULL values are allowed in the primary key. If a duplicate value is inserted or updated MySQL will return an error and the attempted operation will not be performed.
UNIQUE
Same rules as the PRIMARY KEY, with the following exceptions. UNIQUE allows values stored as NULL. We can have multiple UNIQUE indexes in a table. Each non-NULL value uniquely identifies a single row in a table.
Example
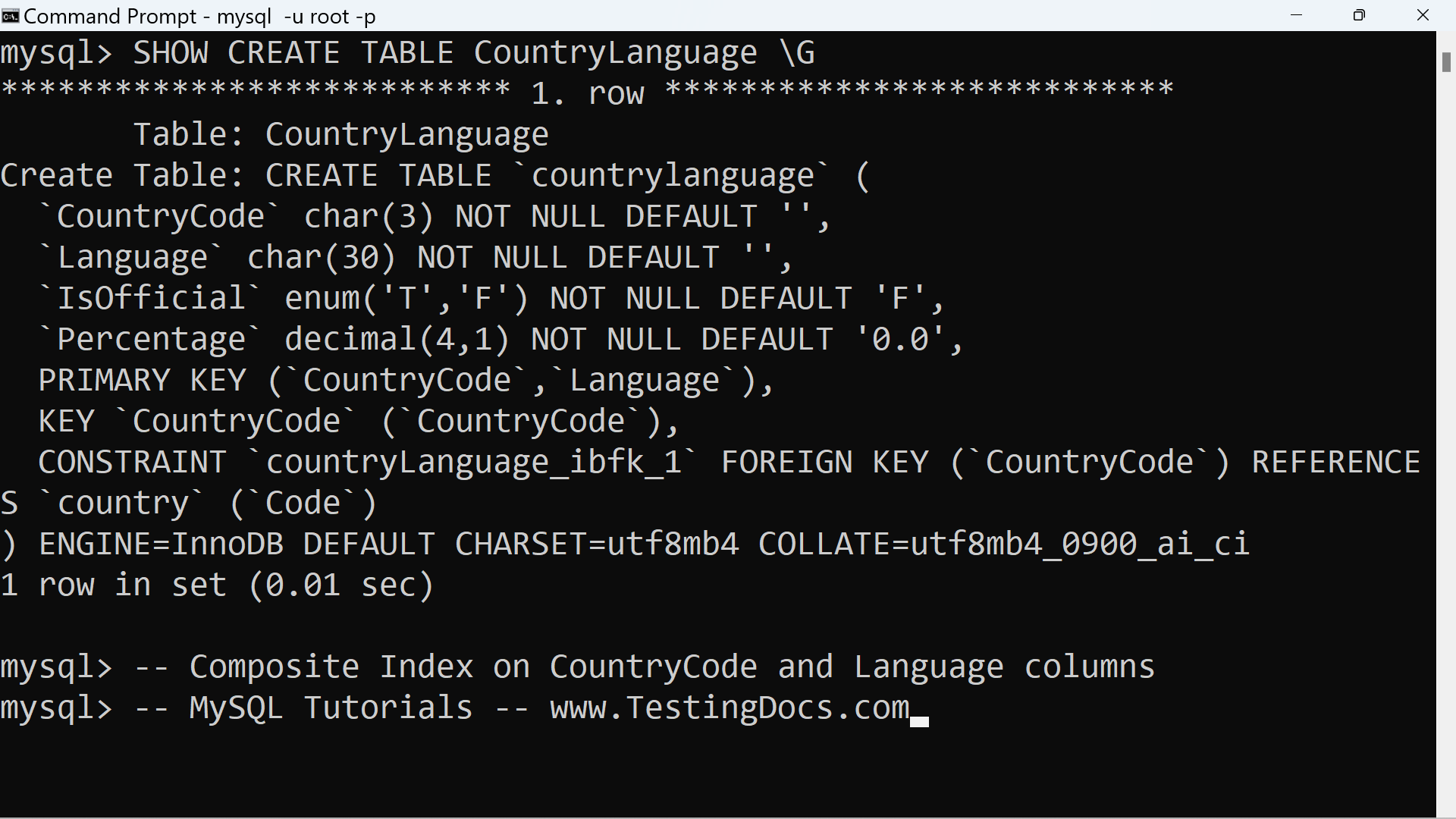
To view indexes in a table
https://www.testingdocs.com/mysql-show-index-statement/
—
MySQL Tutorials
MySQL Tutorials on this website:
https://www.testingdocs.com/mysql-tutorials-for-beginners/
For more information on MySQL Database: